| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 11, Number 7, July 2019, pages 484-488
Burnout Among Staff in a Home Hospital Pilot
Julia Piana, e, Brittnie Cannonb, c, Jeffrey L. Schnippera, d, David M. Levinea, d
aHarvard Medical School; Boston, MA, USA
bHarvard Catalyst Summer Clinical and Translational Research Program; Boston, MA, USA
cUniversity of Michigan-Flint; Flint, MI, USA
dDivision of General Internal Medicine and Primary Care, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
eCorresponding Author: Julia Pian, Harvard Medical School, 118 Kirkland House Mail Center, 95 Dunster St, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA
Manuscript submitted April 18, 2019, accepted May 2, 2019
Short title: Burnout in Home Hospital Pilot
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr3842
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Background: Burnout affects large portions of the healthcare workforce and is associated with increased medical errors, decreased patient experience and adherence, loss of professionalism, and decreased productivity. Little data exists on how novel clinical care settings might impact burnout. We studied the experience and burnout of staff involved in a home hospital pilot, where acutely ill patients were cared for at home as a substitute for traditional hospitalization.
Methods: We analyzed evaluations completed by home hospital staff (physicians, registered nurses, and research assistants) at the conclusion of a 2-month pilot program. Our primary outcome was burnout evaluated by the Mini Z Burnout Survey. Secondary outcomes included overall job satisfaction, work environment, workload, and team evaluation measured on a 5-point Likert scale.
Results: Eight of nine (89%) staff completed evaluations. Seven of eight (88%) staff had no symptoms of burnout; one (13%) was under stress but did not feel burned out. Median overall satisfaction with home hospital was 4.5/5.0 (interquartile range (IQR), 1.0). Most staff (6/8; 75%) “strongly agreed” that their professional values were well-aligned with the program. Three of six (50%) “entirely” or “very much” preferred home hospital to their standard clinical setting. Six of eight (75%) staff felt that their opinions were “entirely” heard; four of eight (50%) felt the team “entirely” valued each of its participants.
Conclusions: Novel clinical care settings like home hospital may lead to low staff burnout, high job satisfaction, and a healthy work environment. Further study is warranted.
Keywords: Home hospital; Burnout; Care delivery innovation
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Burnout is a psychosocial problem that causes emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and perception of less professional achievement [1]. A 2014 study surveyed physicians across the United States and found that 54.4% of physicians reported at least one symptom of burnout, a 9% increase from a similar survey in 2011 [2].
Burnout impacts not only the clinician but can also lead to more medical errors and physician turnover [3, 4], lower quality clinical care [5, 6], and lower patient experience [7]. Clinician burnout is also a barrier to health care reform and leads to lower rates of innovation in the field [8, 9]. Efforts at reducing burnout have focused on improving the existing environments in which physicians work [10], changing work hours and work-home balance [11, 12], or adding wellness activities into physician life [13].
Novel clinical settings may decrease burnout because they provide a new and varied role for the clinician. There has been little investigation of burnout in novel clinical programs, but the studies that do exist display variation in the effect of implementing a new clinical setting [14, 15].
Home hospital shifts care of acutely ill patients from the traditional hospital setting to the home environment. Home hospital care has thrived in several other developed countries [16, 17], but is still relatively new in the United States. We previously demonstrated in a pilot that home hospital decreased cost for home hospital patients with no significant changes in quality, safety, and patient experience [18]. This study describes burnout and team experience among the staff who provided care for home hospital patients in the pilot.
| Materials and Methods | ▴Top |
Study design
We performed a randomized controlled, investigator-initiated trial of home hospital care that was approved by the Partners HealthCare Human Research Committee as more than minimal risk human subjects’ research and was registered at clinicaltrials.gov (NCT02864420). All participants enrolled in the study provided written informed consent [18]. The study was performed at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, an academic medical center, and Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital, a community hospital, between September 12, 2016 and November 13, 2016. As a quality improvement project, we anonymously administered and analyzed Mini Z Burnout Surveys and staff experience surveys completed by home hospital staff at the conclusion of the pilot. We obtained secondary Institutional Review Board approval to analyze and publish our analysis of these surveys. Home hospital staff included an interdisciplinary team of physicians, registered nurses, and research assistants. To maintain anonymity, we did not ask for staff member’s role in the survey.
Exposure
The home hospital intervention has been described elsewhere [18]. Physicians worked 7 days a week, 24 h a day and were on-call at night for any urgent needs. Nurses worked 40-h weeks, 9am to 6pm. Baseline care for each patient included a daily visit from the physician and two daily visits from the registered nurse. The clinical team made extensive use of phone calls, video conferencing, and secure text messaging to monitor patients and coordinate their care. Care was tailored to each patient by expanding the team as needed to include a home health aide, physical therapist, occupational therapist, and/or social worker. The home hospital service had a maximum census of four patients at any given time.
Main measures and outcome
Our primary outcome was burnout evaluated by the Mini Z Burnout Survey (Supplementary Table 1) (www.jocmr.org). The American Medical Association Steps Forward Program designed the Mini Z Burnout Survey to determine workplace stress levels and has been used among a variety of healthcare professionals, including physicians and nurses [19]. The survey asks staff to evaluate their satisfaction with home hospital, stress level, workload, documentation burden, teamwork, and value alignment with leadership on a 5-point Likert scale.
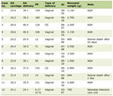 Click to view | Table 1. Mini Z Burnout Survey Results by Final Burnout Score for the Staff Members in the Home Hospital Pilot |
Our secondary outcomes were staff views of the team and home hospital intervention measured by a questionnaire we developed (Supplementary Table 2) (www.jocmr.org). We evaluated staff attitudes toward the team, assessing if they felt that their opinions were heard, if they understood the goal of the team, and if they felt the team valued each of its participants. We ascertained staff attitudes toward the home hospital intervention, including perceived quality of nursing and physician care delivery, patient safety, work preference, and atmosphere of home hospital compared to a traditional clinical setting. Participants were asked to rate their agreement with statements on a 5-point Likert scale: 1-Not at all, 2-Slightly, 3-Moderately, 4-Very Much, and 5-Entirely.
 Click to view | Table 2. Results of the Mini Z Burnout Survey Determining Workplace Stress |
Statistical methods
Due to the limited number of participants, non-parametric descriptive methods were used to analyze data, including interquartile range (IQR) and median.
| Results | ▴Top |
The home hospital staff consisted of MDs (2), RNs (4) and Research Assistants (3). Eight of nine staff (89%) completed an evaluation of home hospital.
Results from the Mini Z Burnout Survey showed that seven of eight (88%) staff had no symptoms of burnout; one (12%) was under stress but did not feel burned out (Table 1). The median overall satisfaction with home hospital was 4.5 out of 5.0 (interquartile range (IQR), 1.0; Table 2). Six of eight (75%) staff stated that they “strongly disagree” or “disagree” with the statement that home hospital causes a great deal of stress (median 2.0/5.0, (IQR, 1.25)). Six of eight staff (75%) “strongly agreed” their professional values were well aligned with those of home hospital leaders, with the other two staff (25%) choosing that they “agreed” with that statement (median 5.0/5.0, (IQR, 0.75)). Seven of eight (88%) staff evaluated “optimal or good” the degree to which the home hospital care team worked effectively together, with the final staff member rating that the team dynamic was “satisfactory” (median 4.0/5.0, (IQR, 1.0)). Five of eight (63%) staff rated that they had “optimal” or “good” control over their workload for home hospital, with the other three staff members rating their workload control as “satisfactory” (median 4.0/5.0 (IQR, 2.0)). Regarding electronic health record (EHR) use, staff favorably rated their proficiency with the EHR (median 4.0/5.0, (IQR, 1.0)), documentation time requirements (median 5.0/5.0 (IQR 1.0)), and amount of time spent on the EHR (median 4.0/5.0 (IQR, 1.25)).
Staff highly rated their agreement with the following statements: “I felt like our team valued each of the participants” (median 5.0/5.0, (IQR, 1.0)), “I felt my opinions were heard” (median 5.0/5.0, (IQR, 1.0)), and “I knew what the goal of our team was” (median 5.0/5.0, (IQR, 0.75)) (Table 3). The program evaluation showed that all of the staff felt “entirely” or “very much” that the logistics of patient care worked optimally (median 4.0/5.0, (IQR, 0)) (Table 3). Staff highly rated their agreement with the following statements: “nursing care was delivered optimally” (5.0/5.0 (IQR 1.0)), “physician care was delivered optimally” (5.0/5.0 (IQR, 0.5)), “I had sufficient support to carry out my duties” (5.0/5.0 (IQR, 0.25)), “patients were cared for safely” (5.0/5.0 (IQR, 1.0)), and “patient experience was optimal” (4.5/5.0 (IQR, 1.0)). Five staff members stated that they “moderately”, “very much”, or “entirely” preferred home hospital over their standard job with only one staff member choosing “not at all” (median 3.5/5.0, (IQR, 1.0)).
 Click to view | Table 3. Team and Program Evaluation |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
We demonstrate a low rate of burnout among staff in a home hospital pilot program. In addition, staff members had high rates of satisfaction with both the home hospital team and the home hospital program.
Drawing from the burnout literature, a 2016 study by Linzer et al surveyed physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants in general internal medicine departments across the country using the same Mini Z Survey to assess burnout, and found 59% of hospitalist staff were under high stress and 33% were suffering from burnout [20]. Compared with these figures, 12% of staff in the home hospital pilot showed stress and 0% noted burnout.
Low rates of burnout during home hospital may exist for several reasons. Linzer et al suggested that some of the issues leading to stress and burnout include high inpatient censuses, communication issues with team and other providers, and differing values from hospital leadership [20]. The home hospital program may improve staff experiences on all fronts. For example, the pilot randomized control trial capped the census of home hospital patients at 4. This represents a similar census for a typical RN, but represents a reduction in patient load for the MD (although the home hospital MD had no mid-level support and was on-call 24 h a day). Meeting patients in their home allows a clinician to get to know a patient in the context of their life and more fully understand them as a person. Stronger connections forged between clinician and patient can lead to even more rewarding healthcare delivery. One also cannot underestimate the power of changes in scenery and setting (from a hospital ward to a patient’s home) in increasing job satisfaction and reducing stress for staff. This provides important variety to a staff member’s daily job not found in traditional hospitals.
Home hospital made use of cutting-edge technology to make communication between a geographically separated team efficient. Since the program relied on long-range communication, including phone, video, and encrypted text messaging, a culture of responsiveness and collaboration pervaded the team leading to a more collegial environment.
Finally, home hospital emphasized a flat hierarchy among all staff. The team goal was apparent, and staff feedback was implemented quickly. In this way, the values of the program leadership were transparent and shared among all staff.
Our study has limitations. Our study lacked a control arm, so we cannot infer causation. Due to our sample size of eight staff members during a pilot study of home hospital, it is difficult to generalize these results to a broader population or a scaled-up program. These findings should ideally be validated in a larger, longer, and controlled study. We were unable to survey staff before the intervention or to survey staff taking care of patients in the traditional hospital control arm. It is possible, for example, that staff who became involved in the home hospital program had a lower or higher baseline rate of burnout.
In addition, due to the short nature of the intervention (2 months), staff may not have yet shown stress and burnout due to the novelty of the intervention and the excitement of working in a new clinical program. Especially at the beginning of a clinical intervention, staff often have to make important decisions about the future of the program which could lead to a high sense of agency and engagement. As the program continues, staff could become more burned out over time as their jobs become increasingly routine.
In conclusion, in a small home hospital pilot, staff showed low rates of burnout and high job satisfaction. Further studies are needed to see if this new clinical program could serve as a model for systems and individuals struggling with burnout.
Acknowledgments
The authors have no acknowledgement to state.
Financial Disclosure
This was an unfunded evaluation.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Informed Consent
All participants enrolled in the study provided written informed consent.
Author Contributions
All of the authors have contributed sufficiently to the project through drafting and revising the manuscript to be included as authors, and all those who are qualified to be authors are listed in the author byline.
| References | ▴Top |
- Shanafelt TD, Boone S, Tan L, Dyrbye LN, Sotile W, Satele D, West CP, et al. Burnout and satisfaction with work-life balance among US physicians relative to the general US population. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(18):1377-1385.
doi pubmed - Shanafelt TD, Hasan O, Dyrbye LN, Sinsky C, Satele D, Sloan J, West CP. Changes in burnout and satisfaction with work-life balance in physicians and the general US working population between 2011 and 2014. Mayo Clin Proc. 2015;90(12):1600-1613.
doi pubmed - Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Bechamps G, Russell T, Dyrbye L, Satele D, Collicott P, et al. Burnout and medical errors among American surgeons. Ann Surg. 2010;251(6):995-1000.
doi pubmed - Shanafelt T, Sloan J, Satele D, Balch C. Why do surgeons consider leaving practice? J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212(3):421-422.
doi pubmed - Firth-Cozens J, Greenhalgh J. Doctors' perceptions of the links between stress and lowered clinical care. Soc Sci Med. 1997;44(7):1017-1022.
doi - Grol R, Mokkink H, Smits A, van Eijk J, Beek M, Mesker P, Mesker-Niesten J. Work satisfaction of general practitioners and the quality of patient care. Fam Pract. 1985;2(3):128-135.
doi pubmed - Haas JS, Cook EF, Puopolo AL, Burstin HR, Cleary PD, Brennan TA. Is the professional satisfaction of general internists associated with patient satisfaction? J Gen Intern Med. 2000;15(2):122-128.
doi pubmed - Dyrbye LN, Shanafelt TD. Physician burnout: a potential threat to successful health care reform. JAMA. 2011;305(19):2009-2010.
doi pubmed - Wallace JE, Lemaire JB, Ghali WA. Physician wellness: a missing quality indicator. Lancet. 2009;374(9702):1714-1721.
doi - Linzer M, Poplau S, Grossman E, Varkey A, Yale S, Williams E, Hicks L, et al. A cluster randomized trial of interventions to improve work conditions and clinician burnout in primary care: results from the Healthy Work Place (HWP) study. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30(8):1105-1111.
doi pubmed - Linzer M, Warde C, Alexander RW, Demarco DM, Haupt A, Hicks L, Kutner J, et al. Part-time careers in academic internal medicine: a report from the association of specialty professors part-time careers task force on behalf of the alliance for academic internal medicine. Acad Med. 2009;84(10):1395-1400.
doi pubmed - Saleh KJ, Quick JC, Sime WE, Novicoff WM, Einhorn TA. Recognizing and preventing burnout among orthopaedic leaders. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(2):558-565.
doi pubmed - Lemaire JB, Wallace JE. Not all coping strategies are created equal: a mixed methods study exploring physicians' self reported coping strategies. BMC Health Serv Res. 2010;10:208.
doi pubmed - Kholdebarin R, Helewa RM, Hochman DJ. Evaluation of a regional acute care surgery service by residents in general surgery. J Surg Educ. 2011;68(4):290-293.
doi pubmed - Helfrich CD, Dolan ED, Simonetti J, Reid RJ, Joos S, Wakefield BJ, Schectman G, et al. Elements of team-based care in a patient-centered medical home are associated with lower burnout among VA primary care employees. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(Suppl 2):S659-666.
doi pubmed - Leff B. Defining and disseminating the hospital-at-home model. CMAJ. 2009;180(2):156-157.
doi pubmed - Montalto M, Lui B, Mullins A, Woodmason K. Medically-managed Hospital in the Home: 7 year study of mortality and unplanned interruption. Aust Health Rev. 2010;34(3):269-275.
doi pubmed - Levine DM, Ouchi K, Blanchfield B, et al. Hospital-level care at home for acutely ill adults: a pilot randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33:(5):729-736.
doi pubmed - Linzer M, Poplau S. Building a sustainable primary care workforce: where do we go from here? J Am Board Fam Med. 2017;30(2):127-129.
doi pubmed - Linzer M, Poplau S, Babbott S, Collins T, Guzman-Corrales L, Menk J, Murphy ML, et al. Worklife and wellness in academic general internal medicine: results from a national survey. J Gen Intern Med. 2016;31(9):1004-1010.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Clinical Medicine Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.


