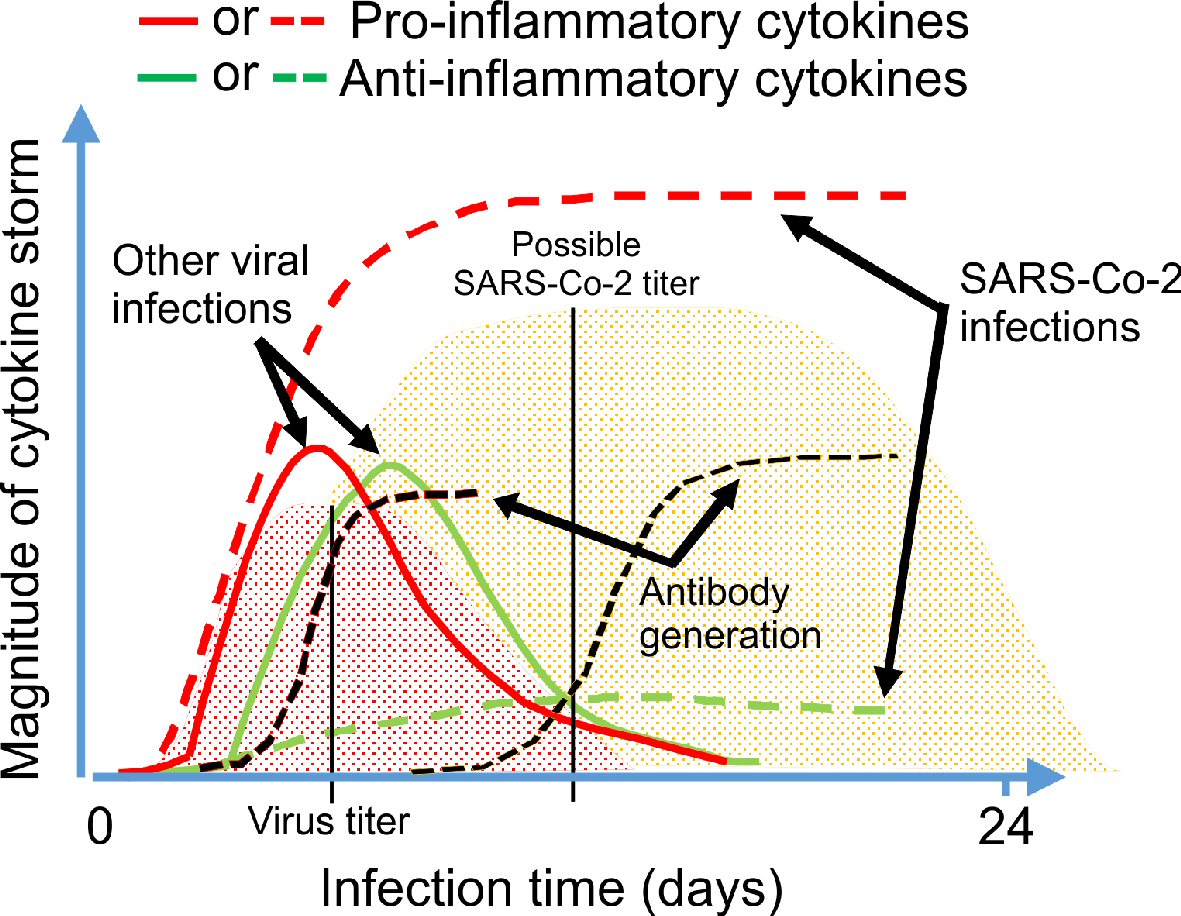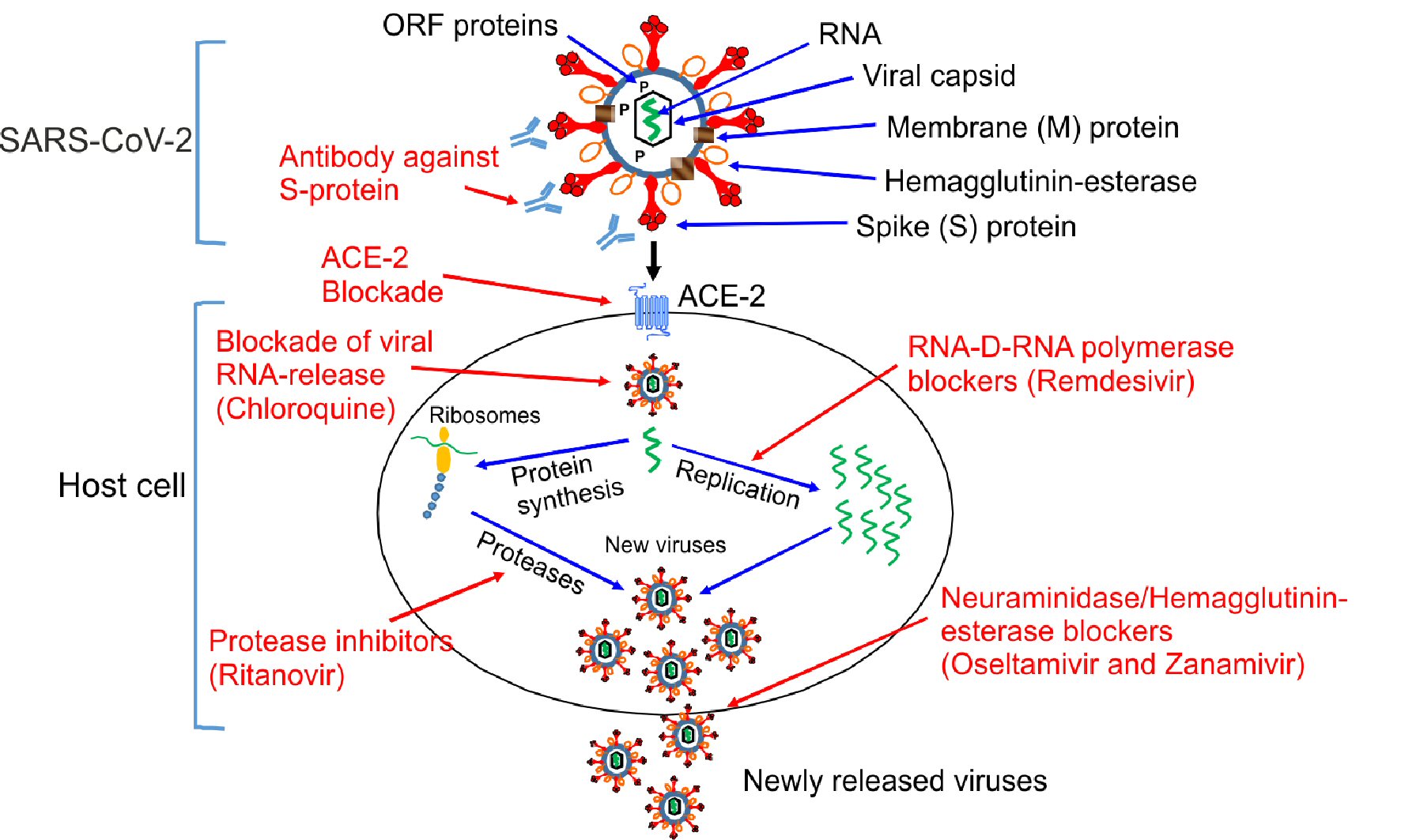
Figure 1. Mechanisms of action of different antiviral drugs. A schematically diagram of SARS-CoV-2 structure and different pathway used by SARS-CoV-2 for the replication in the host cells. Theoretical applicable inhibitory action of certain antiviral drugs used in the treatment of other viral infections, as well as specific SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies would in combination interfere with the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle exerting a possible inhibitory effect on the virus replication, which is shown in red color. ORF proteins: ORF1a, ORF1b, ORF3a, ORF8 and ORF10 [8, 19]. SARS-CoV-2: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; ACE2: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; ORF: open read frame.