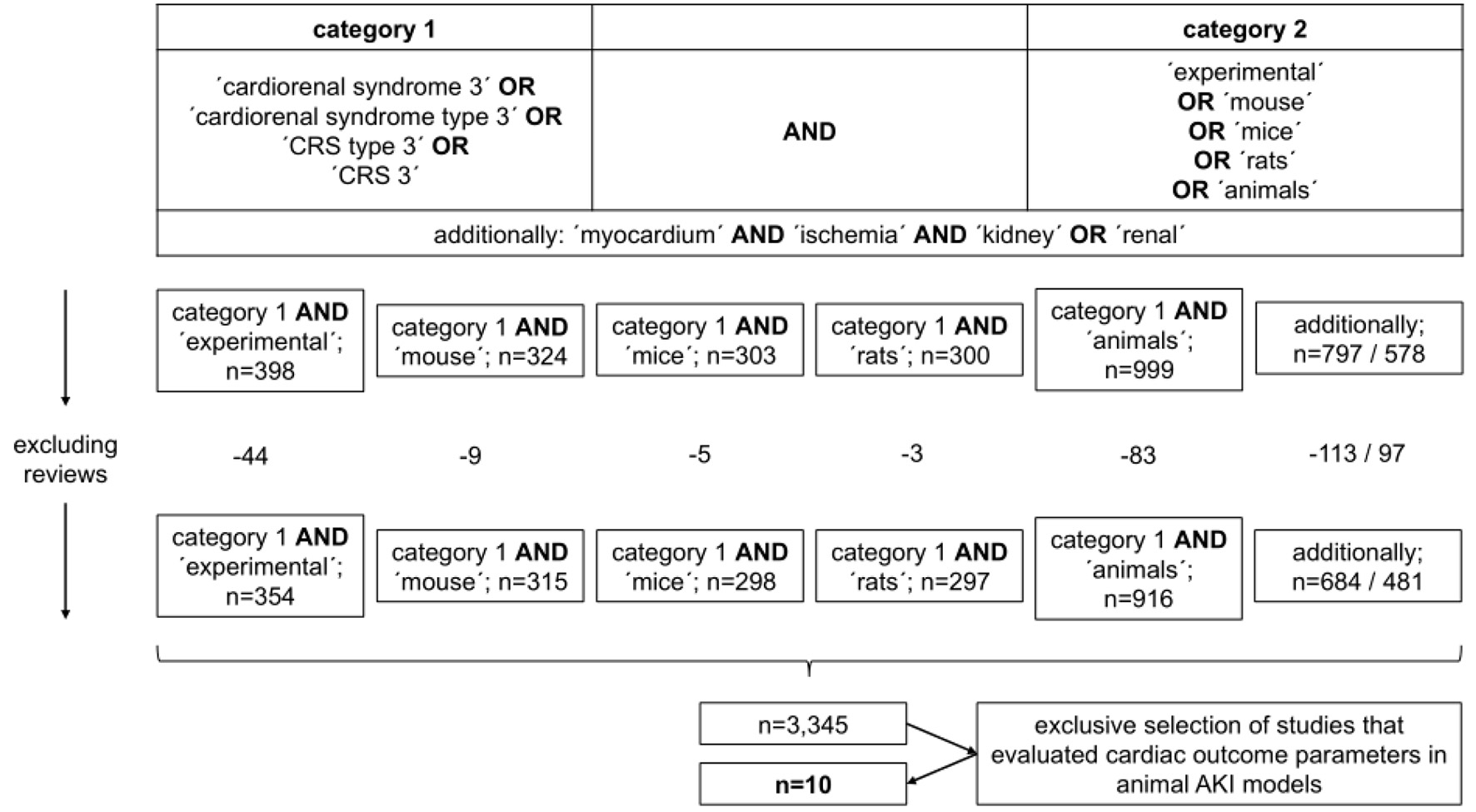
Figure 1. Selection process of references cited in the study.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 14, Number 1, January 2022, pages 22-27
Experimental Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 3: What Is Known so Far?
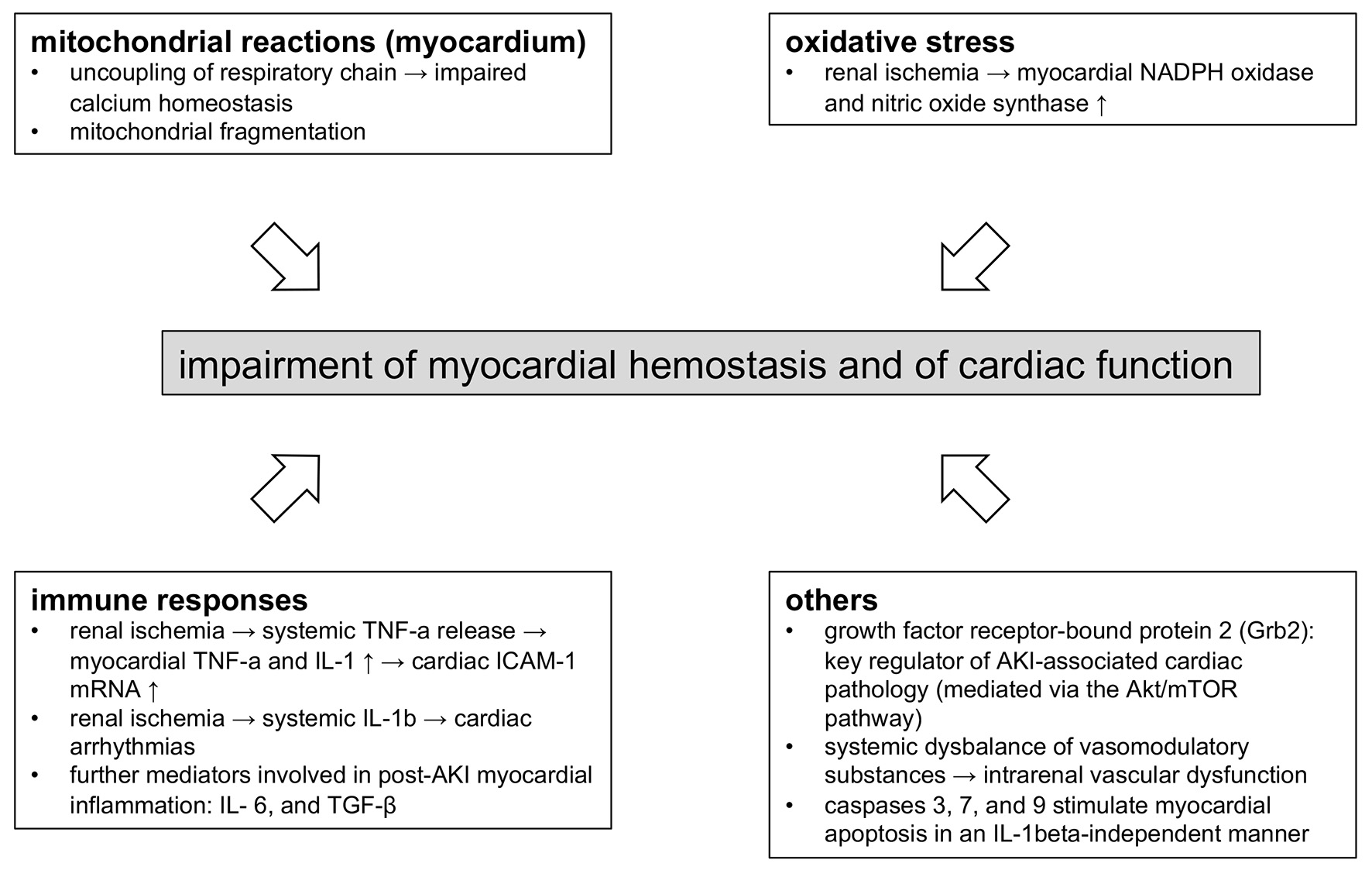
Figures

Table
| CRS type | Characteristics | Pathophysiological hallmarks | Treatment strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| The table exclusively summarizes the most important information. CRS: cardiorenal syndrome; AHF: acute heart failure; AKI: acute kidney injury; CHF: chronic heart failure; CKD: chronic kidney disease; FGF-23: fibroblast growth factor-23; RAS: renin-angiotensin system. | |||
| I | AHF induces AKI | Cardiac output ↓, venous congestion, activation of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone and sympathetic nervous system → impaired renal perfusion | Treatment of respective cause, anti-congestive therapy, vasopressors if mandatory, fluid removal by hemodialysis/hemodiafiltration/slow extended daily dialysis/peritoneal dialysis if mandatory |
| II | CHF aggravates progression of CKD | Low cardiac output and prolonged venous congestion → renal ischemia and subsequent endothelial cell dysfunction | Treatment of respective cause, management of CHF according the current recommendations (beta-blocker, mineralocorticoid antagonist, gliflozine, RAS inhibitor or sacubitril/valsartan), anti-progressive CKD treatment according to current recommendations, kidney replacement therapy if mandatory |
| III | AKI induces acute cardiac complications (e.g., arrhythmias, left ventricular insufficiency, myocardial ischemia) | Hyperhydration due to oligo-anuria, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis, intrarenal inflammation with subsequent systemic inflammation | Treatment of respective cause, treatment of electrolyte disturbances if mandatory, treatment of infections, avoidance of nephrotoxic substances, kidney replacement therapy if mandatory |
| IV | CKD aggravates CHF | Retention of sodium and water, retention of phosphorus, increase of blood FGF-23, renal anemia, CKD-associated endothelial cell dysfunction | Treatment of respective cause, anti-progressive CKD treatment according to current recommendations, particularly: blood pressure control, phosphorus-lowering therapy, bicarbonate supplementation, control of renal anemia, kidney replacement therapy if mandatory |