| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 2, Number 2, April 2010, pages 62-67
Aortic Stiffness in Prediabetic Adults: Relationship to Insulin Resistance
Hamdy Sliema, c, Gamela Nasrb
aDepartments of Internal Medicine, Suez Canal University, Ismailia, Egypt
bDepartments of Cardiology, Suez Canal University, Ismailia, Egypt
cCorresponding author:
Manuscript accepted for publication February 17, 2010
Short title: Short title: Aortic Stiffness in Prediabetic
doi: https://doi.org/10.4021/jocmr2010.03.269w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Background: A decrease in the compliance of the arterial system, termed arterial stiffness, results in increased cardiac workload. Several studies have shown that arterial stiffness is increased in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Also, insulin resistance is generally considered to be of major importance in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus given that glucose intolerance and insulin resistance precede the development of overt diabetes, these factors would be associated with arterial stiffness. This study was to evaluate the state of aortic elasticity in prediabetic adults in relation to insulin resistance.
Methods: A case-control study was performed. A total of 113 consecutive adults with prediabetes were enrolled for the study, 32 adults had insulin resistance (group A) and 81 had insulin sensitive (group B). Forty-five healthy (with normal fasting glucose) adults matched for age and gender were considered as control. All were subjected to full medical history and clinical examination including blood pressure and body mass index. Biochemical studies including lipids profile, fasting glucose and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA IR) test. Echocardiographic studies were done for assessment of the aortic stiffness index.
Results: Significant increase in mean aortic stiffness index was seen in group A than group B. Stiffness was correlated with insulin resistance and the correlation appeared to be independent of glucose tolerance status and obesity. Similar correlations were observed with age, triglycerides and waist circumference.
Conclusions: Prediabetic subjects have an aortic stiffness which represent pattern of cardiovascular risk factors. These changes are predominantly observed in prediabetic subjects with increased HOMA IR and visceral obesity independent of glucose levels.
Keywords: Prediabetes; Insulin resistance; Aortic stiffness index
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, obesity, and aging are associated with high risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) as well as other clinical conditions [1]. The mechanisms through which cardiovascular risk is increased are partially understood. A decrease in the compliance of the central arterial system, termed arterial stiffness, results in increased cardiac workload [2]. As arterial changes can be detected before the appearance of clinically apparent vascular disease, arterial stiffness may act either as a marker for the development of future atherosclerotic disease, or may be more directly involved in the process of atherosclerosis [3].
A number of factors are believed to be responsible for arterial stiffness. These include decreased elastin and increased collagen in the arterial wall, abnormal endothelial regulation of arterial smooth muscle tone, and the accumulation of advanced glycosylation end products (AGE) leading to protein cross-linking [4-6].
Several studies have shown that arterial stiffness is increased in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Also, insulin resistance is generally considered to be of major importance in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus [7].
Given that glucose intolerance and insulin resistance precede the development of overt diabetes, these factors would be associated with arterial stiffness. To investigate this hypothesis, the current study was undertaken to evaluate the state of aortic elasticity in prediabetic adults in relation to insulin resistance.
| Patients and Methods | ▴Top |
Patient selection
A case-control study was performed. A total of 113 consecutive adults with prediabetes were enrolled for the study. All were recruited from the outpatient diabetes and general medicine clinics of Suez Canal University Hospital from May 2007 to October 2009. Thirty-two adults had insulin resistance (group A) and 81 had insulin sensitive (group B). Forty-five healthy (with normal fasting glucose) adults matched for age and gender were considered as a control group.
Exclusion criteria included the following, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, CVD, severe obesity (body mass index > 40 kg/m2), heavy smokers, and aged adults (over 60 years old).
All groups were subjected to full medical history and clinical examination including blood pressure (BP), body mass index (BMI), systemic examination, biochemical and echocardiographic studies, anthropometric measures (weight in kilogram, height in centimeter, BMI, waist circumference). BMI was calculated as weight/height2 (kg/m2) and was used as an estimate of overall adiposity. Normal weight, overweight, and obesity were defined as a BMI less than 25, 25 to 29.9, and 30 or higher, respectively [8]. Waist circumference, a validated estimate of visceral adiposity, was measured to the nearest 0.5 cm. Central obesity is defined as waist circumference > 102 cm in males and > 88 cm in females [9].
Diabetes was diagnosed according to world health organization (WHO) criteria. Blood is drawn after fasting for eight hours. A fasting blood sugar level below 100 mg/dL is considered normal. A fasting blood sugar level between 100 and 126 mg/dL confirms the presence of prediabetes, and more than 126 mg/dL confirms the presence of diabetes in two separate occasions [10]. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA IR) was used as a measure of insulin resistance. It was assessed according to the level of fasting glucose and insulin which were measured with a dextran-charcoal radioimmunoassay. Serum intact pro-insulin was measured by using a highly specific, 2-site monoclonal antibody-based immunoradiometric assay [10, 11]. The formula for the HOMA IR model follows: HOMA IR = (Fasting insulin mU/mL X Fasting glucose mmol/L) / 22.5.
Subjects were divided by their insulin resistance status at baseline (HOMA IR above and below median of 3.0) to insulin resistant and insulin sensitive respectively. The median was based on the overall nondiabetic control group at baseline.
Aortic stiffness index (β) as a characteristic of aortic elasticity was evaluated from ascending aortic diameter. Aortic stiffness index ((β) was evaluated by means of transthoracic echocardiography by use of the formula: (β = ln (SBP/DBP) / (ΔD/ DD), where SBP and DBP are the systolic and diastolic blood pressures, DD is the diastolic aortic diameter,ΔD is the pulsatile change in aortic diameter (systolic diameter minus diastolic diameter) and ln is the natural logarithm [12].
Ethical consideration
Informed consent was obtained from all the adults. The aim and the value of the work were explained in a simplified manner for them. There was no harm inflicted on them. On the contrary all had benefits of the follow-up and the final results of the study. The study was approved by the ethics committee of faculty of medicine, Suez Canal University.
Statistical analysis
Data were presented in terms of mean and standard deviation (SD) of the mean, and percentages. Statistical analysis was carried out by a computer program (SPSS Ver. 11). Student-t test and correlation tests were used to evaluate the results. P value was set at less than 0.05 for statistically significant results and less than 0.0001 for highly significant results.
| Results | ▴Top |
Baseline characteristics of 113 (60 males and 53 females) prediabetic adults, mean age 43.1 years, with and without insulin resistance versus 45 control (24 males and 21 females), mean age 44.4 years are shown in Table 1, 36.2% of the prediabetic adults had insulin resistance, 63.8% had insulin sensitive. No significant differences were observed between both prediabetic adult and control groups regarding BMI, waist circumference, blood pressure, and plasma lipids. Regarding aortic stiffness index, no significant difference was observed between either all prediabetic cases or group B and control group, while high significant differences were observed between group A and both group B and control (Fig 1). Except waist circumference all the mentioned parameters were nearly similar in both male and female prediabetic adults.
Correlation between aortic stiffness index and different variables of insulin resistant prediabetic group (group A) is shown in Table 2. There was statistically significant coefficient correlation with HOMA IR, waist circumference, triglycerides and age. No correlation was observed with fasting glucose, BMI, blood pressure and total lipids. Similarly, no correlations were found with overall prediabetic population variables.
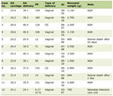 Click to view | Table 1. Clinical and Biochemical Studies of Both Case and Control Groups |
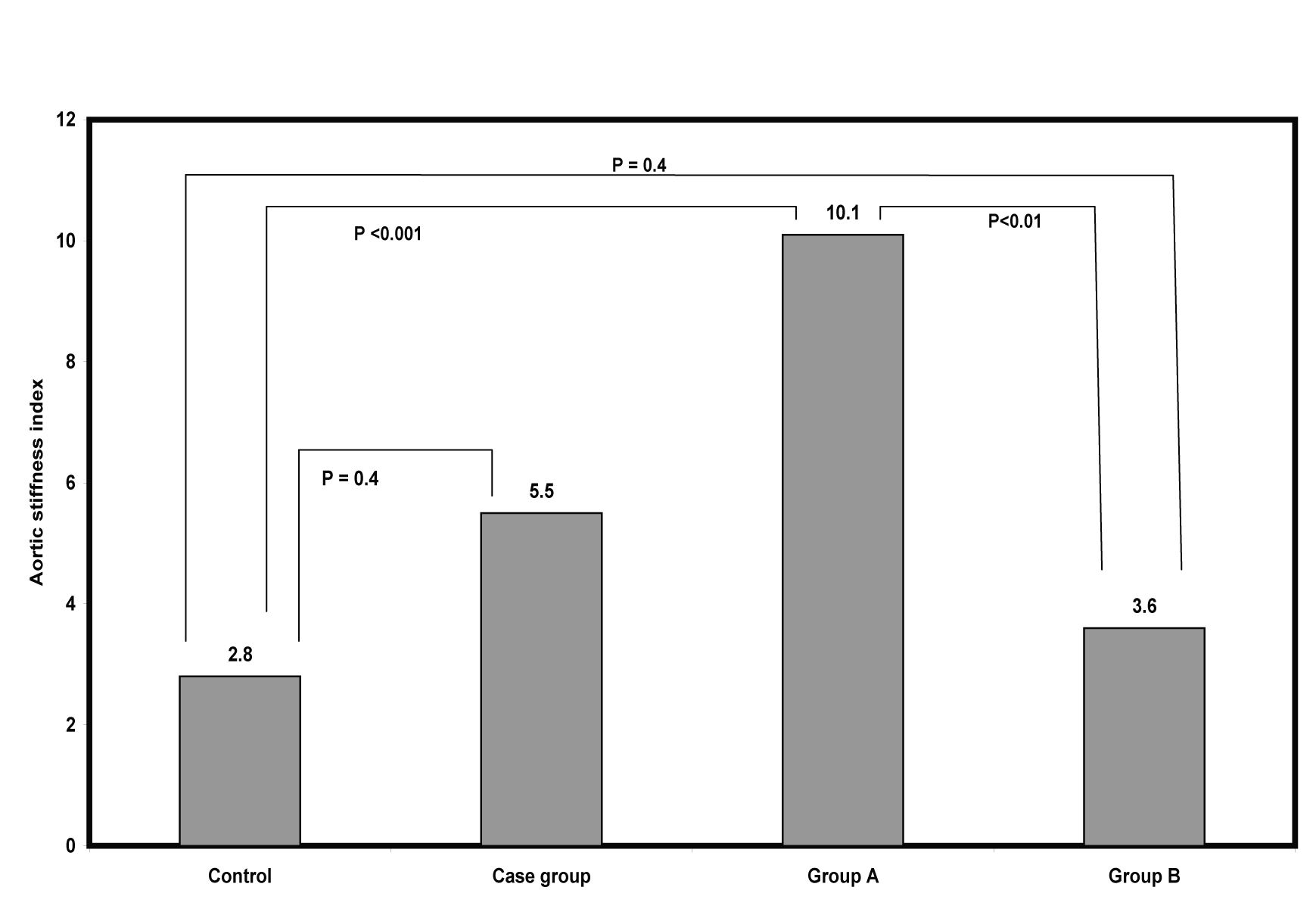 Click for large image | Figure 1. Mean Values of Aortic Stiffness Index in Case and Control Groups. |
 Click to view | Table 2. Correlation Coefficient Between Aortic Stiffness Index and Different Variables in Group A |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with a marked increase in CVD. Increased risk factors for CVD before the onset of type 2 diabetes have been shown in several populations [1, 10, 13]. It is not known whether the increased atherogenicity of the prediabetic state is primarily due to increased insulin resistance or impaired blood glucose [14].
There has been much recent interest in the relationship between arterial stiffness and CVD. Pulse pressure, pulse wave velocity, and echographic surrogate measures of arterial stiffness, indicate that arterial stiffness increases both with age and in certain disease states that are themselves associated with increased cardiovascular risk, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, obesity, and end-stage renal failure [15-18].
However, the state of arterial elasticity in prediabetes has received little attention. We therefore studied prediabetic normotensive adults in whom the prevalence of insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance is high, to test the hypotheses that insulin resistance is associated with arterial stiffness and that this relationship is dependent or independent of glucose tolerance status.
The main finding of current study is that, insulin resistance is associated with arterial stiffness and that the association appears to be independent of glucose tolerance status and obesity. Hyperglycemia has been shown to lead to the formation of advanced glycosylation endproducts (AGEs). Therefore, it has been suggested that individuals with prediabetes may have increased central arterial stiffness due to prolonged exposure to elevated glucose levels [4, 6]. Results from the present study did not identify an increase in central arterial stiffness among individuals with insulin sensitive prediabetes. Furthermore, no correlation was found between arterial stiffness and fasting glucose measurements. Our data suggest that insulin resistance may be more important in the development of central arterial stiffness than accumulation of AGEs.
The mechanism underlying the relationship between insulin resistance and arterial stiffness is unknown, and current cross-sectional study cannot identify the causative factor. Studies have shown that insulin-resistant states are associated with decreased endothelium-dependent vasodilation [19]. In addition, insulin has been shown to induce vascular smooth muscle proliferation and migration in cell culture [20].
Previous studies have shown that visceral fat in young healthy individuals and older adults is associated with increased central arterial stiffness [18, 21, 22]. The present study confirms this association. In agreement with a recent study by Sabio et al [16], we observed that abdominal adiposity as measured by waist circumference was strongly and adversely associated with aortic stiffness, whereas body mass index as a measure of general adiposity was not. In addition, the present study found that insulin resistance appears to be more strongly associated with arterial stiffness than with measures of obesity. These results suggest that the obesity-arterial stiffness relationship may be mediated in part through increasing insulin resistance. In general, adipocytes, in particular from visceral abdominal regions, produce several bioactive peptides which in turn impact on vascular structure and function [23, 24].
However, increased distending pressure tends to reduce the elasticity of a given arterial segment through the recruitment of collagen fibers [25, 26]. Nevertheless, in our study, as all subjects were normotensive, such the association was not held.
We should point out that the total lipids had insignificant correlation with aortic stiffness. When the components of the lipids were considered separately, aortic stiffness showed direct associations only with triglycerides
In current study, age was an independent predictor of aortic stiffness. It is known that different arterial segments respond differently to aging. Aorta, an elastic artery, loses its compliance with advancing age, whereas compliance in the peripheral, predominantly muscular, arteries appears less closely related to age [15, 27, 28].
In conclusion, we have shown that prediabetic subjects have an aortic stiffness which represent pattern of cardiovascular risk factors, and these changes are predominantly observed in prediabetic subjects with increased HOMA IR and visceral obesity. As the aortic elasticity changes in the prediabetic state are limited to subjects with insulin resistance, the use of insulin-sensitizing agents to prevent diabetes could have a beneficial effect on CVD. None of the studied pre diabetic adult had cardiac complications. The data of the current study report that, as changes can be detected before the appearance of clinically apparent vascular disease, arterial stiffness may act as a marker for the development of future CVD. It is likely that over the next few years measurement of arterial stiffness will become an increasingly important part of the process of risk assessment, and may possibly also improve the monitoring of therapy [29]. Additional studies will be needed to assess the effect of an improvement in insulin sensitivity to decrease arterial stiffness.
It is important to note several limitations in this study design. First, the sample size was relatively small. Second, this study enrolled a relatively population of older individuals carefully screened to exclude diabetes and hypertension. Further research will be needed to confirm whether these results generalize to middle-aged, more insulin-sensitive individuals and those with hypertension through a large community based study.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the important contributions of many individuals to this study: Prof and Dr Ola Leheta, Prof and Dr. Amal Yousef for coordinating the study. Diabetes and cardiology unites nursing staff for their technical support.
| References | ▴Top |
- Isomaa B, Almgren P, Tuomi T, Forsen B, Lahti K, Nissen M, Taskinen MR,
et al . Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2001;24(4):683-689.
pubmed - Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Asmar R, Gautier I, Laloux B, Guize L, Ducimetiere P,
et al . Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 2001;37(5):1236-1241.
pubmed - Laurent S, Katsahian S, Fassot C, Tropeano AI, Gautier I, Laloux B, Boutouyrie P. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of fatal stroke in essential hypertension. Stroke. 2003;34(5):1203-1206.
pubmed - Singh R, Barden A, Mori T, Beilin L. Advanced glycation end-products: a review. Diabetologia. 2001;44(2):129-146.
pubmed - Arcaro G, Cretti A, Balzano S, Lechi A, Muggeo M, Bonora E, Bonadonna RC. Insulin causes endothelial dysfunction in humans: sites and mechanisms. Circulation. 2002;105(5):576-582.
pubmed - Steinberg HO, Chaker H, Leaming R, Johnson A, Brechtel G, Baron AD. Obesity/insulin resistance is associated with endothelial dysfunction. Implications for the syndrome of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(11):2601-2610.
pubmed - Martens FM, van der Graaf Y, Dijk JM, Olijhoek JK, Visseren FL. Carotid arterial stiffness is marginally higher in the metabolic syndrome and markedly higher in type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients with manifestations of arterial disease. Atherosclerosis. 2008;197(2):646-653.
pubmed - Sunyer FX, Maggio Ca, Pi G. Obesity and type 2 diabetes, Endocrinol Metab. Clin North Am. 2000;3(1):521-8.
- Grundy SM. Multifactorial causation of obesity: implications for prevention. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998;67(3 Suppl):563S-572S.
pubmed - Haffner SM, Mykkanen L, Festa A, Burke JP, Stern MP. Insulin-resistant prediabetic subjects have more atherogenic risk factors than insulin-sensitive prediabetic subjects: implications for preventing coronary heart disease during the prediabetic state. Circulation. 2000;101(9):975-980.
pubmed - Ferreira I, Boreham CA, Twisk JW, Gallagher AM, Young IS, Murray LJ, Stehouwer CD. Clustering of metabolic syndrome risk factors and arterial stiffness in young adults: the Northern Ireland Young Hearts Project. J Hypertens. 2007;25(5):1009-1020.
pubmed - Oliver JJ, Webb DJ. Noninvasive assessment of arterial stiffness and risk of atherosclerotic events. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23(4):554-566.
pubmed - Hu FB, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Colditz G, Liu S, Solomon CG, Willett WC. Diet, lifestyle, and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in women. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(11):790-797.
pubmed - Scott CL. Diagnosis, prevention, and intervention for the metabolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 2003;92(1A):35i-42i.
pubmed - Safar ME, Thomas F, Blacher J, Nzietchueng R, Bureau JM, Pannier B, Benetos A. Metabolic syndrome and age-related progression of aortic stiffness. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(1):72-75.
pubmed - Sabio JM, Vargas-Hitos J, Zamora-Pasadas M, Mediavilla JD, Navarrete N, Ramirez A, Hidalgo-Tenorio C,
et al . Metabolic syndrome is associated with increased arterial stiffness and biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(10):2204-2211.
pubmed - Mahmud A, Almuntaser I, Brown A, King G, Crean P, Feely J. Left ventricular structural and functional changes in the metabolic syndrome. J Cardiometab Syndr. 2009;4(2):81-88.
pubmed - Blacher J, Safar ME, Guerin AP, Pannier B, Marchais SJ, London GM. Aortic pulse wave velocity index and mortality in end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2003;63(5):1852-1860.
pubmed - van Popele NM, Westendorp IC, Bots ML, Reneman RS, Hoeks AP, Hofman A, Grobbee DE,
et al . Variables of the insulin resistance syndrome are associated with reduced arterial distensibility in healthy non-diabetic middle-aged women. Diabetologia. 2000;43(5):665-672.
pubmed - Schram MT, Henry RM, van Dijk RA, Kostense PJ, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Heine RJ,
et al . Increased central artery stiffness in impaired glucose metabolism and type 2 diabetes: the Hoorn Study. Hypertension. 2004;43(2):176-181.
pubmed - Ferreira I, Snijder MB, Twisk JW, van Mechelen W, Kemper HC, Seidell JC, Stehouwer CD. Central fat mass versus peripheral fat and lean mass: opposite (adverse versus favorable) associations with arterial stiffness? The Amsterdam Growth and Health Longitudinal Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(6):2632-2639.
pubmed - Sutton-Tyrrell K, Newman A, Simonsick EM, Havlik R, Pahor M, Lakatta E, Spurgeon H,
et al . Aortic stiffness is associated with visceral adiposity in older adults enrolled in the study of health, aging, and body composition. Hypertension. 2001;38(3):429-433.
pubmed - Okamoto Y, Arita Y, Nishida M, Muraguchi M, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Igura T,
et al . An adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, adheres to injured vascular walls. Horm Metab Res. 2000;32(2):47-50.
pubmed - Matsuzawa Y, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Shimomura I. Adiponectin and metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(1):29-33.
pubmed - Benetos A, Laurent S, Asmar RG, Lacolley P. Large artery stiffness in hypertension. J Hypertens Suppl. 1997;15(2):S89-97.
pubmed - Franklin SS. Arterial stiffness and hypertension: a two-way street? Hypertension. 2005;45(3):349-351.
pubmed - Scuteri A, Najjar SS, Muller DC, Andres R, Hougaku H, Metter EJ, Lakatta EG. Metabolic syndrome amplifies the age-associated increases in vascular thickness and stiffness. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(8):1388-1395.
pubmed - Lee AT, Cerami A. Role of glycation in aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992;663:63-70.
pubmed - Mackenzie IS, Wilkinson IB, Cockcroft JR. Assessment of arterial stiffness in clinical practice. QJM. 2002;95(2):67-74.
pubmed
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Clinical Medicine Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.


