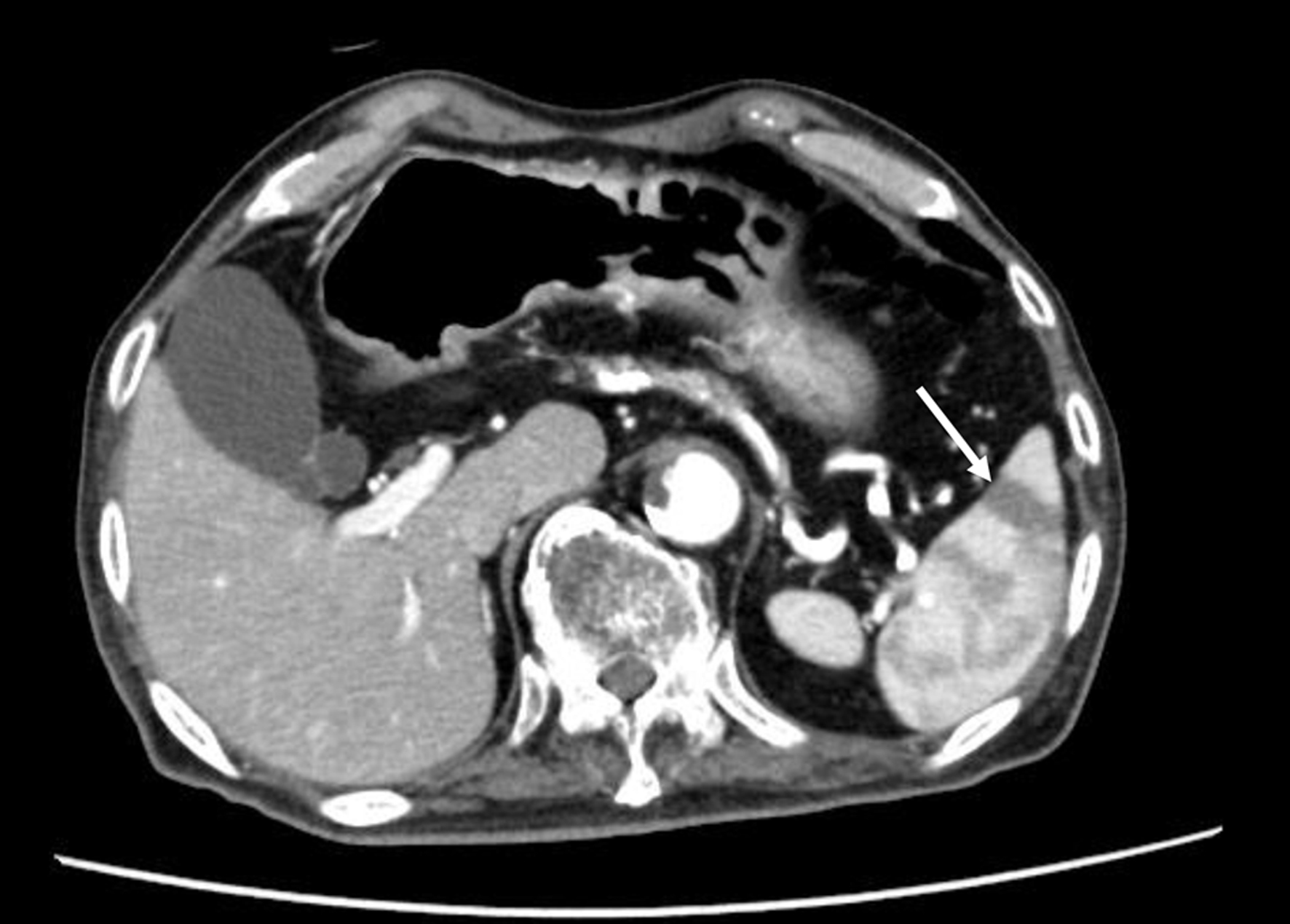
Figure 1. The contrast-enhanced CT scan finding of patients with splenic infarction. The arrow indicates splenic infarction. CT: computed tomography.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 15, Number 1, January 2023, pages 38-50
Clinical, Hematological, Biochemical and Radiological Characteristics for Patients With Splenic Infarction: Case Series With Literature Review
Figures

Tables
| The percentage of patients with abdominal pain, fever, and tachycardia is calculated using the number of cases described in the electronic medical record as the denominator. Fever and tachycardia mean body temperature > 38 °C and heart rate > 100 beats/min, respectively. | |
| Sex (male/female) | 11/7 |
| Age (years) | 78 ± 10 |
| Body height (cm) | 159 ± 8 |
| Body weight (kg) | 56 ± 13 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.9 ± 4.2 |
| Abdominal pain (n, %) | 5/10, 50% |
| Maximal body temperature (°C) | 38.0 ± 1.0 |
| Fever (n, %) | 8/14, 57.1% |
| Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 131 ± 24 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 68 ± 16 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 91 ± 20 |
| Tachycardia (n, %) | 6/15, 40% |
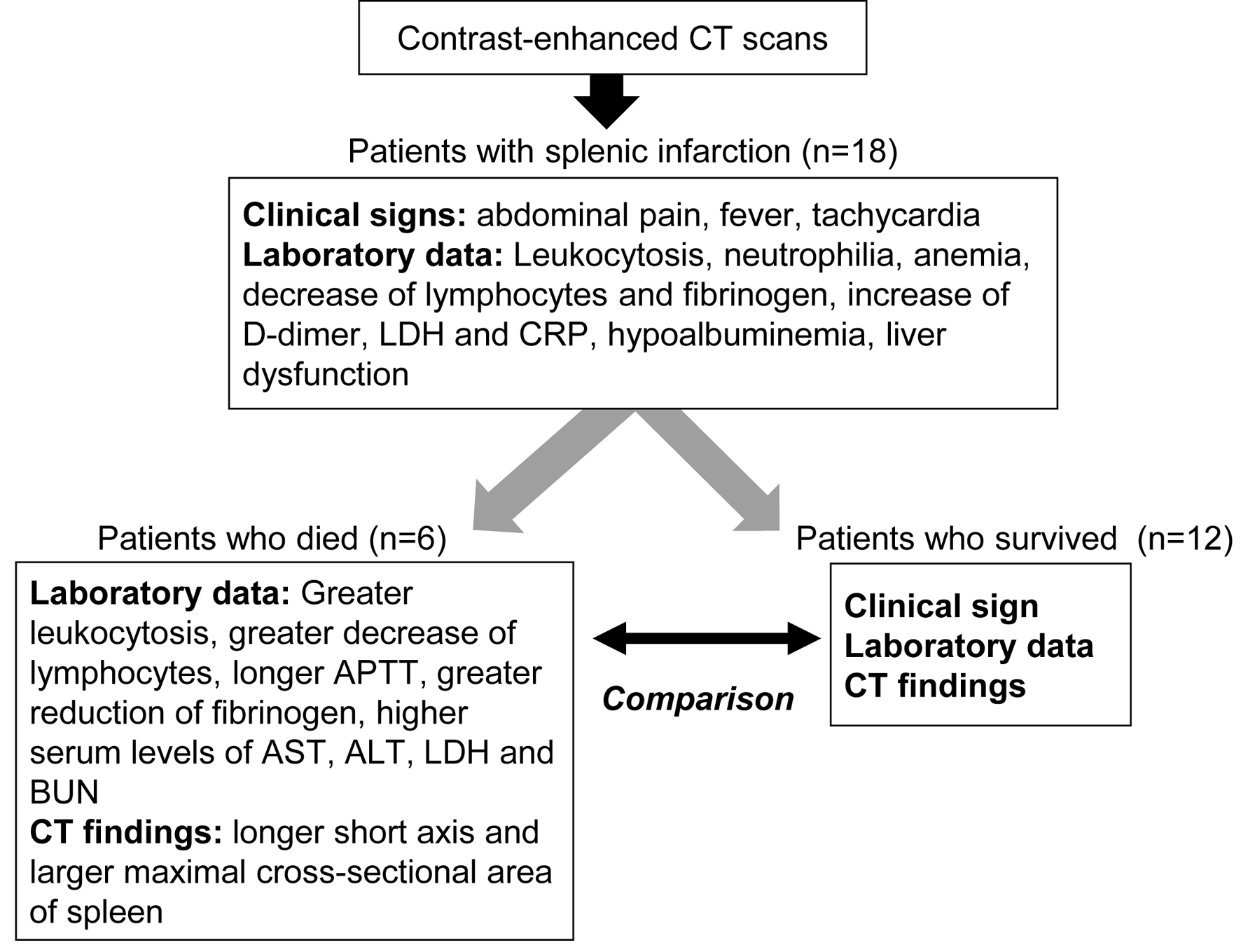
| Clinical outcome (death/survival) | 6/12 |
| Laboratory examination | n | Values in patients | Normal range |
|---|---|---|---|
| APTT: activated partial thromboplastin time; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; CRP: C-reactive protein; CK: creatine kinase; γ-GT: γ-glutamyl transferase; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; PG: plasma glucose; PT: prothrombin time; RBCs: red blood cells; WBCs: white blood cells. | |||
| Blood cells | |||
| WBCs (cells/µL) | 18 | 12,500 ± 9,000 | 3,300 - 8,600 |
| Neutrophils (%) | 16 | 75 ± 22 | 42 - 74 |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 16 | 12 ± 10 | 18 - 50 |
| Monocytes (%) | 16 | 6 ± 3 | 2 - 10 |
| Eosinophils (%) | 16 | 1 ± 1 | 1 - 5 |
| Basophils (%) | 15 | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 0 - 1 |
| RBCs (cells × 104/µL) | 18 | 385 ± 100 | 435 - 555 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 18 | 10.9 ± 3.1 | 13.7 - 16.8 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 18 | 33.3 ± 8.2 | 40.7 - 50.1 |
| Platelets (cells × 104/µL) | 18 | 19 ± 12 | 15.8 - 34.8 |
| Coagulation fibrinolytic system | |||
| PT (international normalized ratio) | 13 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1 |
| APTT (s) | 11 | 37.3 ± 20.8 | 20 - 40 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 6 | 461 ± 265 | 150 - 400 |
| D-dimer (mg/mL) | 7 | 380.5 ± 800.0 | < 1.0 |
| Biochemistry | |||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 18 | 3.0 ± 0.8 | 4.1 - 5.1 |
| AST (U/L) | 18 | 87 ± 107 | 13 - 30 |
| ALT (U/L) | 18 | 48 ± 48 | 10 - 42 |
| γ-GT (U/L) | 17 | 127 ± 122 | 13 - 64 |
| LDH (U/L) | 17 | 412 ± 294 | 124 - 222 |
| CK (U/L) | 14 | 193 ± 400 | 59 - 248 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 18 | 20 ± 7 | 8 - 20 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 18 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 0.65 - 1.07 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 14 | 7.2 ± 7.4 | 0.00 - 0.14 |
| PG (mg/dL) | 8 | 142 ± 77 | 73 - 109 |
| Long axis of spleen (cm) | 9.3 ± 1.7 |
| Short axis of spleen (cm) | 3.8 ± 1.1 |
| Maximal cross-sectional area of spleen (cm2) | 36.2 ± 15.4 |
| Volume of spleen (cm3) | 299.4 ± 220.4 |
| Cases | Age | Sex | Comorbidity | Abdominal pain | Maximal body temperature (°C) | Heat rate (beats/min) | History of anticoagulant use | Start of anticoagulant | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NA: not available. | |||||||||
| 1 | 88 | Female | Abdominal aortic dissection, Atrial fibrillation | + | 35.8 | 101 | Death | ||
| 2 | 70 | Male | Pancreatic carcinoma | NA | 37.7 | 87 | Death | ||
| 3 | 79 | Male | Septic shock | NA | 38.9 | 126 | Death | ||
| 4 | 79 | Female | Cerebral infarction | + | 39.1 | 72 | + | Death | |
| 5 | 91 | Female | Liver cirrhosis, heart failure | NA | 37.4 | 85 | Death | ||
| 6 | 87 | Male | Diabetes, dehydration | + | 38.5 | 103 | + | Death | |
| 7 | 52 | Female | Infective endocarditis, sigmoid colon cancer | - | 39.0 | 120 | Survival | ||
| 8 | 84 | Female | Pyelonephritis | NA | 38.7 | 74 | Survival | ||
| 9 | 76 | Female | Malignant lymphoma | + | 38.4 | 122 | + | Survival | |
| 10 | 70 | Male | Unknown | NA | NA | NA | Survival | ||
| 11 | 80 | Male | Pancreatic carcinoma | + | 38.6 | 78 | Survival | ||
| 12 | 67 | Female | Lung cancer | NA | NA | NA | Survival | ||
| 13 | 70 | Female | Unknown | NA | NA | NA | Survival | ||
| 14 | 71 | Female | Atrial fibrillation | - | 37.4 | 83 | + | Survival | |
| 15 | 80 | Female | Colon cancer, renal infarction, protein C deficiency | - | 37.8 | 77 | + | Survival | |
| 16 | 88 | Female | Atrial fibrillation | - | NA | 60 | + | Survival | |
| 17 | 85 | Male | Diabetic gangrene, colon cancer | NA | 38.7 | 102 | Survival | ||
| 18 | 87 | Male | Atrial fibrillation | - | 37.9 | 75 | + | Survival | |
| Patients who died | Patients who survived | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| The percentage of patients with abdominal pain, fever, and tachycardia is calculated using the number of cases described in the electronic medical record as the denominator. Fever and tachycardia mean body temperature > 38 °C and heart rate > 100 beats/min, respectively. | |||
| Sex (male/female) | 3/3 | 4/8 | 0.157 |
| Age (years) | 82.3 ± 7.1 | 75.8 ± 10.0 | 0.198 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 19.0 ± 4.0 | 23.0 ± 3.7 | 0.2 |
| Maximal body temperature (°C) | 37.7 ± 1.1 | 38.3 ± 0.5 | 0.245 |
| Fever (n, %) | 3/6, 50% | 5/8, 62.5% | 0.78 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 126 ± 23 | 135 ± 24 | 0.497 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 69 ± 15 | 67 ± 17 | 0.859 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 96 ± 17 | 88 ± 20 | 0.487 |
| Tachycardia (n, %) | 3/6, 50% | 3/9, 33.3% | 0.22 |
| Laboratory examination | Patients who died | Patients who survived | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| APTT: activated partial thromboplastin time; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; CRP: C-reactive protein; CK: creatine kinase; γ-GT: γ-glutamyl transferase; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; PG: plasma glucose; PT: prothrombin time; RBCs: red blood cells; WBCs: white blood cells. | |||
| Blood cells | |||
| WBCs (cells/µL) | 19,633 ± 9,222 | 8,950 ± 6,561 | 0.017 |
| Neutrophils (%) | 86 ± 5 | 69 ± 25 | 0.124 |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 6 ± 4 | 16 ± 10 | 0.049 |
| Monocytes (%) | 6 ± 3 | 7 ± 3 | 0.938 |
| Eosinophil (%) | 0.5 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 1.3 | 0.191 |
| Basophils (%) | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 0.3 ± 0.5 | 1 |
| RBCs (cells × 104/µL) | 369 ± 109 | 393 ± 94 | 0.656 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.2 ± 2.4 | 11.3 ± 3.4 | 0.511 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 31.7 ± 6.4 | 34.2 ± 8.9 | 0.567 |
| Platelets (cells × 104/µL) | 15.7 ± 7.0 | 20.6 ± 12.9 | 0.425 |
| Coagulation fibrinolytic system | |||
| PT (international normalized ratio) | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 0.174 |
| APTT (seconds) | 58 ± 31 | 29 ± 5 | 0.045 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 55 ± 5 | 541 ± 214 | 0.042 |
| D-dimer (mg/mL) | 1,127 ± 1,041 | 8 ± 5 | 0.098 |
| Biochemistry | |||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 3.2 ± 0.8 | 0.166 |
| AST (U/L) | 176 ± 143 | 43 ± 36 | 0.011 |
| ALT (U/L) | 84 ± 54 | 31 ± 31 | 0.022 |
| γ-GT (U/L) | 127 ± 120 | 127 ± 123 | 1 |
| LDH (U/L) | 628 ± 374 | 296 ± 137 | 0.026 |
| CK (U/L) | 362 ± 612 | 98 ± 127 | 0.271 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 26 ± 7 | 16 ± 5 | 0.005 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.97 ± 0.41 | 0.79 ± 0.22 | 0.249 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 6.6 ± 5.7 | 7.5 ± 8.2 | 0.848 |
| PG (mg/dL) | 121 ± 23 | 149 ± 87 | 0.709 |
| Computed tomographic findings | Patients who died | Patients who survived | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long axis of spleen (cm) | 9.9 ± 1.7 | 8.9 ± 1.7 | 0.283 |
| Short axis of spleen (cm) | 4.5 ± 1.1 | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 0.039 |
| Maximal cross-sectional area of spleen (cm2) | 46.1 ± 17.0 | 31.3 ± 11.7 | 0.058 |
| Volume of spleen (cm3) | 423.8 ± 282.1 | 237.4 ± 146.4 | 0.101 |
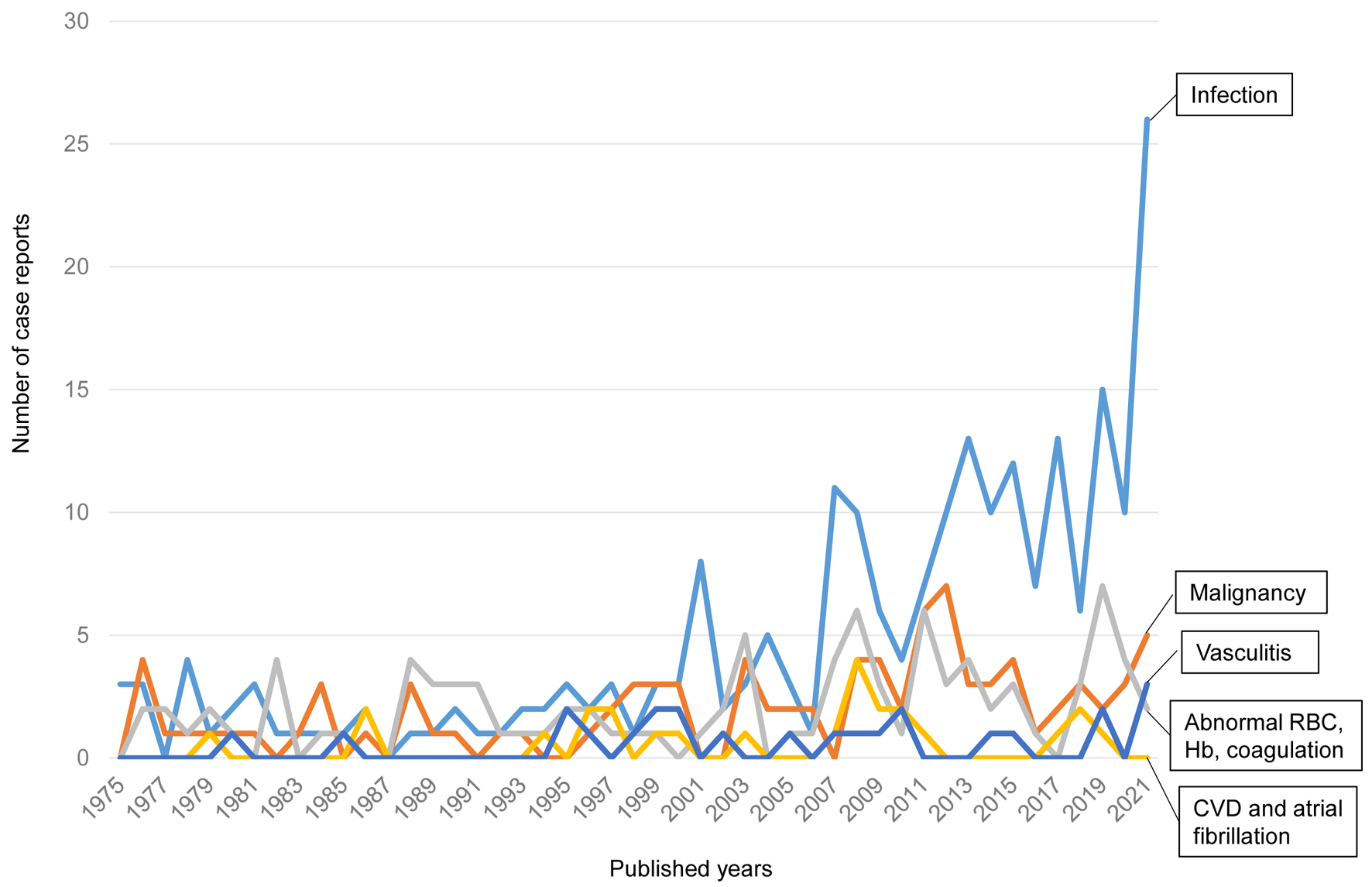
| Causes of splenic infarction | References |
|---|---|
| COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019; ANCA: anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody. | |
| Infection | |
| Cytomegalovirus | [6-8] |
| Epstein-Barr virus | [9-15] |
| Infective endocarditis | [16-22] |
| COVID-19 | [23-35] |
| Dengue virus | [36] |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae | [37, 38] |
| Malaria | [39, 40] |
| Scrub typhus | [41, 42] |
| Aspergillus pericarditis | [43] |
| Babesiosis | [44] |
| Malignancy including neoplasm and myeloproliferative diseases | |
| Polycythemia vera | [45] |
| Essential thrombocythemia | [46] |
| Ovarian carcinoma | [47] |
| Acute T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia | [48] |
| Angiosarcoma | [49] |
| B-cell lymphoma | [50, 51] |
| Abnormal red blood cells and hemoglobin, and coagulation abnormality | |
| Hereditary spherocytosis | [52] |
| Sickle cell disease | [53-57] |
| Hemoglobin SE disease | [58] |
| β-Thalassemia | [59] |
| Protein C deficiency | [60] |
| Antiphospholipid syndrome | [61] |
| Vasculitis | |
| ANCA-associated vasculitis | [62-64] |
| Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis | [65] |
| Cardiovascular disease, atrial fibrillation | |
| Atrial fibrillation | [66, 67] |