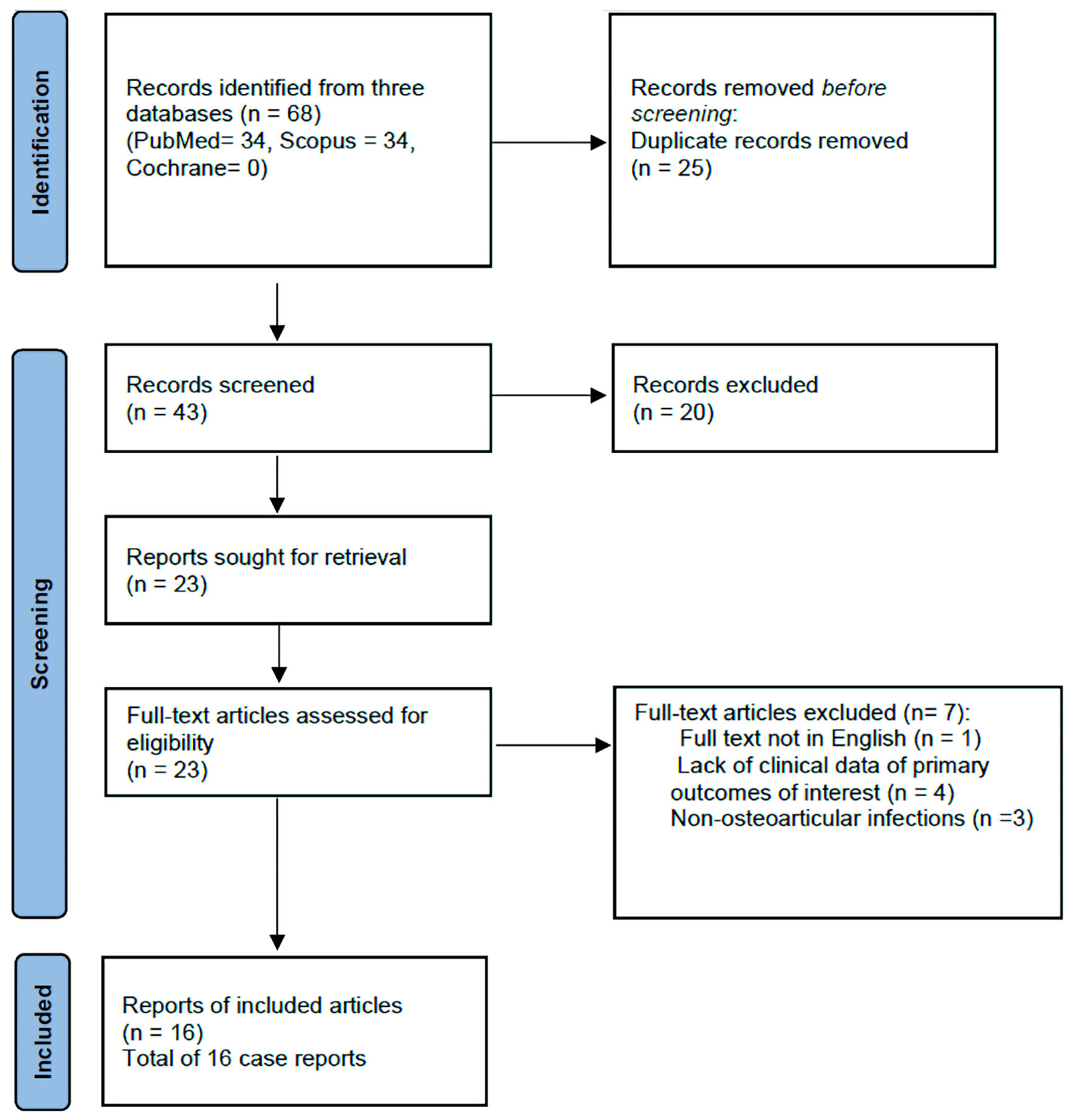
Figure 1. Flow diagram of systematic review search.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 15, Number 4, April 2023, pages 187-199
A Rare Pathogen of Bones and Joints: A Systematic Review of Osteoarticular Infections Caused by Gemella morbillorum
Figure

Tables
| Study | Study type | Clear aim | Consecutive patients inclusion | Prospective data collection | Appropriate endpoints | Unbiased assessment | Follow-up period | Loss of 5% of follow-up | Prospective data size calculation | Total score | Study quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All 16 studies were evaluated using the methodological index for non-randomized studies (MINORS) scale. The items in the MINORS scale are scored 0 (not reported), 1 (reported but inadequate), or 2 (reported and adequate). The quality of each study was categorized according to the total score of each study: poor (0 - 5 points), moderate (6 - 10 points), and good (11 - 16 points). Thirteen studies were rated as having moderate quality (MINORS score 6 - 10), and 3 of poor quality (MINORS score 0). | |||||||||||
| Omran et al, 1993 [13] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 | Moderate |
| Desmottes et al, 2018 [30] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 | Moderate |
| Roche et al, 2005 [14] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 | Moderate |
| van Dijk et al, 1999 [18] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 8 | Moderate |
| Czarnecki et al, 2007 [19] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 | Moderate |
| von Essen et al, 1993 [21] | Case report | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | Poor |
| Pardo-Pol et al, 2022 [22] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 8 | Moderate |
| Medina-Gens et al, 2007 [23] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 7 | Moderate |
| Giger et al, 2016 [15] | Case report | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 7 | Moderate |
| Savides et al, 2007 [29] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 6 | Moderate |
| Eisenberger et al, 1998 [25] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 | Moderate |
| Garcia-Bordes et al, 2010 [27] | Case report | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 5 | Poor |
| Sono et al, 2018 [26] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 6 | Moderate |
| Singer et al, 2021 [24] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 8 | Moderate |
| Namazi et al, 2022 [28] | Case report | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4 | Poor |
| Ann et al, 2013 [20] | Case report | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 7 | Moderate |
| Author, year of publication | Age (years)/gender | Affected joint and/or bone/clinical syndrome | Possible predisposing factors | Presumed source of Gemella morbillorum | Blood culture | Extra-articular infection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GI: gastrointestinal. | ||||||
| Omran et al, 1993 [13] | 48/male | Native wrist septic arthritis adjacent to an infected ipsilateral dialysis access graft with Gemella bacteremia | Immunosuppression (end-stage renal disease hemodialysis) | An odontogenic source with Gemella bacteremia | Positive | Infected ipsilateral dialysis access graft |
| Poor dental hygiene and concurrent multiple dental caries | ||||||
| Desmottes et al, 2018 [30] | 90/female | Native knee septic arthritis | Underlying joint disease (concurrent acute pseudogout) | Not identified | Negative | None |
| Roche et al, 2005 [14] | 42/male | Native knee septic arthritis | Not identified | Not identified | Negative | None |
| van Dijk et al, 1999 [18] | 42/male | Native hip septic arthritis with trochanteric osteomyelitis | Not identified | Not identified | Negative | None |
| Czarnecki et al, 2007 [19] | 75/male | Native knee septic arthritis | Immunosuppression (diabetes mellitus) | Not identified | Positive | Infective endocarditis |
| von Essen et al, 1993 [21] | 45/female | Periprosthetic elbow joint infection | Prosthetic joint (within 1 year of surgery which was complicated by two periarticular fistulas that warranted two revision surgeries) | Not identified | Not available | Not available |
| Pardo-Pol et al, 2022 [22] | 60/female | Periprosthetic hip joint infection | Prosthetic joint (10 years prior, with revision surgery of one part 5 years prior) | GI source (Gemella translocation, in the setting of decompensated liver disease) | Negative | None |
| Immunosuppression (immunotherapy for severe psoriasis) | ||||||
| Decompensated chronic liver disease | ||||||
| Medina-Gens et al, 2007 [23] | 41/female | Periprosthetic hip joint infection | Prosthetic joint (10 years prior) | An odontogenic source with Gemella bacteremia | Positive | Infective endocarditis |
| Recent dental infection | ||||||
| Giger et al, 2016 [15] | 74/male | Thoracic vertebrae T5 and T6 osteomyelitis | Recent endoscopic intervention | GI source (Gemella bacteremia following esophageal biopsy) | Positive (blood culture also grew Streptococcus mitis) | None |
| Immunosuppression (chemotherapy for esophageal cancer) | ||||||
| Savides et al, 2007 [29] | 78/male | Thoracic vertebrae T5 and T6 osteomyelitis | Recent endoscopic intervention (endoscopic posterior mediastinal lymph node biopsy) | GI source (Gemella bacteremia following endoscopic intervention) | Positive | Posterior mediastinitis (contagious spread) |
| Eisenberger et al, 1998 [25] | 55/female | Thoracic vertebrae T6 and T7 osteomyelitis | Immunosuppression (chronic steroids use and cytotoxic therapy for renal transplant) | Hematogenous spread from distant infectious culprit (cardiac vegetations) | Positive | Infective endocarditis (cardiac vegetations were present prior to osteomyelitis) |
| Garcia-Bordes et al, 2010 [27] | 53/male | Lumbar discitis at L1 with an epidural abscess at T12 - L1 level | Recent non-operative lumbar fracture | Not identified | Negative | None |
| Immunosuppression (diabetes mellitus) | ||||||
| Sono et al, 2018 [26] | 81/male | Lumbar discitis at the L5/S1 level | Recent periodontitis | An odontogenic source with suspected transient Gemella bacteremia | Negative | None |
| Singer et al, 2021 [24] | 49/male | Osteomyelitis and discitis at T10 - 11 and L4 - L5 | Underlying joint disease (ankylosing spondylitis) | An odontogenic source with Gemella bacteremia | Positive | Infective endocarditis |
| Poor dental hygiene and concurrent dental abscess | ||||||
| Namazi et al, 2022 [28] | 74/female | Sacral osteomyelitis with presacral abscess formation | Gynecological surgery (vaginal hysterectomy with persistent sacrovaginal fistula that represented a nidus of chronic deep pelvic infection) | Gynecological tract (supported by polymicrobial growth on blood and drained abscess cultures) | Positive (blood culture also grew Streptococcus constellatus) | |
| Ann et al, 2013 [20] | 72/female | Sternal osteomyelitis with large sub-sternal abscess formation | Recent blunt anterior chest wall trauma | Not identified | Negative | Anterior mediastinitis (contagious spread) |
| Author/year of publication | Surgical management | Antibiotic therapy | Antibiotic susceptibility | Duration of antibiotic therapy (weeks) | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omran et al, 1993 [13] | Not performed | Vancomycin and gentamicin for 1 day then vancomycin (penicillin allergic) | Penicillin, cephalothin, clindamycin, erythromycin, and vancomycin | 6 | Full recovery remained well at 6 months follow-up |
| Desmottes et al, 2018 [30] | Arthroscopic articular washout | Amoxicillin/clavulanic followed by oral amoxicillin based on susceptibility | Penicillin | 6 | Full recovery at 6 weeks |
| Roche et al, 2005 [14] | Arthroscopic articular washout | Benzylpenicillin and flucloxacillin followed by flucloxacillin and amoxicillin | Penicillin, amoxicillin, and vancomycin | 6 | Full recovery at 6 weeks |
| van Dijk et al, 1999 [18] | Two articular washouts, followed by delayed bone grafting | Penicillin and clindamycin for 6 weeks, followed by oral clindamycin for 3 weeks | Penicillin and clindamycin, but resistance to gentamicin | 10 | Full recovery remained well at 18 months follow-up |
| Czarnecki et al, 2007 [19] | Percutaneous needle aspiration and irrigation of the joint | Ceftriaxone monotherapy | Not available | 6 | Full recovery at 3 months, cardiac vegetation resolved by 6 weeks |
| von Essen et al, 1993 [21] | Two-stage arthroplasty revision | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available |
| Pardo-Pol et al, 2022 [22] | Debridement, antibiotics, irrigation, and implant retention followed by repeated debridement | Daptomycin and ceftazidime, followed by cefotaxime monotherapy, followed by oral amoxicillin | Penicillin and cefotaxime | 12 | Full recovery at 3 months follow-up, remained well at 18 months follow-up |
| Medina-Gens et al, 2007 [23] | Prothesis removal and delayed replacement at two-stage surgery | Cloxacillin and gentamicin, then cefotaxime replaced cloxacillin based on susceptibility, then the latter was switched to penicillin G after 2 weeks rifampin and teicoplanin replaced penicillin G (suspicion of penicillin allergy) | Penicillin, cefotaxime, gentamicin, and vancomycin | 15 | Full recovery |
| Remained well at 18 months follow-up | |||||
| Giger et al, 2016 [15] | Vertebroplasty for suspected pathological fracture, then decompressive laminectomy for epidural abscess | Empiric amoxicillin/clavulanate was switched to ceftriaxone and metronidazole for 4 weeks, which were replaced by oral moxifloxacin (that was later switched to clindamycin). | Clindamycin and moxifloxacin | 12 | Full recovery at 12 weeks |
| Also, oral fluconazole and caspofungin were added for Candida albicans isolated from epidural abscess | Remained well at 6 months follow-up | ||||
| Savides et al, 2007 [29] | Not performed | Ceftriaxone for a total of 12 weeks, and then oral amoxicillin for several months | Not available | 24 | Full recovery |
| Eisenberger et al, 1998 [25] | Not performed | Ceftriaxone, clindamycin, and benzylpenicillin for 5 weeks followed by oral penicillin V and clindamycin for further 4 weeks | Penicillin and cephalosporins | 9 | Full recovery |
| Garcia-Bordes et al, 2010 [27] | Decompressive laminectomy for epidural abscess | Imipenem and vancomycin in the first 2 weeks, then switched to ceftriaxone for 4 weeks based on susceptibility | High resistance to penicillin and oxacillin | 6 | Full recovery at 6 weeks |
| Sono et al, 2018 [26] | Percutaneous needle aspiration of intervertebral disc | Empiric vancomycin and ceftriaxone were switched to ampicillin for 4 weeks; then, oral amoxicillin for further 3 weeks. | Penicillin | 8 | Full recovery |
| Singer et al, 2021 [24] | No surgery was performed for lumbar osteomyelitis | Piperacillin-tazobactam, followed by ceftriaxone and gentamicin for 3 weeks, and then ceftriaxone monotherapy for 3 weeks | Penicillin and ceftriaxone | 6 | Full recovery at 6 weeks, remained well at 2-year follow-up |
| Tooth extraction and washout for dental abscess | |||||
| Valvular replacement for infective endocarditis | |||||
| Namazi et al, 2022 [28] | Imaging-guided percutaneous drainage of pre-sacral collection drained, gynecological surgery for resection of the fistula tract | Empiric vancomycin, cefepime, and metronidazole were switched to ceftriaxone monotherapy | Penicillin and cephalosporins | 6 | Full recovery |
| Ann et al, 2013 [20] | Debridement and sub-sternal abscess drainage followed by delayed sternal defect reconstruction | Ampicillin/sulbactam for 5 weeks, then switched to oral amoxicillin/clavulanate | Clindamycin, erythromycin, penicillin G, and vancomycin | 8 | Full recovery at 8 weeks |