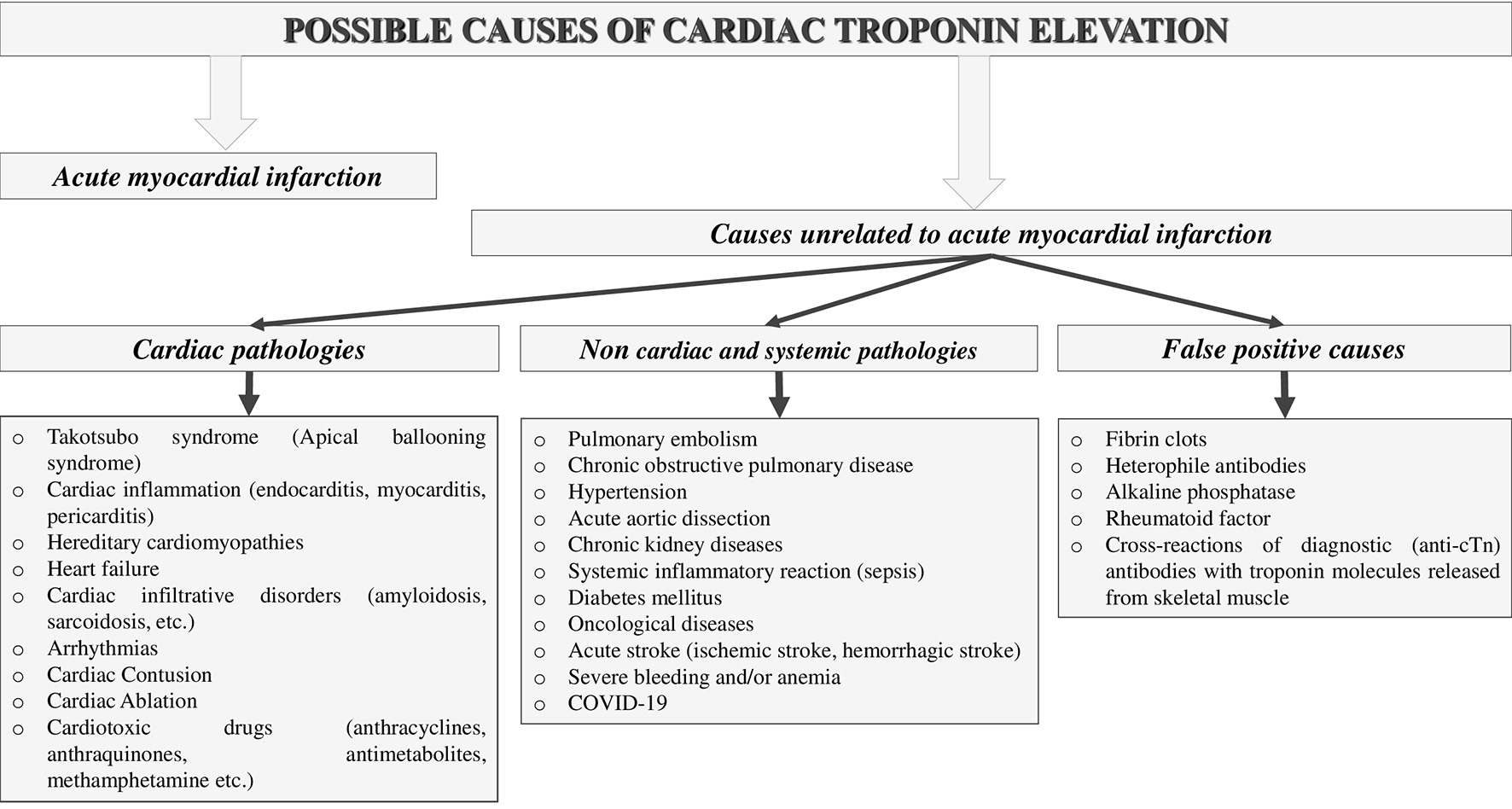
Figure 1. Possible causes of cardiac troponin elevation.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 14, Number 2, February 2022, pages 80-87
False-Positive Causes in Serum Cardiac Troponin Levels
Figure

Tables
| Troponin immunoassay (company; manufacturer) | Biomarker concentration that indicates an extremely low probability of an NSTEMI diagnosis, ng/L | Biomarker concentration that indicates a low probability of an NSTEMI diagnosis, ng/L | Changes in biomarker concentration after 1 h at which a diagnosis of NSTEMI should be excluded, ng/L | Biomarker concentration that indicates a high probability of an NSTEMI diagnosis, ng/L | Changes in biomarker concentration after 1 h at which a diagnosis of NSTEMI should be confirmed, ng/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (Elecsys; Roche) | < 5 | < 12 | < 3 | ≥ 52 | ≥ 5 |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (Architect; Abbott) | < 4 | < 5 | < 2 | ≥ 64 | ≥ 6 |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (Centaur; Siemens) | < 3 | < 6 | < 3 | ≥ 120 | ≥ 12 |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (Access; Beckman Coulter) | < 4 | < 5 | < 4 | ≥ 50 | ≥ 15 |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (Clarity; Singulex) | < 1 | < 2 | < 1 | ≥ 30 | ≥ 6 |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (Vitros; Clinical Diagnostics) | < 1 | < 2 | < 1 | ≥ 40 | ≥ 4 |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (Pathfast; LSI Medience) | < 3 | < 4 | < 3 | ≥ 90 | ≥ 20 |
| Troponin immunoassay (company; (manufacturer) | Biomarker concentration that indicates an extremely low probability of an NSTEMI diagnosis, ng/L | Biomarker concentration that indicates a low probability of an NSTEMI diagnosis, ng/L | Changes in biomarker concentration after 2 h at which a diagnosis of NSTEMI should be excluded, ng/L | Biomarker concentration that indicates a high probability of an NSTEMI diagnosis, ng/L | Changes in biomarker concentration after 2 h at which a diagnosis of NSTEMI should be confirmed, ng/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (Elecsys; Roche) | < 5 | < 14 | < 4 | ≥ 52 | ≥ 10 |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (Architect; Abbott) | < 4 | < 6 | < 2 | ≥ 64 | ≥ 15 |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (Centaur; Siemens) | < 3 | < 8 | < 7 | ≥ 120 | ≥ 20 |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (Access; Beckman Coulter) | < 4 | < 5 | < 5 | ≥ 50 | ≥ 20 |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (Clarity; Singulex) | < 1 | To be determined | To be determined | ≥ 30 | To be determined |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (Vitros; Clinical Diagnostics) | < 1 | To be determined | To be determined | ≥ 40 | To be determined |
| High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (Pathfast; LSI Medience) | < 3 | To be determined | To be determined | ≥ 90 | To be determined |
| Major factors | Reason of interference | References |
|---|---|---|
| Fibrin clots | Competitive interaction of fibrin clots with diagnostic antibodies | [17-19, 30, 31] |
| Heterophile antibodies | Cross interaction of heterophile antibodies with anti-cTn included in the diagnostic test system | [19, 20, 32-37] |
| Alkaline phosphatase | Endogenous alkaline phosphatase can catalyze the enzymatic reaction in immunoassay and thereby amplify the signal, which is proportional to the concentration of cardiac troponins in the sample | [3, 21, 22, 38, 39] |
| Rheumatoid factor | Nonspecific interaction of rheumatoid factor (autoantibodies) with diagnostic antibodies | [3, 27, 33, 40-45] |
| Cross-reactions of diagnostic (anti-cTn) antibodies with troponin molecules released from skeletal muscle | Cross-reactions of diagnostic antibodies with skeletal troponin molecules released into the bloodstream during skeletal muscle injury Re-expression of cardiac troponin molecules in skeletal muscles after injury and the release of these molecules into the bloodstream from skeletal muscle fibers | [47-49, 53] |