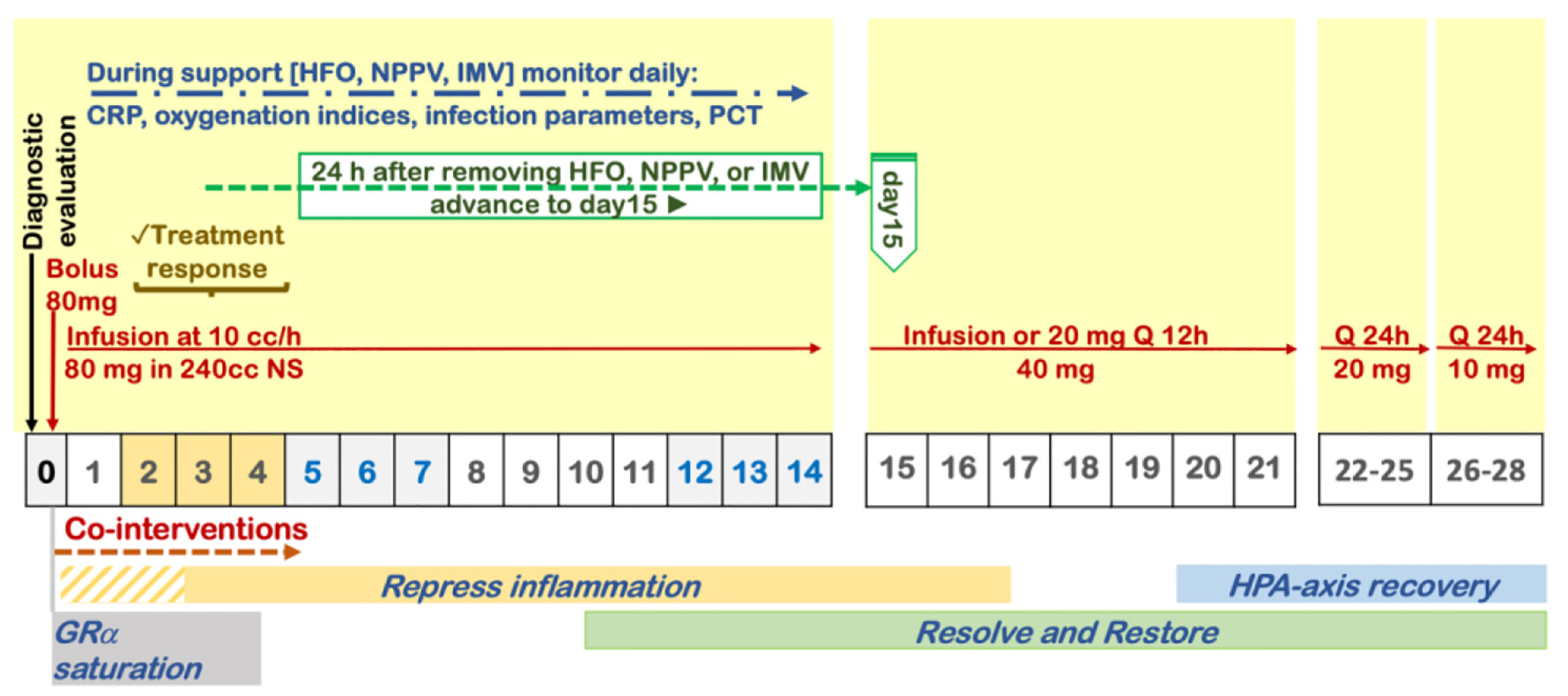
Figure 1. Protocol for prolonged corticosteroid treatment recommended by the Corticosteroid Guideline Task Force of the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM).
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 14, Number 2, February 2022, pages 53-79
“MATH+” Multi-Modal Hospital Treatment Protocol for COVID-19 Infection: Clinical and Scientific Rationale
Figures

Tables
| Medication | Indication/initiation | Recommended dosing | Titration/duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| aContinue low molecular weight heparin 1 mg/kg twice daily in ward patients transferred to intensive care units unless contraindicated. For patients with end-stage renal disease, use unfractionated heparin. bConsider extended thromboprophylaxis. CRP: C-reactive protein; DOAC: direct oral anti-coagulant; ICU: intensive care unit; IMV: invasive mechanical ventilation; IU: International Units; IV: intravenous; NIPPV: non-invasive positive pressure ventilation; O2: oxygen; PO (per os): oral administration; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate. | |||
| Methylprednisolone | A. Mild hypoxemia: requires O2 via NC to maintain saturation > 92%. | 40 mg IV bolus, then 20 mg IV twice daily | A1. Once off O2, then taper with 20 mg daily for 3 days then 10 mg daily for 3 days, monitor CRP response. A2. If FiO2, or CRP increase move to B. |
| B. Moderate-severe hypoxemia (high-flow O2, NIPPV, IMV). | COVID-19 respiratory failure protocol (Fig. 2). Preferred: 80 mg IV bolus, followed by 80 mg/240 mL normal saline IV infusion at 10 mL/h. Alternate: 40 mg IV twice daily | B1. Once off IMV, NPPV, or high-flow O2, decrease to 20 mg twice daily. Once off O2, then taper with 20 mg/day for 3 days then 10 mg/day for 3 days. B2. If no improvement in oxygenation in 2 - 4 days, double dose to 160 mg daily. B3. If no improvement and increase in CRP/ferritin, move to “pulse dose” below. | |
| C. Refractory illness/cytokine storm | “Pulse” dose with 125 mg IV every 6 - 8 h | Continue for 3 days then decrease to 80 mg IV daily dose above (B). If still no response or CRP/ferritin high/rising, consider “Salvage therapy” below | |
| Ascorbic acid | O2 < 4 L on hospital ward | 500 - 1,000 mg oral every 6 h | Until discharge |
| O2 > 4 L or in ICU | 1.5 - 3 g intravenously every 6 h | Sooner of 7 days or discharge from ICU, then switch to oral dose above | |
| Thiamine | ICU patients | 200 mg IV twice daily | Sooner of 7 days or discharge from ICU |
| Heparin (low molecular weight) | Hospital ward patients with moderate severity not requiring high-flow oxygen | 1 mg/kg twice daily. Monitor anti-Xa, target 0.2 - 0.5 IU/mL. Adjust dose and monitor for eGFR | Until discharge then start DOAC at half dose for 4 weeksb |
| ICU patientsa | 0.5 mg/kg twice daily. Monitor anti-Xa levels, target 0.6 - 1.1 IU/mL. Adjust dose and monitor for eGFR | Later of: discharge from ICU or off oxygen, then decrease to hospital ward dosing above | |
| Vitamin D | Hospital ward patients on ≤ 4 L O2 | Calcifediol preferred: 0.532 mg PO day 1, then 0.266 mg PO day 3 and 7 and weekly thereafter. Cholecalciferol: 10,000 IU/day PO or 60,000 IU day 1, 30,000 IU days 3 and 7 and then weekly | Until discharge from ICU |
| ICU patients or on > 4 L O2 | Cholecalciferol 480,000 IU (30 mL) PO on admission, then check vitamin D level on day 5, if < 20 ng/mL, 90,000 PO IU/day for 5 days | Until discharge from ICU | |
| Spironolactone | All patients | 100 mg twice daily | 10 days |
| Dutasteride | All patients (except pregnant patients) | 2 mg on day 1, then 1 mg daily (finasteride 10 mg daily | 10 days |
| Fluvoxamine | All patients | 50 - 100 mg twice daily | |
| Atorvastatin | ICU patients | 80 mg PO daily | Until discharge |
| Melatonin | Hospitalized patients | 6 - 12 mg PO at night | Until discharge |
| Zinc | Hospitalized patients | 75 - 100 mg PO daily | Until discharge |
| Famotidine | Hospitalized patients | 40 - 80 PO mg twice daily | Until discharge15 days |
| Therapeutic plasma exchange | Patients refractory to pulse dose steroids | Five sessions, every other day | Completion of five exchanges |
| Published RCTs/cohort studies of corticosteroid therapy in COVID-19 | Absolute difference in mortality rate (Rx group vs. control group) | Estimated number needed to treat to save one life |
|---|---|---|
| Table is provided by Pierre Kory Flccc.org. COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019. | ||
| Methylprednisolone - hospital patients [54] | 5.9% vs. 42.9% | 2.7 |
| Methylprednisolone - ICU patients [44] | 7.2% vs. 23.3% | 6.2 |
| Methylprednisolone - hospital patients [35] | 13.6% vs. 26.3% | 7.8 |
| Methylprednisolone - ARDS patients [53] | 46.0% vs. 61.8% | 6.3 |
| Methylprednisolone - percent on oxygen [36] | 13.9% vs. 23.9% | 10.0 |
| CoDEX - dexamethasone - mechanical ventilation [52] | 56.3% vs. 61.5% | 19.2 |
| RECOVERY trial (dexamethasone) [51] | ||
| Percent on oxygen | 23.3% vs. 26.2% | 28.6 |
| Percent on mechanical ventilation | 29.3% vs. 41.4% | 8.4 |
| Hydrocortisone - CAPE COVID - ICU patients [60] | 14.7% vs. 27.4% | 7.9 |
| Hydrocortisone - REMAP-CAP - ICU patients [49] | 28% vs. 33% | 20.0 |
| Study type | Intervention | Outcome IVAA vs. control | Comments/level of evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Based on level 5 evidence (cited in text) and current studies, we recommend the use of IVAA as adjunctive therapy in patients with COVID-19. IVAA: intravenous ascorbic acid; SOFA: sequential organ failure assessment; RCT: randomized controlled trial; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-6: interleukin-6; IL-8: interleukin-8; CRP: C-reactive protein; SIRS: systemic inflammatory response syndrome; IVC: intravenous vitamin C. | |||
| RCT of 56 COVID-19 pneumonia and multiple organ injury ICU patients. Age: 67 ± 13 years. Severe COVID-19 PaO2/FIO2 < 300 [81] | IVAA: 24 g/day (n = 27) or placebo (n = 29) for 7 days (*corticosteroid allowed) (time to treatment 11 - 25 days to onset of symptoms) | IVAA: lower ICU and hospital mortality in patients with SOFA scores ≥ 3 (3 - 10 days, P = 0.03). No difference in ventilation-free days (26.5 vs. 10.5 days, P = 0.56) | IVAA group had higher PaO2/FIO2 and lower IL-6 levels on admission. Level of evidence 2 |
| Open label RCT of 150 patients with severe COVID-19. Age: 52 - 53 years [82] | IVAA: 50 mg/kg/day + standard therapy or standard therapy (75 per group) | IVAA: sooner to symptom-free status (7.1 ± 1.8 vs. 9.6 ± 2.1) (P < 0.0001). No difference in mortality or need for mechanical ventilation | Corticosteroids allowed. Level of evidence 2 |
| Open label RCT of 60 patients with severe COVID-19. Age: 57 - 61 years [83] | IVC 6 g/day + standard therapy or standard therapy (n = 30 per group) for 5 days | Lower body temperature on third day of hospitalization (P = 0.001) Improvement in oxygen saturation on third day of hospitalization (P = 0.014). No difference in mortality | Both groups received dexamethasone. Level of evidence 2 |
| Retrospective cohort study of 76 patients with moderate to severe COVID-19. Age: 52 - 71 years [84] | IVAA: 6 g/12 h on first day, 6 g/day for following 4 days + standard therapy (n = 30) or standard therapy (n = 46) for 5 days | Improved oxygenation in treatment group. Decrease in pro-inflammatory biomarkers. Reduced risk of 28-day mortality (HR: 0.14, 95% CI: 0.03 - 0.72, P = 0.037) | Level of evidence 3 |
| Propensity matched before and after retrospective analysis of 110 patients with moderate COVID-19 pneumonia. Age: 31 - 47 years [85] | IVAA: 100 mg/kg/day + standard therapy or standard therapy (55 per group) for 7 days | Fewer patients progressing to severe type of COVID-19 (P = 0.03). Reduction in incidence and progression of SIRS (P = 0.008) | Level of evidence 3 |
| Retrospective analysis of 232 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Age: 46 - 74 years [86] | IVAA: 2 g/day + standard therapy (n = 153) or standard therapy (n = 170) | Shorter length of hospital stay (7 vs. 8 days, P = 0.05). No difference in re-admission rate (P = 0.94), admission to ICU, need for advanced oxygen support (P = 0.49), and mortality (P = 0.52). Need for advanced medical treatment (P < 0.001) | Level of evidence 3 |
| Retrospective study of 34 critically ill patients with COVID-19. Age: 53 - 77 years [87] | IVAA: 1.5 g/6 h + standard therapy (n = 8) or standard therapy (n = 24) for 4 days | Higher rate of hospital mortality in treatment group (19 (79%) vs. 7 (88%), P = 0.049) and SOFA score. No difference in daily vasopressor requirement or ICU length of stay | Higher baseline SOFA score in IVAA group. Level of evidence 3 |
| Retrospective study of 236 patients with severe COVID-19. Age: 57 - 73 years [88] | IVAA: 100 mg/kg/6 h on day 1 then 100 mg/kg/12 h for the next 5 days + standard therapy (n = 85) or standard therapy (n = 151 | Reduction in inflammatory markers (CRP, P = 0.032; IL-6, P = 0.005; TNF-α, P = 0.015) | Level of evidence 3 |
| Retrospective study of 113 patients with severe COVID-19 and cardiac injury. Age: 59 - 77 years [89] | IVAA: 100 mg/kg/6 h on day 1 then 100 mg/kg/12 h for the next 5 days + standard therapy (n = 51) or standard therapy (n = 62) | IVAA was associated with ameliorated cardiac injury (P = 0.04). Reduced levels of inflammatory markers (CRP, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α) at 21 days of hospitalization | Level of evidence 3 |
| Trial details | Dose | Outcomes | Comments/level of evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Based on level 5 evidence (cited in text) and current studies, we recommend the use of melatonin as adjunctive therapy in patients with COVID-19. CRP: C-reactive protein. | |||
| Randomized single blind trial. Treatment: n = 14. Control: n = 17. Age: 25 - 65 years. Hospitalized mild moderate COVID-19 [145] | 6 mg melatonin at bedtime for 14 days | Improved declined CRP in treatment group. Percentage of recovery (based on symptoms) in patients who took melatonin was higher than that of patients in the control group (85.7% vs. 47.1%) | Corticosteroids given. Level of evidence 2 |
| Double blind randomized controlled trial. Treatment: n = 24. Control: n = 20. Age: 36 - 64 years. Mild to moderate COVID-19 [146] | 3 mg melatonin three times a day for 14 days | Faster time to symptom resolution, faster time to discharge. Improvement in CRP | Unclear if standard of care included corticosteroids. Level of evidence 2 |
| Randomized open label study. Treatment: n = 48. Control: n = 48. Age: 36 - 69 years. Mild to moderate COVID-19 [147] | 3 mg at bedtime for 7 days | Improvement in oxygenation | Higher usage of methylprednisolone in control group. Level of evidence 2 |
| Retrospective study. Patients: n = 791. Mean age: 56 years. Patients received melatonin: n = 112 [148] | 112 patients received melatonin | Improved survival in those patients who received melatonin | Study adjusted for comorbidities and therapy including corticosteroids. Level of evidence 3 |
| Trial details | Dose | Outcomes | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Based on level 5 evidence (cited in text) and current studies we recommend use of vitamin D as adjunctive therapy. BMI: body mass index; CRP: C-reactive protein; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; ICU: intensive care unit; IL-6: interleukin-6. | |||
| Randomized single blind trial. Treatment: n = 14 Control: n = 17. Age: 25 - 65 years. Hospitalized mild COVID-19. Mean age 51 ± 15 years, healthy cohorts no comorbidities. Asymptomatic to mild COVID-19 [225] | Oral cholecalciferol 60,000 IU daily for 7 days (if target 25(OH)D concentration > 50 ng/mL not achieved on day 7; same dose continued, if target achieved weekly 60,000 IU) | Significant rapid disappearance of viral mRNA in treatment group at 21 days (62%vs. 20%) significant decrease in fibrinogen. No difference in procalcitonin, CRP, ferritin or D-dimer | Level of evidence 2. Placebos were not identical |
| Double masked randomized open label trial. Treatment: n = 50. Control: n = 26. Age: 43 - 63 years. Moderately severe COVID-19 [14] | Oral calcifediol 0.532 mg on day of admission and 0.266 on day 3, 7 and weekly until discharge | Need for ICU admission was lower in the group receiving intervention (2% vs. 50%, P < 0.001). Two patients in control group died, none in the intervention group died | Level of evidence 2 |
| Randomized open label study. Treatment: n = 44. Control: n = 43. Age: 20 - 83 years. Vitamin level less than 30. Mild to moderate COVID-19 [226] | Cholecalciferol 60,000 IU daily for 8 days in participants with BMI 18 - 25 kg/m2 and 10 days for participants with BMI > 25 kg/m2 | Significant reduction of inflammatory markers (CRP, LDH, ferritin, IL-6, N/L ratio) in intervention group compared to control group. No difference in hospital stay or mortality | Level of evidence 2. Adjustment made for comorbidities |
| Double blind randomized trial. Treatment: n = 119. Control: n = 118. Mean age: 56 ± 15 years. Moderate to severe COVID-19 [227] | Single dose of oral cholecalciferol 200,000 IU | No significant difference between groups in median length of hospital stay (7 vs. 7, P = 0.94), mortality (7.6% vs. 5.1%, P = 0.43). No significant difference in need for ventilation or length of ventilation. No significant difference in post-hoc analysis on patients with vitamin D deficiency. | Level of evidence 2. Patient could enroll for up to 10 days from development of symptoms; 60% of patients in both groups received corticosteroids |