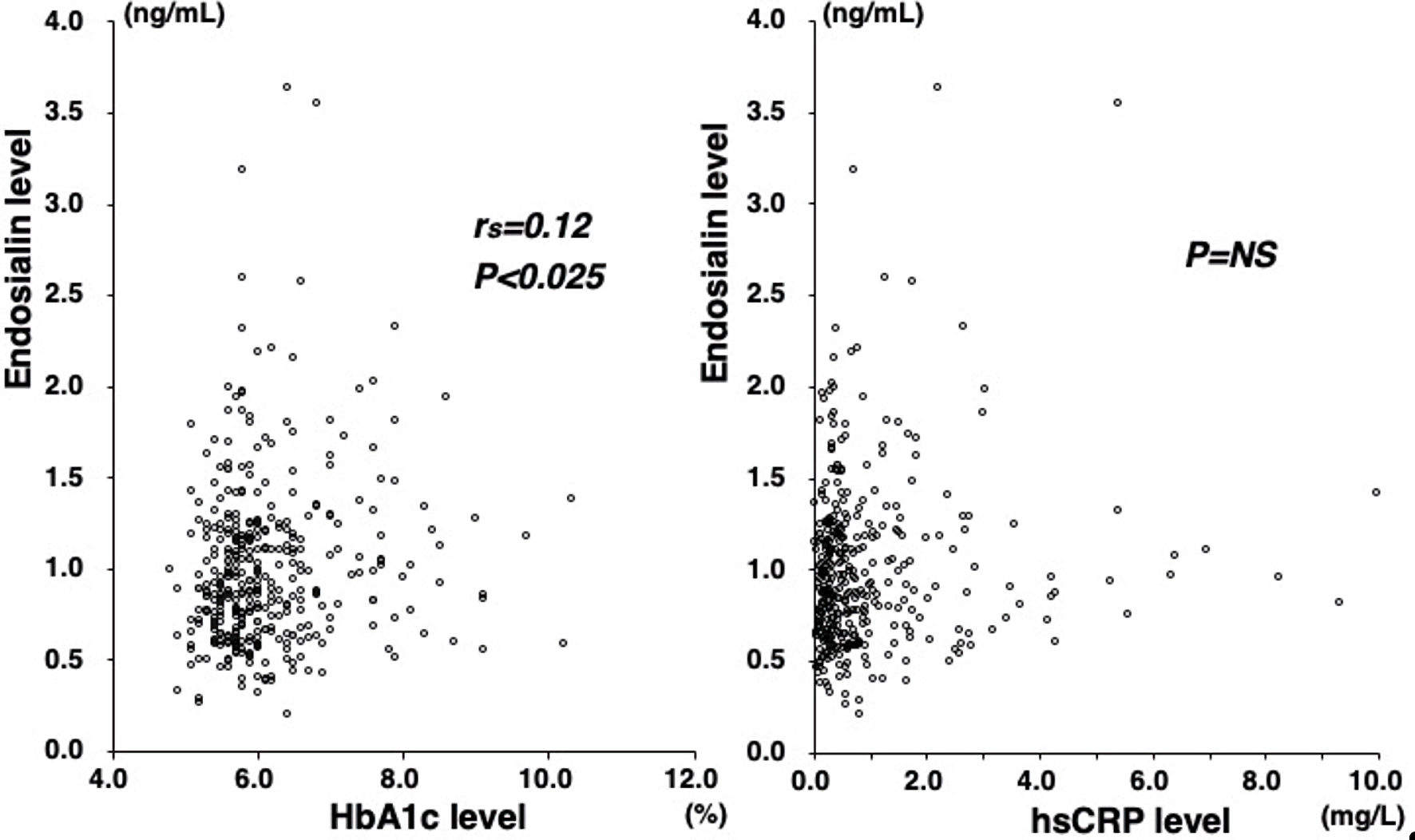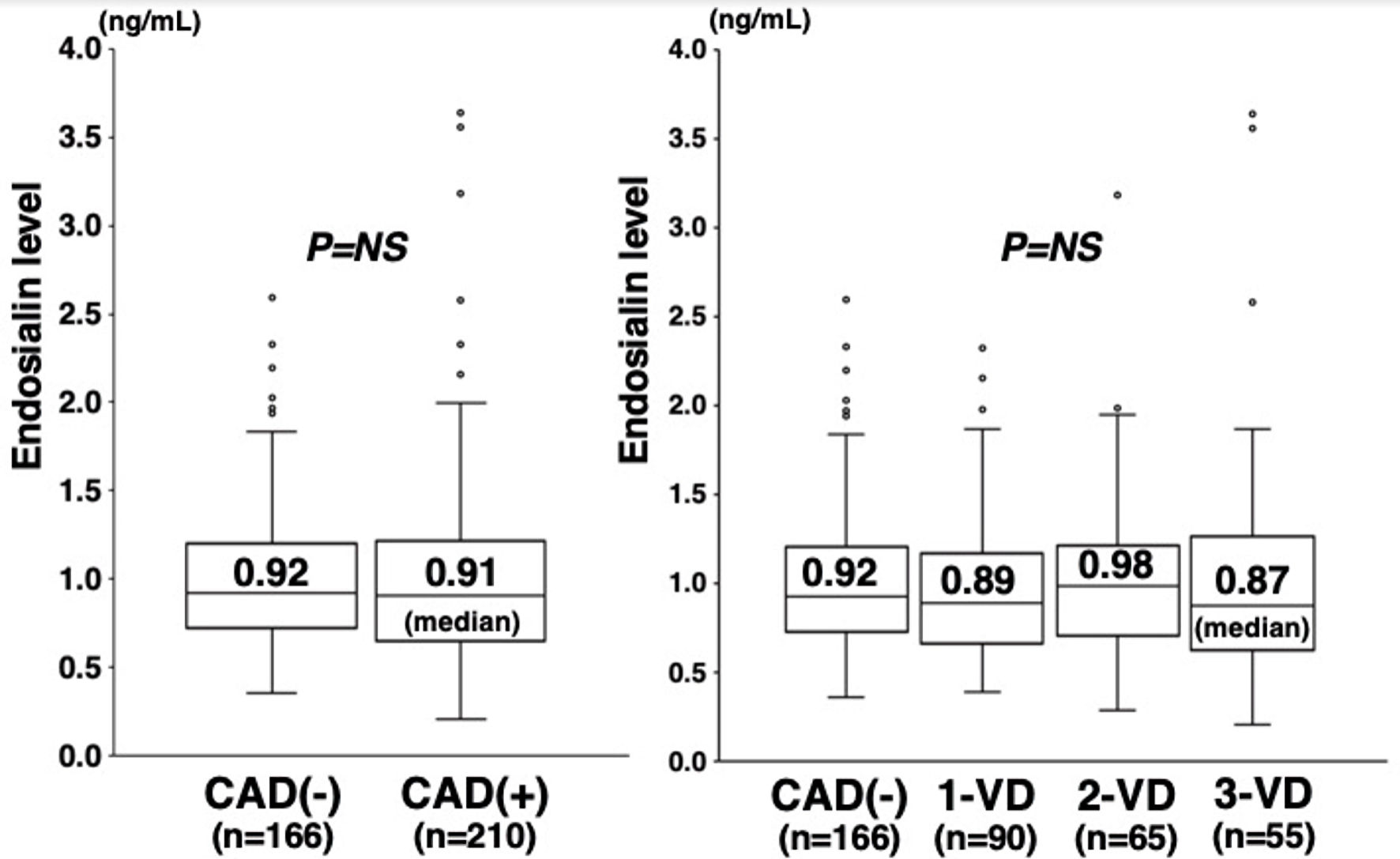
Figure 1. Plasma endosialin levels and the presence of CAD or the number of stenotic coronary vessels. Plasma endosialin levels did not significantly differ between patients with and without CAD (0.91 vs. 0.92 ng/mL) (left). No significant difference was found in endosialin levels among the four groups of CAD(-), 1-VD, 2-VD, and 3-VD (0.92, 0.89, 0.98, and 0.87 ng/mL) (right). The central line represents the median, and the box represents the 25th to 75th percentiles. The whiskers represent the lowest and highest value in the 25th percentile minus 1.5 IQR and 75th percentile plus 1.5 IQR, respectively. NS: not significant; CAD: coronary artery disease; 1-VD: one-vessel disease; 2-VD: two-vessel disease; 3-VD: three-vessel disease; IQR: interquartile range.