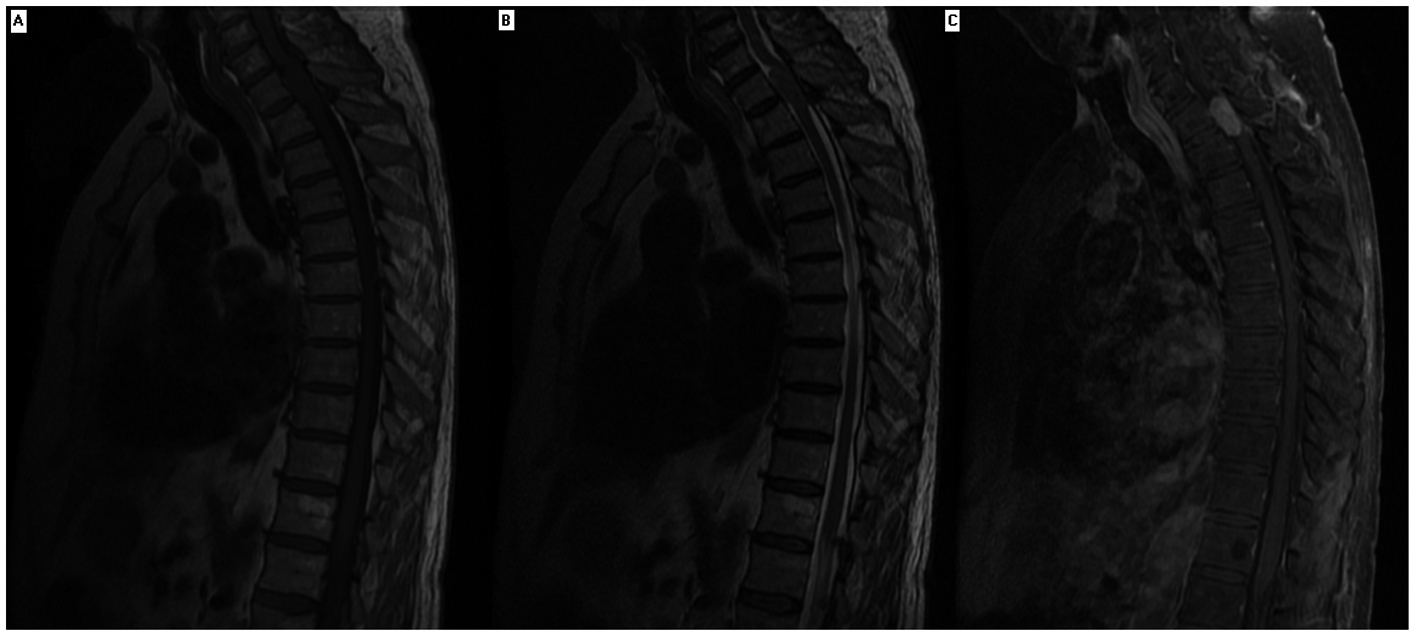
Figure 1. Magnetic resonance imaging of thoracic spine of a patient with paraplegia. Contrast enhancing magnetic resonance imaging showed solid homogenous intradural extramedullary mass extends from level of first thoracic vertebrae superior endplate to superior aspect of second thoracic vertebrae resulting in spinal cord compression. The mass was isointense on MRI T1 and T2 sequence.