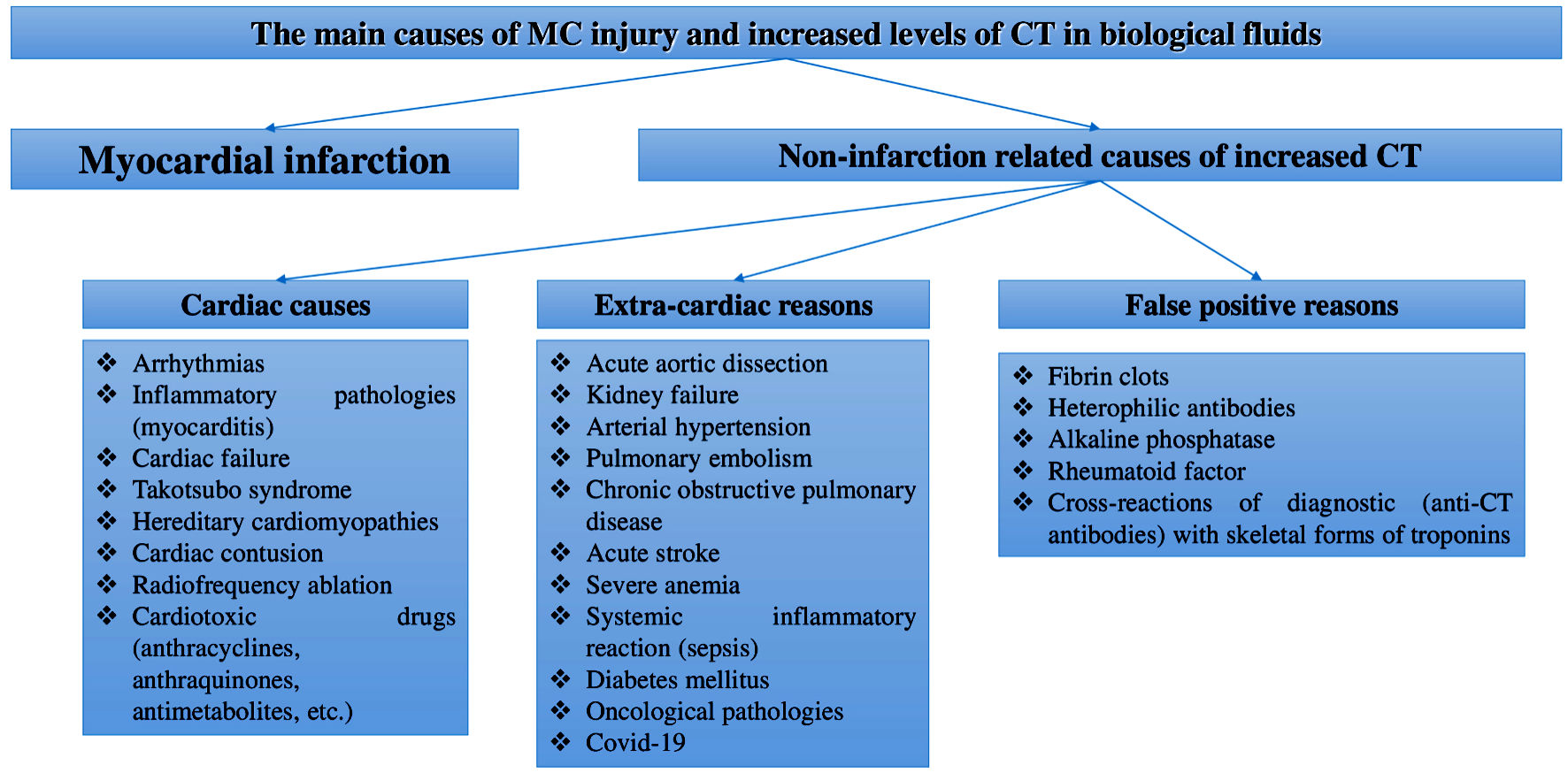
Figure 1. Main reasons of MC injury and increased CTs levels in body fluids. MCs: myocardial cells; CT: cardiospecific troponin; COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 14, Number 11, November 2022, pages 448-457
Hypertension as One of the Main Non-Myocardial Infarction-Related Causes of Increased Cardiospecific Troponins: From Mechanisms to Significance in Current Medical Practice
Figures

Table
| No. | Number of patients, diagnosis | Biomaterials | Prevalence and degree of CTs increase in case of HT, predictive significance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aIncreased/elevated level of CTs is a level exceeding the standard 99 percentile provided by the manufacturer of the immunotest. BP: blood pressure; CTs: cardiospecific troponins; CT-T: cardiospecific troponin T; CT-I: cardiospecific troponin I; HT: hypertension. | ||||
| 1 | Primary HT, n = 306 | Serum | Increaseda CT-T levels were observed in 47% of patients with high BP and were associated with left ventricular hypertrophy and poor long-term prognosis. | [52] |
| 2 | Primary HT, n = 20 | Urine | CT-I levels in the urine of patients with high BP (HT) were significantly higher than in patients with normal BP. Reference intervals for CTs levels in the urine have not yet been established. | [54] |
| 3 | Primary HT, n = 467 | Serum | Increaseda CT-I levels were observed in 15% of patients with high BP and were associated with the risk of chronic congestive cardiac failure. | [100] |
| 4 | Primary HT, n = 171 | Serum | Increaseda CT-I levels were observed in 32% of patients with high BP and were associated with the increased risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) and the risk of coronary heart disease. | [101] |
| 5 | Primary HT, n = 929 | Serum | Increaseda CT-I levels were observed in 31% of patients with high BP and were associated with the risk of myocardial infarction and pulmonary edema. | [102] |
| 6 | Secondary (gestational) HT, n = 880 | Serum | Elevateda CT-I levels were a strong independent predictor of pregnancy-induced HT or preeclampsia. | [103] |