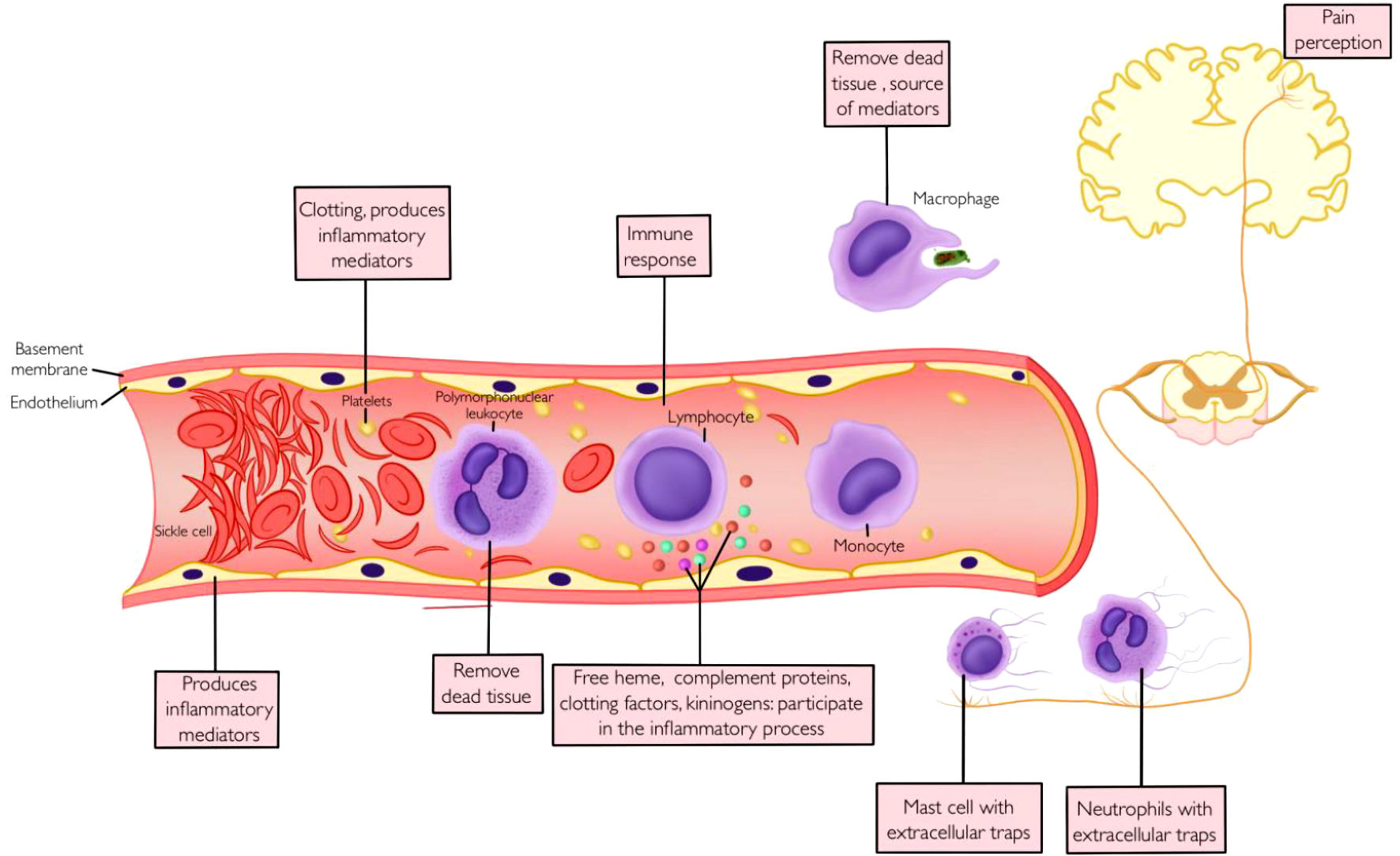
Figure 1. Vaso-occlusion, inflammation and pain.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 15, Number 1, January 2023, pages 10-22
Improving the Emergency Department Management of Sickle Cell Vaso-Occlusive Pain Crisis: The Role and Options of Sublingual and Intranasally Administered Analgesia
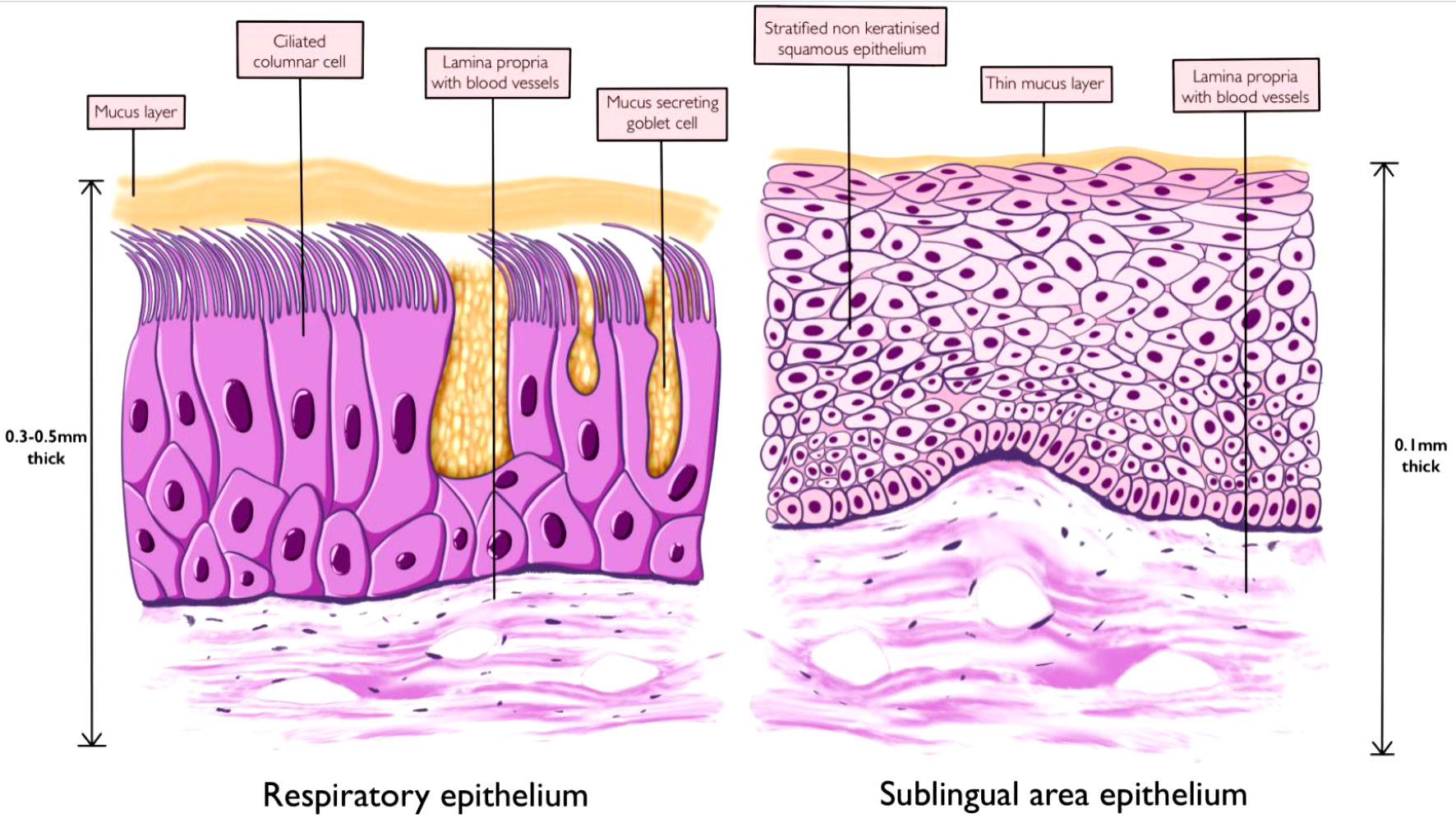
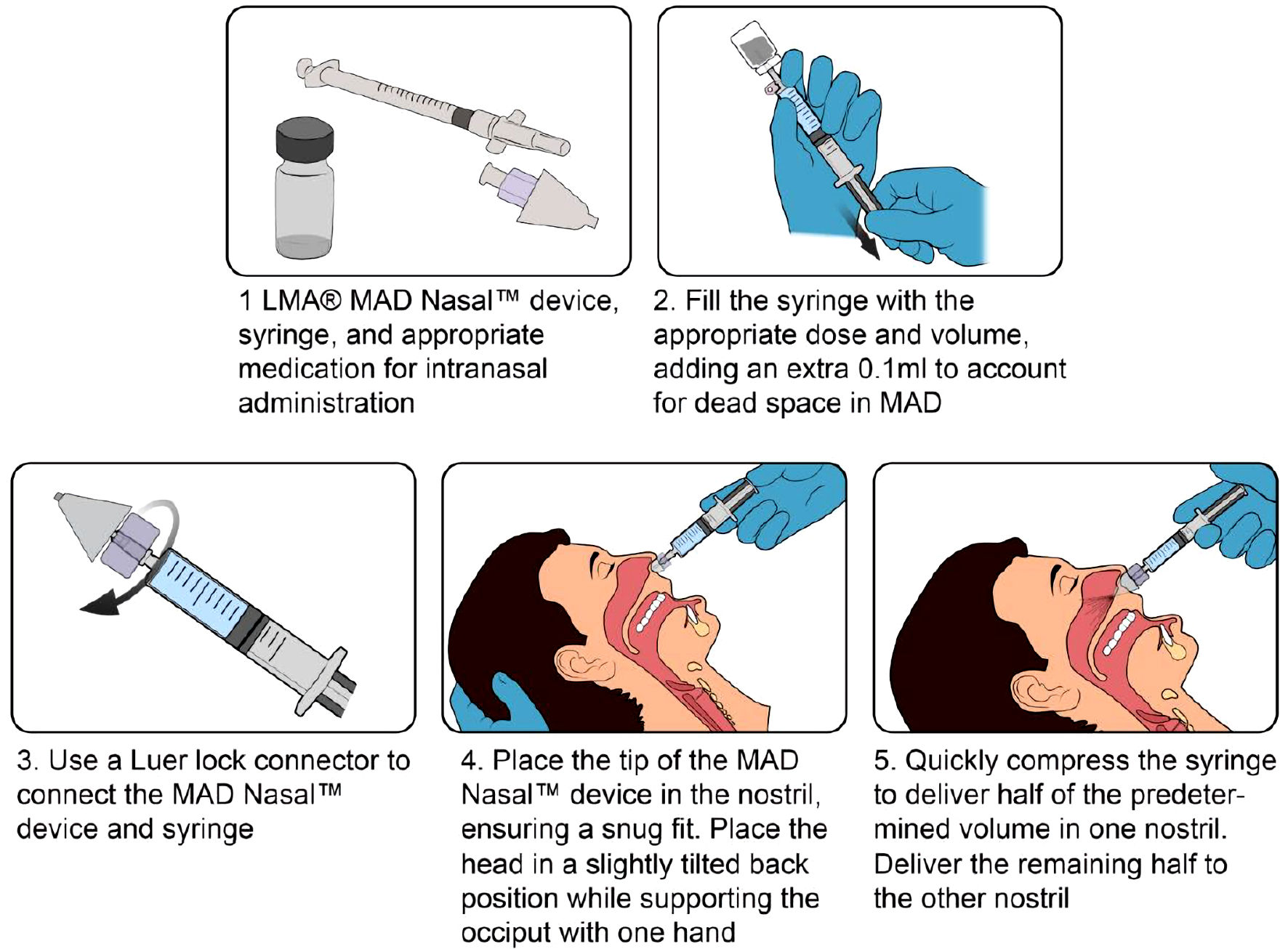
Figures

Tables
| Drug | Available intranasal products | Pharmacokinetics | Intranasal dose | Adverse effectsa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aAdverse events due to local effect of medication, medication-specific systemic adverse events not included. bDepend on dosage. cLimited evidence on pediatric use. | ||||
| Fentanyl [28, 41, 43-45, 50, 51] | Fentanyl citrate 50 µg/mL solution | Bioavailability: 55-89% | Adult: initial dose of 0.5 - 2 µg/kg (maximum of 100 µg/dose) | Nasal congestion, throat irritation, headache, unpleasant taste |
| Onset of action: 2 - 10 min | ||||
| Peak effect: 12 - 21 min | Pediatric (≥ 1 year old and weighing at least 10 kg): initial dose of 1 - 1.5 µg/kg (maximum of 100 µg/dose) | |||
| Duration of action: at least 60 minb | ||||
| Hydromorphone [28, 53-56] | Hydromorphone hydrochloride 1 mg/mL | Bioavailability: 50-60% | Adult: initial dose 4 - 8 mg | Unpleasant taste, dizziness, rhinitis |
| Onset of action: about 5 min | ||||
| Peak effect: 20 - 30 min | Pediatric: 0.03 - 0.06 mg/kgc | |||
| Duration of action: 90 - 180 min | ||||
| Ketorolac [57, 59, 63-67] | 8 sprays/1.7 g nasal spray bottle of ketorolac tromethamine (1 spray is equivalent to 15.75 mg in a 100 µL solution) | Bioavailability: 67-75% | Adult: < 65 years: one 15.75 mg spray in each nostril (31.5 mg/dose) every 6 - 8 h (maximum dose of 63 mg/day) | Nasal irritation, dysgeusia |
| Onset of action: 5 - 20 min | ≥ 65 years of age, renal impairment, weight < 50 kg: one 15.75 mg spray in one nostril (15.75 mg/dose) | |||
| Peak effect: 30 - 52 min | Pediatric: not recommended | |||
| Duration of action: about 180 min | ||||
| Drug | Available products | Pharmacokinetics | Equivalent dose to 15 mg of oral morphine | Adverse effectsa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aAdverse events due to local effect of medication, medication-specific systemic adverse events not included. bNo sublingual formulations are available in the United States. AE: adverse events. N/A: limited information on the pharmacokinetics of sublingual oxycodone. | ||||
| Fentanyl [81-85] | Spray: available in 100, 200, 400, 600, 800, 1,200, and 1,600 µg strengths | Bioavailability: 70-76% | 100 µg | No AE specific to the sublingual route |
| Onset of action: 5 - 15 min | ||||
| Tablet: available in 100, 200, 300, 400, 600, and 800 µg strengths | Peak effect: about 60 min | |||
| Duration of action: about 180 min | ||||
| Sufentanil [72-77] | Tablet: available in 30 µg strengths | Bioavailability: 47-57% | 30 µg | No AE specific to the sublingual route |
| Onset of action: 15 - 30 min | ||||
| Peak effect: 40 - 75 min | ||||
| Duration of action: at least 60 min | ||||
| Buprenorphine [86, 88-90, 91] | Tablet: available in 2 and 8 mg strengths | Bioavailability: 12-94% | 0.4 mg | No AE specific to the sublingual route |
| Onset of action: 30 - 60 min | ||||
| Peak effect: 60 - 240 min | ||||
| Duration of action: 6 - 12 h (for doses < 4 mg) and 24 - 72 h (for > 16 mg) | ||||
| Oxycodone [92, 93] | 5, 10 mg soluble tablets, 20 mg/mL concentrated oral solutionsb | Bioavailability: < 20% | 10 mg | No AE specific to the sublingual route |
| Onset of action: N/A | ||||
| Peak effect: N/A | ||||
| Duration of action: N/A | ||||