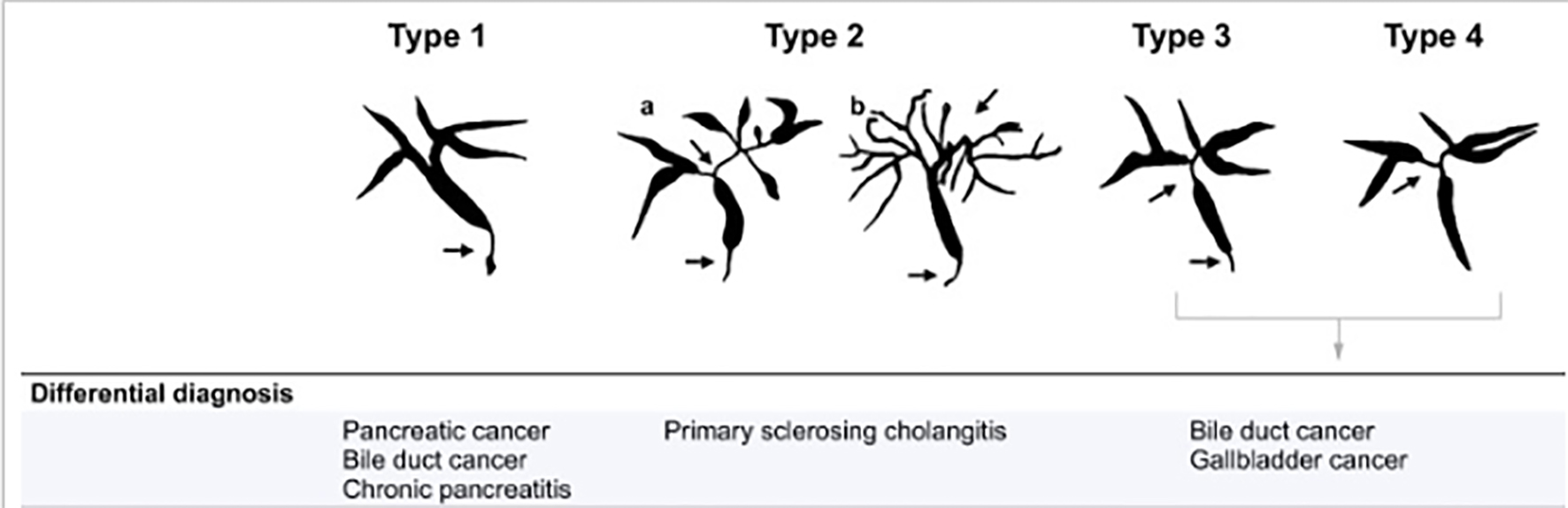
Figure 1. The different types of IgG4-SC with the differential diagnosis. Arrows indicate sites of strictures/stenosis. IgG4-SC: immunoglobulin G4 scelrosing cholangitis.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 13, Number 2, February 2021, pages 75-81
Isolated Type Immunoglobulin G4 Sclerosing Cholangitis: The Misdiagnosed Cholangiocarcinoma
Figure

Tables
| Diagnostic criterion | Description |
|---|---|
| IgG4-SC: immunoglobulin G4 scelrosing cholangitis; HPF; high-power field; AIP: autoimmune pancreatitis. | |
| Histology of bile duct | There is lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing cholangitis on resection specimens (lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with > 10 IgG4-positive cells per HPF within and around bile ducts with associated obliterative phlebitis and storiform fibrosis). Bile duct biopsy specimens often do not provide sufficient tissue for a definitive diagnosis; however, presence of > 10 IgG4-positive cells per HPF (in the biopsy specimen) is suggestive of IgG4-SC. |
| Imaging of bile duct | There are one or more strictures involving intra-hepatic, proximal extra-hepatic, or intra-hepatic bile ducts. There are fleeting/migrating biliary strictures. |
| Serology | There is an increase in serum IgG4 level (normal: 8 - 140 mg/dL). |
| Other organ involvement | Pancreas: there are classic features of AIP on imaging or histology (diffusely enlarged pancreas with delayed enhancement and capsule-like rim). Suggestive imaging findings include focal pancreatic mass/enlargement without pancreatic duct dilation, multiple pancreatic masses, focal pancreatic duct stricture without upstream dilation and pancreatic atrophy. There is retroperitoneal fibrosis. Renal lesions: there are single or multiple parenchymal low-attenuation lesions (round, wedge shaped or diffuse patchy). There is salivary/lacrimal gland enlargement. |
| Response to steroid therapy | There is normalization of liver enzymes or resolution of stricture (although complete resolution of stricture may not be seen early in the course of treatment or in patients with predominantly fibrotic strictures). |
| IgG4-SC | Cholangiocarcinoma | |
|---|---|---|
| IgG4-SC: immunoglobulin G4 scelrosing cholangitis; M: male; F: female; IgG4: immunoglobulin G4. | ||
| Age | Middle age to elderly | Middle age to elderly |
| Sex | M > F | M > F |
| Clinical presentation | Jaundice and weight loss | Painless jaundice |
| Elevated IgG4 levels | 70-90% | 13.5-22% |