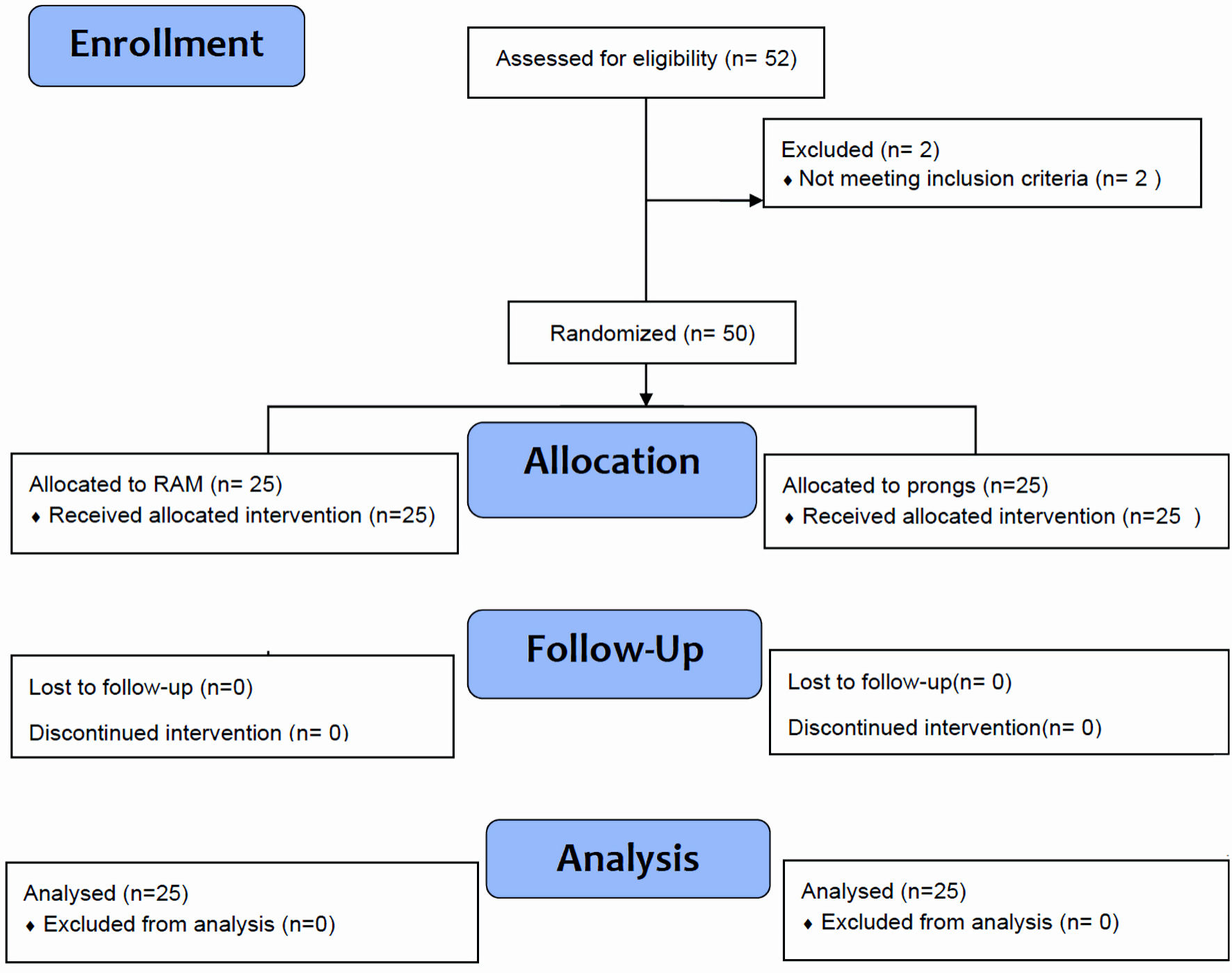
Figure 1. “ProRAM” randomized trial flow diagram for neonates ≥ 32 weeks of gestation.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 16, Number 1, January 2024, pages 24-30
RAM Cannula Versus Bi-Nasal Prongs as Respiratory Device Interfaces in Neonates of Thirty-Two or More Weeks of Gestation With Respiratory Distress: The First “ProRAM” Randomized Trial Report
Figures

Tables
| Characteristics | RAM (n = 25) | Prong (n = 25) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| aGroup B streptococcus (GBS)-positive screen or positive urine culture during current pregnancy. bCoronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) positive mothers at time of delivery. SD: standard deviation; PROM: premature rupture of membrane; UTI: urinary tract infection; Apgar: appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration. | |||
| Gestational age (weeks), mean ± SD | 36 ± 2 | 36 ± 2 | 1.000 |
| Birth weight (g), mean ± SD | 2,600 ± 600 | 2,500 ± 670 | 0.600 |
| Small for age | 5 (20%) | 3 (12%) | 0.702 |
| Male sex | 10 (4%) | 14(6%) | 0.396 |
| Cesarean section | 20 (80%) | 22 (88%) | 0.700 |
| Maternal diseases (hypertension, diabetes, hypothyroidism, pre-eclampsia) | 3 | 8 | 0.170 |
| Maternal infectious risk factor (PROM, UTI, GBSa, COVID-19 infectionb) | 12 | 9 | 0.567 |
| Antenatal steroids | 18 (72%) | 16 (64%) | 0.800 |
| Apgar scores (mean ± SD) | |||
| 1st min | 7 ± 1.6 | 7 ± 1.9 | 1.000 |
| 5th min | 9 ± 0.28 | 9 ± 0.6 | 1.000 |
| Low Apgar score < 6 | |||
| 1st min | 3 | 4 | 1.000 |
| 5th min | 0 | 0 | 1.000 |
| RAM (25) | Prong (25) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SD: standard deviation; FiO2: fraction of inspired oxygen. | |||
| Average respiratory rate (RR) at admission, mean ± (SD) | 61 (41) | 61 (41) | |
| RR ≤ 60 | 13 | 13 | |
| RR 60 - 70 | 8 | 7 | |
| RR 70 - 80 | 3 | 4 | |
| RR > 80 | 1 | 1 | |
| Average FiO2 at admission, mean ± (SD) | 23% (29%) | 23% (29%) | |
| FiO2 at admission 21% (n) | 20 | 21 | |
| FiO2 at admission 21-40% (n) | 4 | 4 | |
| FiO2 at admission > 40% (n) | 1 | 0 | |
| Mean duration of O2 support hours (SD) | 40.7 (72.6) | 154.6 (255) | 0.037 |
| Total O2 support < 6 h | 8 | 9 | |
| Total O2 support 6 - 72 h | 14 | 8 | |
| Total O2 support 73 h - ≤ 1 week | 1 | 2 | |
| Total O2 support > 1 week | 2 | 6 | |
| Need for upgrade of respiratory support (to NIPPV) | 2 (8%) | 4(16%) | 0.667 |
| Need for intubation | 0 | 1 (4%) | 1 |
| Received surfactant | 0 | 1 (4%) | 1 |
| Received antibiotics (%) | 7 (28%) | 8 (32%) | 1 |
| Mean duration of antibiotics, days ± (SD) | 4 (3) | 7 (6) | 1 |
| Final diagnosis | |||
| Prolonged transition | 8 (32%) | 9 (36%) | |
| Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) | 15 (60%) | 12 (48%) | |
| Respiratory distress syndrome | 2 (8%) | 4(16%) | |
| Nasal injury (total) | 0 | 5 (20%) | 0.05 |
| Nasal mucosal edema | 0 | 1 (4%) | |
| Nasal septal injury | 0 | 3 (12%) | |
| Nasal bridge injury | 0 | 1 (4%) | |
| Pneumomediastinum | 2 (8%) | 1 (4%) | 1 |
| Pneumothorax | 0 | 1 (4%) | 1 |
| Mortality | 0 | 0 | |