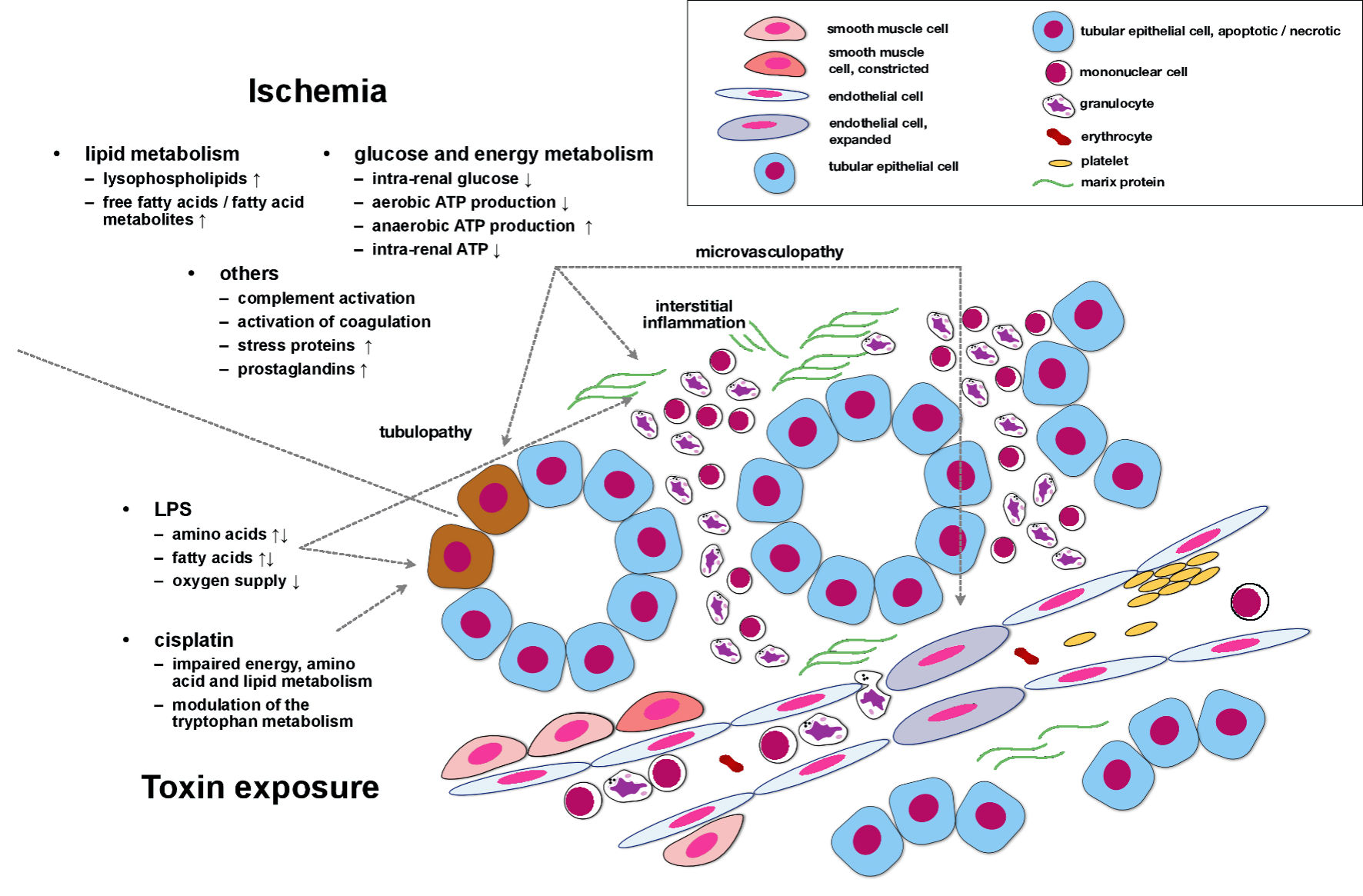
| Ischemic AKI | | |
| Liu et al, 2012 [42] | Bilateral renal ischemia (45 min) in Sprague-Dawley rats, L-carnitine pretreatment in one group | Increase of serum lysophospholipids and free fatty acids, decreased activity of serum phospholipase A2/ischemia-associated dysregulation of lipid metabolism |
| Wei et al, 2014 [44] | Bilateral renal ischemia in mice (25 min), analyzes at 2 or 48 h or at 7 days after reperfusion | Alterations in glucose, lipid, and purine metabolism/identification of candidates involved in energy depletion and inflammation |
| Huang et al, 2018 [45] | Unilateral renal ischemia in rats (45 min) | Increased availability of stress signaling proteins (proteomics analysis), increase of cortical lipid metabolites, accompanied by lower tissue glucose levels |
| Fox et al, 2019 [46] | Experimental cardiorenal syndrome type 3 (6) in mice (bilateral renal ischemia for 22 min) | Intrarenal amino acid depletion and oxidative stress, intracardiac stimulation of anaerobic ATP synthesis/experimental confirmation of reno-cardiac cross-talk in AKI |
| Davidson et al, 2022 [49] | Cardiopulmonary bypass including so-called deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (CPB/DHCA) in piglets | Stimulated anaerobic glycolysis in AKI piglets/anaerobic glycolysis as potential biomarker of early AKI in CPB |
| Toxic AKI | | |
| Izquierdo-Garcia et al, 2019 [52] | Living Escherichia coli for sepsis induction in pigs | Multiple metabolic abnormalities in kidney tissue, serum, and urine, correlations between certain urine metabolites and established AKI biomarkers/metabolomics help to identify novel AKI biomarker molecules |
| Qu et al, 2020 [53] | Intraperitoneal cisplatin injections (Sprague-Dawley rats), urine and renal tissue analyzes | Dysregulation of tissue amino acid and lipid metabolism; additional identification of AKI biomarker candidates in urine samples |
| Gao et al, 2021 [54] | LPS-induced multiorgan failure in rats | Significant tissue damage in liver, lungs, colon, and kidney, alteration of more than 50 metabolic pathways upon LPS administration/conclusion rather vague |
| Ping et al, 2021 [55] | LPS treatment of Sprague-Dawley rats | Stimulation of aerobic and anaerobic metabolism, impaired oxygen supply, abnormalities in fatty acid metabolism/alterations proposed as key events in sepsis-associated AKI |
| Tan et al, 2021 [56] | Cisplatin-induced AKI in Sprague-Dawley rats, targeted analysis of the tryptophan metabolism | Identification of indoxyl sulfate as key regulator of tissue damage in cisplatin-induced AKI |
| Xiong et al, 2021 [59] | Cisplatin-induced AKI in Sprague-Dawley and Wistar rats | Intrarenal uncoupling protein (UCP) 1 inhibits intrarenal lipid clearance |
| Other types of AKI | | |
| Xue et al, 2021 [61] | Murine model of heat stroke-related AKI | Intrarenal enrichment of unsaturated fatty acids |