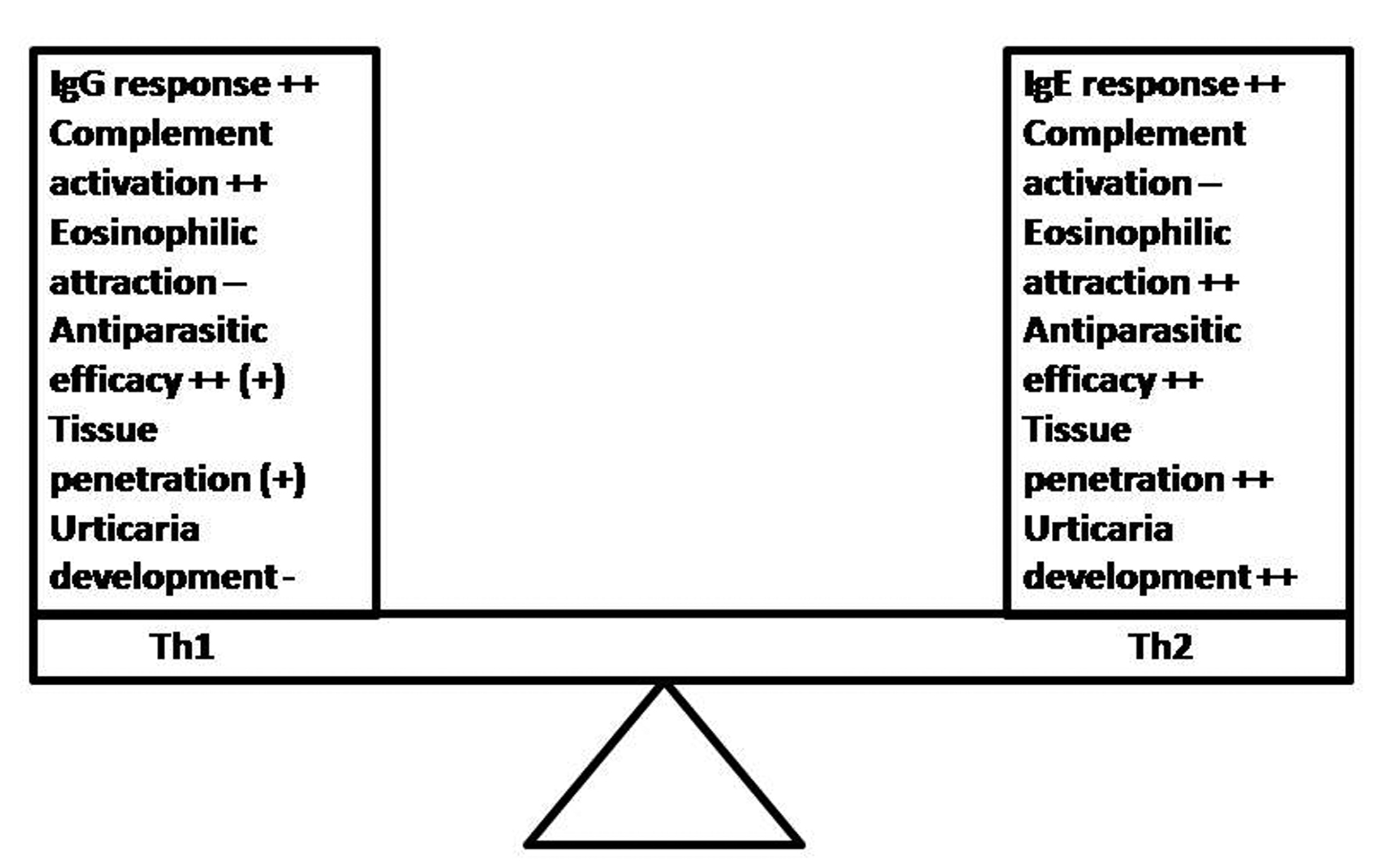
Figure 1.. Th1 vs. Th2 response during parasitoses and the development of allergic skin symptoms: Although both responses provide antiparasitic effects, the Th1 response seems to be superior to the Th2 one. Maybe the Th2 response is a host-response, chosen by the parasite that is associated with better survival and hostile tissue penetration. The eosinophil chemotaxis and the avoidance of complement-dependent innate mechanisms are targets of parasite-induced host immune modulation in order to improve its development and survival possibilities within hostile organism.