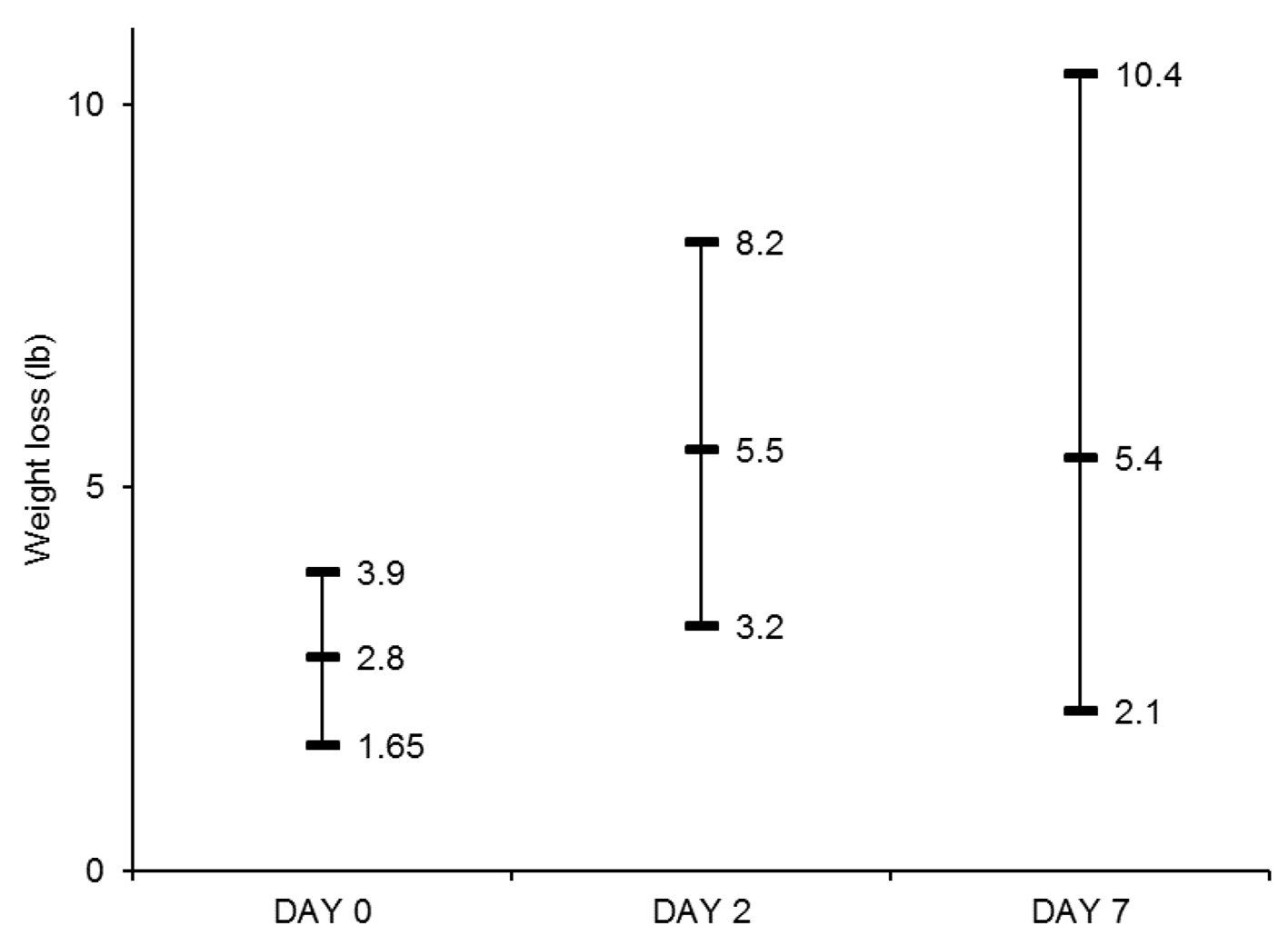
Figure 1. Median Weight loss (lb) and interquartile range at day 0, day 2 and day 7. Weight losses at day 2 and day 7 were significantly higher than that at day 0 (P < 0.05 for both comparisons).
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 13, Number 4, April 2021, pages 245-251
Outpatient Intravenous Diuretic Clinic: An Effective Strategy for Management of Volume Overload and Reducing Immediate Hospital Admissions
Figure

Tables
| IV: intravenous; SBP: systolic blood pressure; NYHA: New York Heart Association; Cr: creatinine. |
| Primary diagnosis of heart failure |
| Signs and symptoms of acute decompensated heart failure (weight gain, dyspnea) |
| Symptoms refractory to higher doses of oral diuretics |
| No acute cardiovascular issue (acute coronary syndrome, new arrhythmia, pulmonary embolism) |
| SBP > 100 or at baseline SBP |
| Heart rate 50 - 120 |
| Does not have NYHA class IV symptoms (dyspnea at rest, home inotropes) |
| Cr ≤ 2.5 or near baseline (increase < 0.5) |
| O2 saturation ≥ 90% on ≤ 2 L oxygen by nasal cannula or within 2 L baseline oxygen requirement |
| On ≤ 260 mg lasix daily or 10 mg bumex daily at home |
| Labs: blood glucose < 400 mg/dL, Na > 120 mmol/L, T bilirubin < 3 mg/dL |
| Values are represented as n (%) or median (interquartile range). HFrEF: heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; ICM: ischemic cardiomyopathy; NYHA: New York Heart Association; Afib: atrial fibrillation; CAD: coronary artery disease; COPD: chronic obstructive lung disease; CKD: chronic kidney disease; DM2: diabetes mellitus type 2; HLD: hyperlipidemia; HTN: hypertension; ACE-I: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB: angiotensin II receptor blocker; BB: beta-blocker; MRA: mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; ICD: implantable cardioverter defibrillator; CRT-D: cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator. | ||
| Age | 72 (67 - 80) | |
| Male | 25 (93) | |
| Weight, lb | 238 (189 - 275) | |
| HFrEF | 14 (52) | |
| ICM | 13 (48) | |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Afib | 15 (56) | |
| CAD | 13 (48) | |
| COPD | 8 (30) | |
| CKD 3 or above | 23 (85) | |
| DM2 | 18 (67) | |
| HLD | 14 (52) | |
| HTN | 18 (67) | |
| Loop diuretic | ||
| Furosemide | 8 (30) | |
| Bumetanide | 18 (67) | |
| Torsemide | 1 (4) | |
| Total loop diuretic dose (oral furosemide equivalent), mg | 160 (120 - 240) | |
| Thiazide diuretic | 14 (52) | |
| HFrEF (14) | HFpEF (13) | |
| ACE-I or ARB | 4 (29) | 5 (38) |
| Sacubitril-Valsartan | 2 (14) | 0(0) |
| BB | 12 (86) | 10 (77) |
| MRA | 8 (57) | 8 (62) |
| Isosorbide | 0 (0) | 1 (8) |
| Hydralazine | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Digoxin | 1 (7) | 0 (0) |
| Devices | ||
| ICD only | 1 (8) | 0 (0) |
| CRT-D | 7 (50) | 0 (0) |
| CardioMEMS | 2 (14) | 1 (8) |
| Before IV diuresis | After IV diuresis | |
|---|---|---|
| Values are represented as median (interquartile range). IV: intravenous; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide. | ||
| Lab | ||
| Serum sodium, mmol/L | 138 (136 - 139) | 138 (136 - 140) |
| Serum potassium, mmol/L | 4 (3.5 - 4.5) | 3.9 (3.4 - 4.3) |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dL | 1.59 (1.27 - 1.82) | 1.55 (1.25 - 1.95) |
| Serum BUN, mg/dL | 33.5 (24.8 - 51.2) | 33 (23 - 49) |
| BNP, pg/mL | 597 (145 - 1,466) | - |
| Hemodynamics | ||
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 111 (101.5 - 127.5) | 116 (108 - 125) |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 67 (58 - 75) | 68 (62 - 76) |
| Heart rate | 78 (75 - 82) | 79 (72 - 82) |
| Clinic outcomes | ||
| Urine output, mL | 1,500 (1,030 - 2,600) | |
| Weight loss, lb | 2.8 (1.7 - 3.9) | |
| Outcomes | HFrEF* (N = 14) | HFpEF* (N = 13) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Values are expressed as median (interquartile range). HFpEF: heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; HFrEF: heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. | |||
| Urine output, mL | 1,350 (935 - 1,900) | 1,686 (1,362 - 2,637) | 0.25 |
| Weight loss, lb | |||
| Day 0 | 2.6 (1.6 - 3.7) | 2.8 (1.9 - 4.4) | 0.65 |
| Day 2 | 7.1 (3.2 - 11.4) | 5.4 (3.8 - 7.9) | 0.53 |
| Day 7 | 6.7 (1.5 - 10.9) | 4.6 (2.3 - 8.4) | 0.51 |
| *Values are expressed as median (interquartile range). | |
| Clinic visit* | $1,076 (960 - 1,233) |
| Hospital admission* | $11,471 (4,818 - 26,880) |
| Hospital admission per day* | $1,912 (535 - 2,987) |
| Estimated cost saving (per admission prevented) | $10,395 |
| Values are represented as n (%). AKI is defined as increase in Cr by 0.3 mg/dL. Severe hypokalemia is defined as potassium < 3.0 mmol/L and mild-moderate hypokalemia as 3.0 - 3.5 mmol/L. AKI: acute kidney injury. | |
| Arrhythmia | 0 |
| AKI | 0 |
| Hypotension | 0 |
| Severe hypokalemia | 1 (3) |
| Mild-moderate hypokalemia | 22 (65) |
| Same-day admission | 1 |