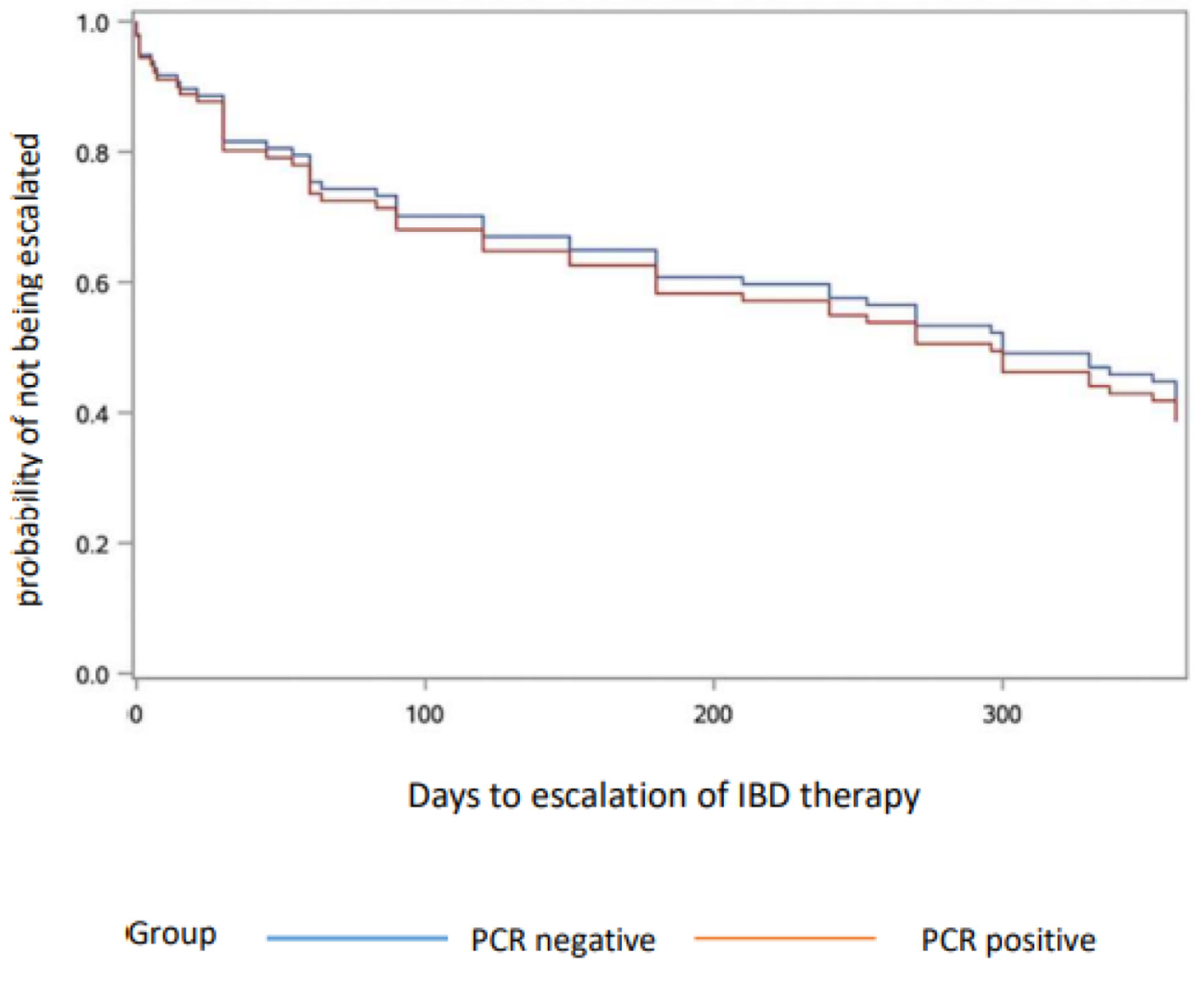
Figure 1. Escalation of IBD therapy. PCR: polymerase chain reaction; IBD: inflammatory bowel disease.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Letter to the Editor
Volume 13, Number 12, December 2021, pages 572-574
Clostridiodes difficile Treatment Guided by Polymerase Chain Reaction Stool Testing Does not Alter Outcomes for Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Figure

Table
| Demographics | PCR-positive | PCR-negative | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Continuous factors (age and IBD duration) compared using the paired t-test. **Categorical factors (IBD therapy escalation, addition/change in biologic) compared using McNemar’s test. No comparison carried out for ulcerative colitis, as there were no discordant pairs. PCR: polymerase chain reaction; IBD: inflammatory bowel disease; SD: standard deviation. | |||
| Total cases | 46 | 46 | |
| Age (years) | < 0.0021* | ||
| Mean (SD) | 45.8 (20.8) | 43.8 (19.8) | |
| Range | 20 - 92 | 18 - 85 | |
| IBD duration in years | < 0.7451* | ||
| Mean (SD) | 7.9 (5.9) | 7.5 (7.1) | |
| Range | 0 - 26.0 | 0.1 - 37.0 | |
| Ulcerative colitis, N (%) | 28 (60.9) | 28 (60.9) | |
| Total IBD therapy escalation at 1 year, N (%) | 30 (65.2) | 26 (56.5) | < 0.3458** |
| Addition of biologic therapy or change of biologic therapy at 1 year, N (%) | 18 (39.1) | 12 (26.1) | 0.1088** |