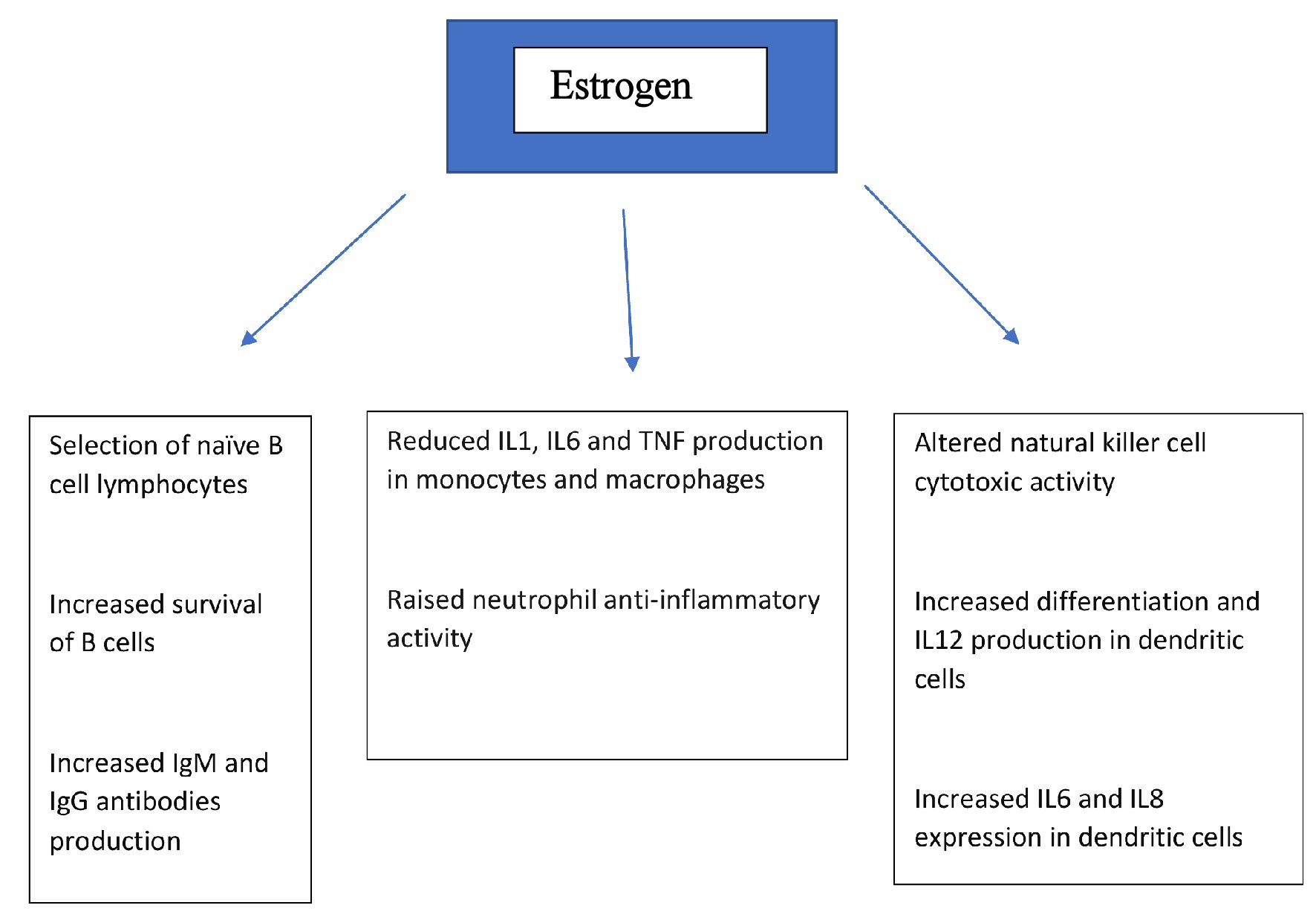
Figure 1. Effects of estrogen on various components of immune system. IL: interleukin; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; Ig: immunoglobulin.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 12, Number 10, October 2020, pages 634-639
Could Estrogen Protect Women From COVID-19?
Figure

Table
| Year | Authors | Study conclusion |
|---|---|---|
| HIV: human immunodeficiency virus. | ||
| 1992 | Manyonda et al [27] | Therapeutic doses of estrogen modulated immune responses in postmenopausal women. |
| 2000 | Smith et al [12] | Estrogen prevented vaginal transmission of simian immunodeficiency virus in macaques. |
| 2004 | Miller et al [23] | Estrogen attenuated the early vascular injury response by negatively modulating proinflammatory mediator expression and chemotactic activity of injured vessels for neutrophils in rats. |
| 2007 | Hsieh et al [24] | Estrogen showed protective effect on lung injury mediated via downregulation of lung MIF and TLR4-induced cytokine/chemokine production. |
| 2010 | Hayashida et al [19] | Estrogen inhibits the production of hepatitis C infectious particles in human cells. |
| 2012 | Furusyo et al [20] | Selective estrogen receptor modulator improved the efficacy of treatment of postmenopausal women with chronic hepatitis C. |
| 2013 | Murakami et al [21] | Selective estrogen receptor modulators seemed to target multiple steps of hepatitis C viral life cycle: attachment, entry, replication, and post replication events in viral culture system. |
| 2013 | Johansen et al [13] | Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) acted as potent inhibitors of viral infection in mice. |
| 2013 | Rodriguez-Garcia et al [17] | Estrogen reduces susceptibility of human CD4+ T cells and macrophages to HIV infection. |
| 2014 | Robinson et al [15] | Estrogen regulates neutrophils mediated inflammation and tissue repair during influenza virus infection in mice. |
| 2015 | Villa et al [25] | Estrogen accelerates the resolution of inflammation in macrophagic cells in mice cell lines. |
| 2016 | Peretz et al [16] | Estrogenic compounds reduced influenza A virus replication in primary human nasal epithelial cells derived from females. |
| 2016 | Engelmann et al [28] | Estrogen affected immune homeostasis and humoral immune responses in postmenopausal women. |
| 2017 | Fan et al [14] | Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) selectively inhibited Ebola virus entry and infection in human cell lines. |
| 2019 | Lamin et al [22] | Tamoxifen protects from vesicular stomatitis virus infection in mice. |