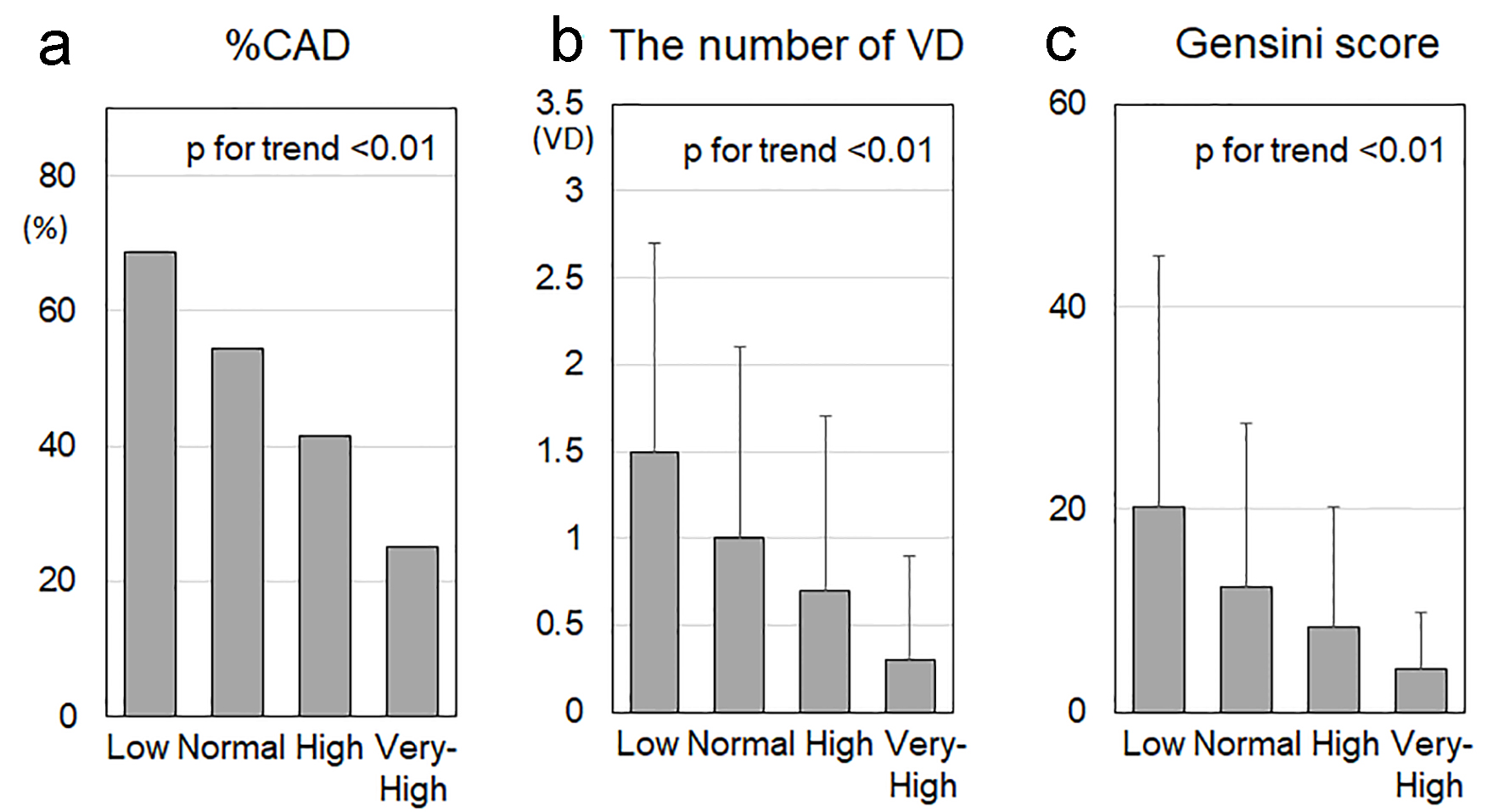
Figure 1. %CAD (a), number of VD (b) and Gensini score (c) in the low, normal, high and very-high HDL-C groups. CAD: coronary artery disease; VD: vessel disease; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. †P < 0.05, *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001.