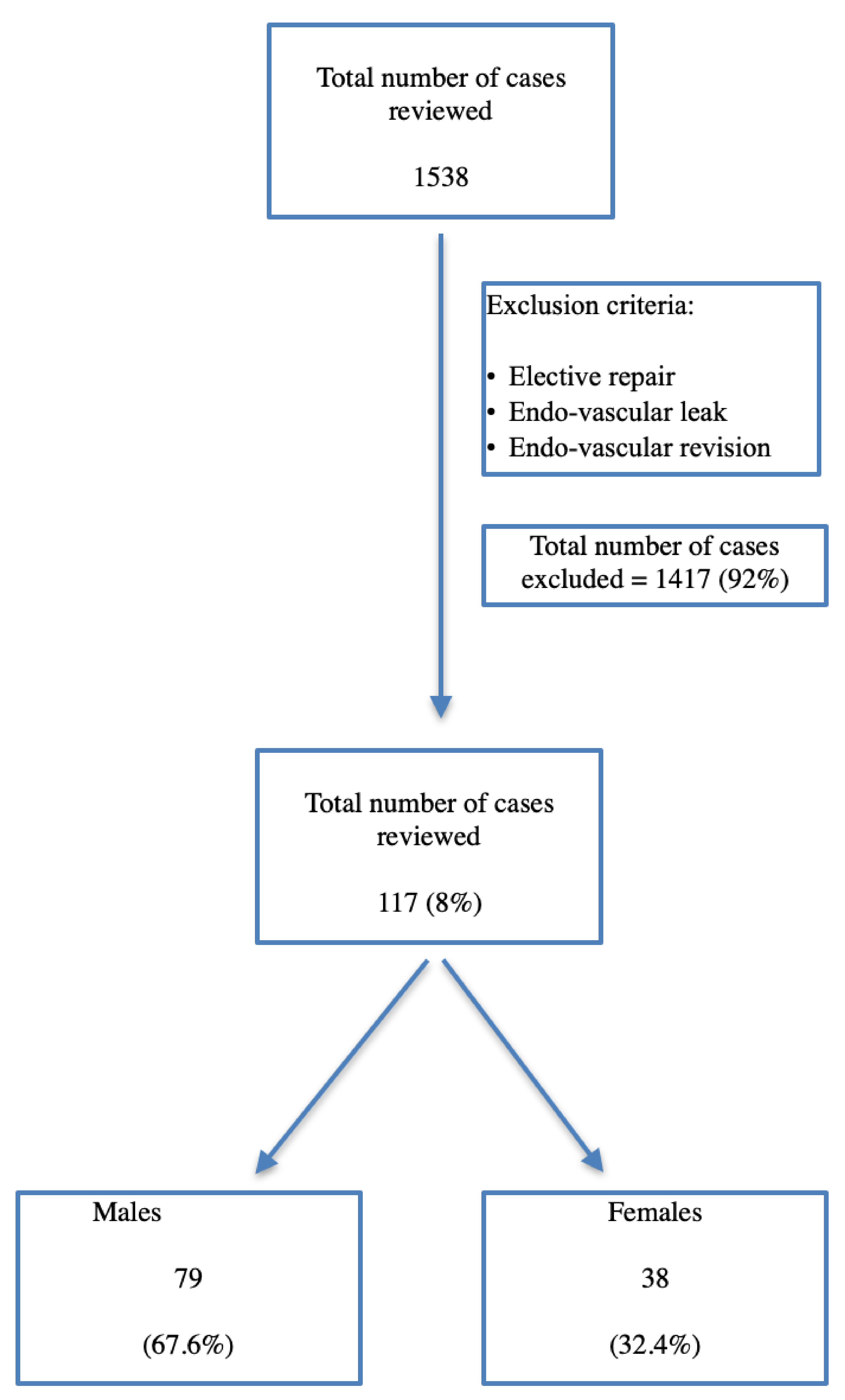
Figure 1. Inclusion and exclusion criteria of the study.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 12, Number 12, December 2020, pages 794-802
Gender-Based Differences in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Rupture: A Retrospective Study
Figures

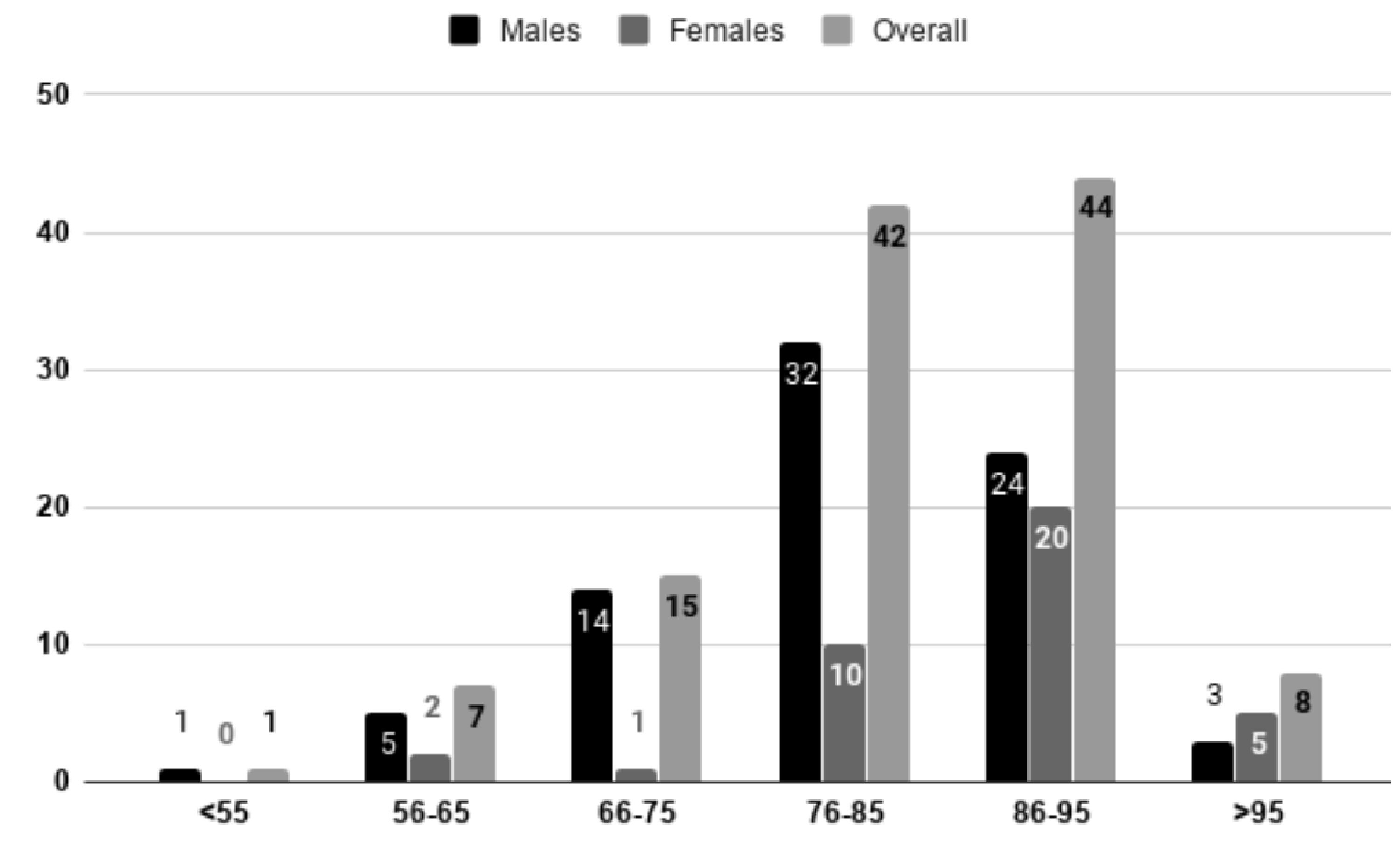
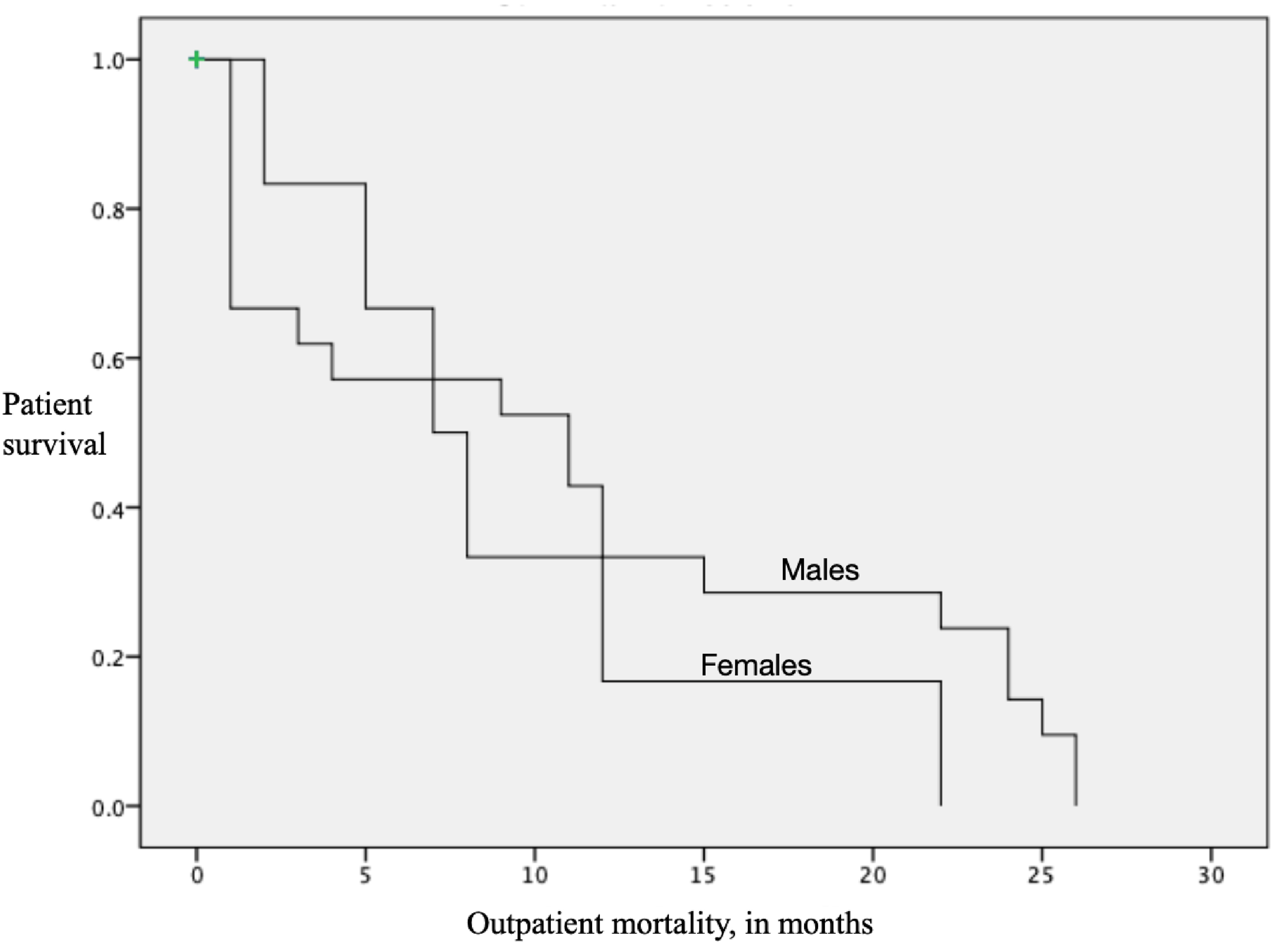
Tables
| Characteristic | Males (n = 79) | Females (n = 38) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| aMajor comorbidities are defined as diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases including coronary artery, cerebrovascular and carotid artery diseases. bAge was adjusted for BMI, smoking history, hypertension, comorbidities, use of aspirin, statin, clopidogrel, beta-blockers, previous history of aneurysm, size and location of aneurysm. BMI: body mass index; SD: standard deviation. | |||
| Site, n (%) | |||
| Facility 1 | 52 (65.8) | 20 (52.6) | |
| Facility 2 | 27 (34.2) | 18 (47.4) | 0.17 |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| Caucasian | 79 (100) | 38 (100) | |
| Others | 0 | 0 | N/A |
| BMI, n (%) | 0.02 | ||
| Normal (< 25.0) | 15 (25.8) | 11 (58.0) | |
| Overweight (25.1 - 30) | 24 (41.3) | 6 (31.5) | |
| Obese (> 30.0) | 19 (32.9) | 2 (10.5) | |
| Smoking, n (%) | 66 (83.5) | 26 (68.4) | 0.06 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 66 (83.5) | 33 (86.8) | 0.64 |
| Major comorbidities, n (%)a | 38 (48.1) | 20 (52.6) | 0.64 |
| Aspirin, n (%) | 40 (50.6) | 18 (47.4) | 0.10 |
| Statin, n (%) | 40 (50.6) | 18 (47.4) | 0.74 |
| Clopidogrel, n (%) | 7 (8.9) | 5 (13.1) | 0.47 |
| Beta-blocker, n (%) | 24 (30.4) | 14 (36.8) | 0.48 |
| Age at rupture, mean (SD)b | 75.8 (10.0) | 82.4 (8.6) | 0.005 |
| Characteristic | Males (n = 79) | Females (n = 38) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CT: computerized tomography; SD: standard deviation. | |||
| Location of the aneurysm, n (%) | 0.28 | ||
| Infrarenal | 75 (94.9) | 34 (89.5) | |
| Suprarenal | 0 (0) | 1 (2.6) | |
| Both | 4 (5.1) | 3 (7.9) | |
| Involvement of iliac arteries, n (%) | 0.42 | ||
| Left | 6 (7.6) | 1 (2.6) | |
| Right | 9 (11.4) | 4 (10.5) | |
| Both | 12 (15.2) | 3 (7.9) | |
| None | 52 (65.8) | 30 (78.9) | |
| Size of aneurysm at rupture (cm), mean (SD) | 8.23 (1.84) | 7.46 (2.09) | 0.04 |
| Known history of AAA repair, n (%) | 46 (58.2) | 19 (50) | 0.34 |
| Previous surgical history of AAA repair, n (%) | 23 (29.1) | 4 (10.5) | 0.04 |
| AAA size at earlier diagnosis, (cm), mean (SD) | 4.0 (3.3) | 5.0 (2.6) | 0.03 |
| Characteristic | Males (n = 79) | Females (n = 38) | P valuec |
|---|---|---|---|
| aAdjusted for tobacco use, age, size at presentation, major comorbidities and use of cardio-protective medications. bThe incidence of surgery was adjusted for age, major comorbidities and size at presentation. cThe overall mortality was still at a statistically significant level of less than 0.05 even for the unadjusted sample. However, the postoperative mortality for the unadjusted sample was 0.26 as compared to 0.05 for the adjusted sample. | |||
| Overall mortality, n (%)a | 25 (31.6) | 26 (68.4) | 0.001 |
| Operative course | |||
| Surgical management, n (%)b | 74 (93.7) | 24 (63.2) | 0.03 |
| Type of surgeryb | |||
| EVAR, n (%) | 57 (72.2%) | 16 (42.1%) | < 0.01 |
| Open, n (%) | 17 (21.5%) | 8 (21.1%) | |
| None, n (%) | 5 (6.3%) | 14 (36.8%) | |
| Postoperative coursea | Males (n = 74) | Females (n = 24) | |
| Ventilator requirement, n (%) | 44 (59.5) | 18 (75) | 0.17 |
| Requirement of vasopressors, n (%) | 40 (54.1) | 17 (70.8) | 0.15 |
| Unexpected postoperative complications, n (%) | 38 (48.6) | 10 (58.3) | 0.41 |
| Length of stay in intensive care unit, days (SD) | 4.1 (4.1) | 5.5 (6.0) | 0.02 |
| Postoperative mortality, n (%)a | 21 (21.4) | 12 (50.0) | 0.05 |