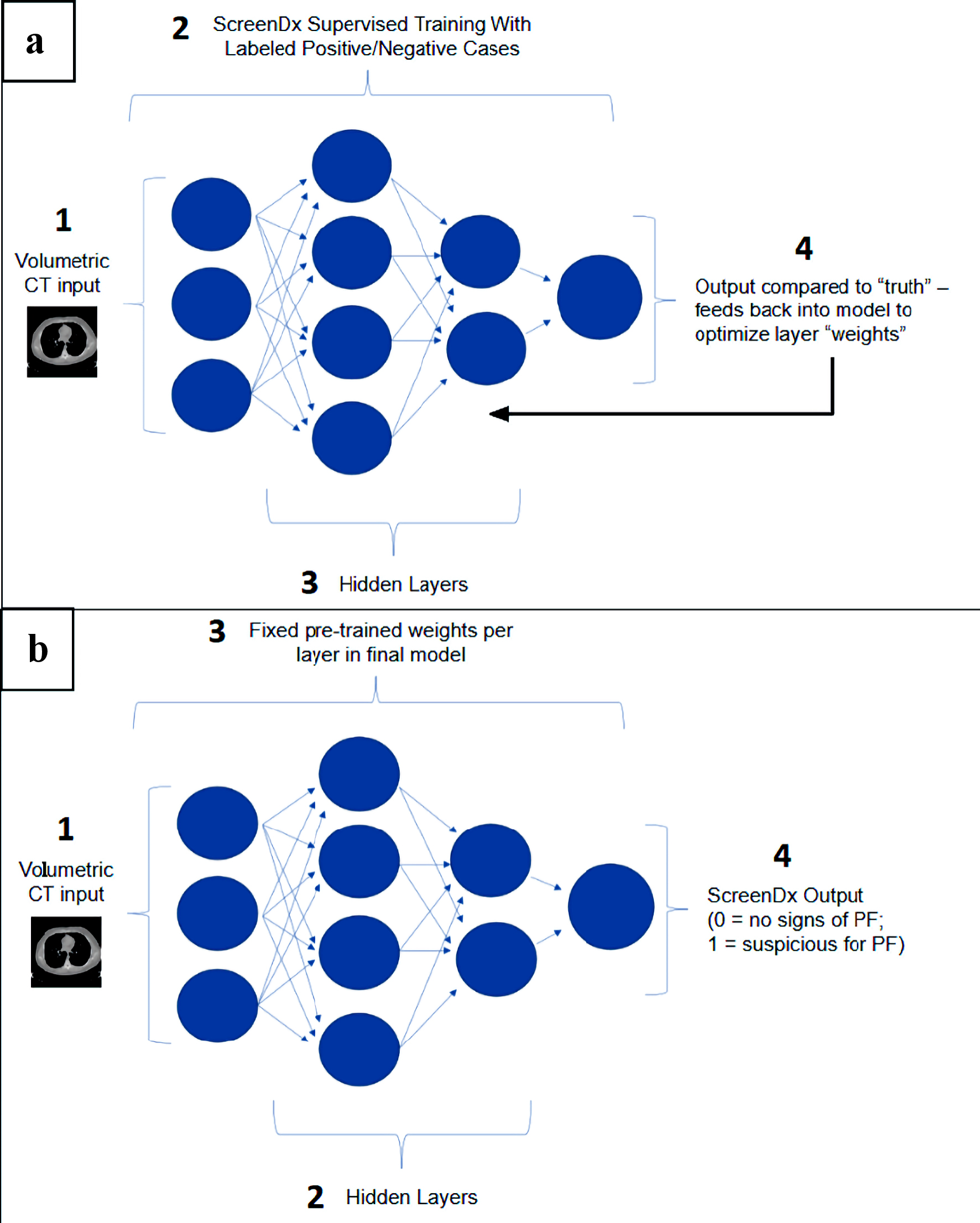
Figure 1. ScreenDx-LungFibrosis™ analysis algorithm. (a) ScreenDx-LungFibrosis™ supervised training: The analysis algorithm receives volumetric CT input normalized to standardized pixel values (1) from thousands of labeled cases (i.e., positive or negative for PF). It is then trained (2) using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) that incorporates thousands of features via hidden layers (3) into the network. Algorithm output (4) is compared to the “truth”, established by the labeled cases, and feeds back into the model to optimize layer weights. (b) ScreenDx-LungFibrosis™ evaluation of new cases. The analysis algorithm receives volumetric CT input normalized to standardized pixel values (1) from new cases, which proceed through pre-trained hidden layers (2) with fixed weights per layer (3) to create a binary output (4) of 0 (no signs of PF) or 1 (suspicious for PF). PF: pulmonary fibrosis; CT: computed tomography.