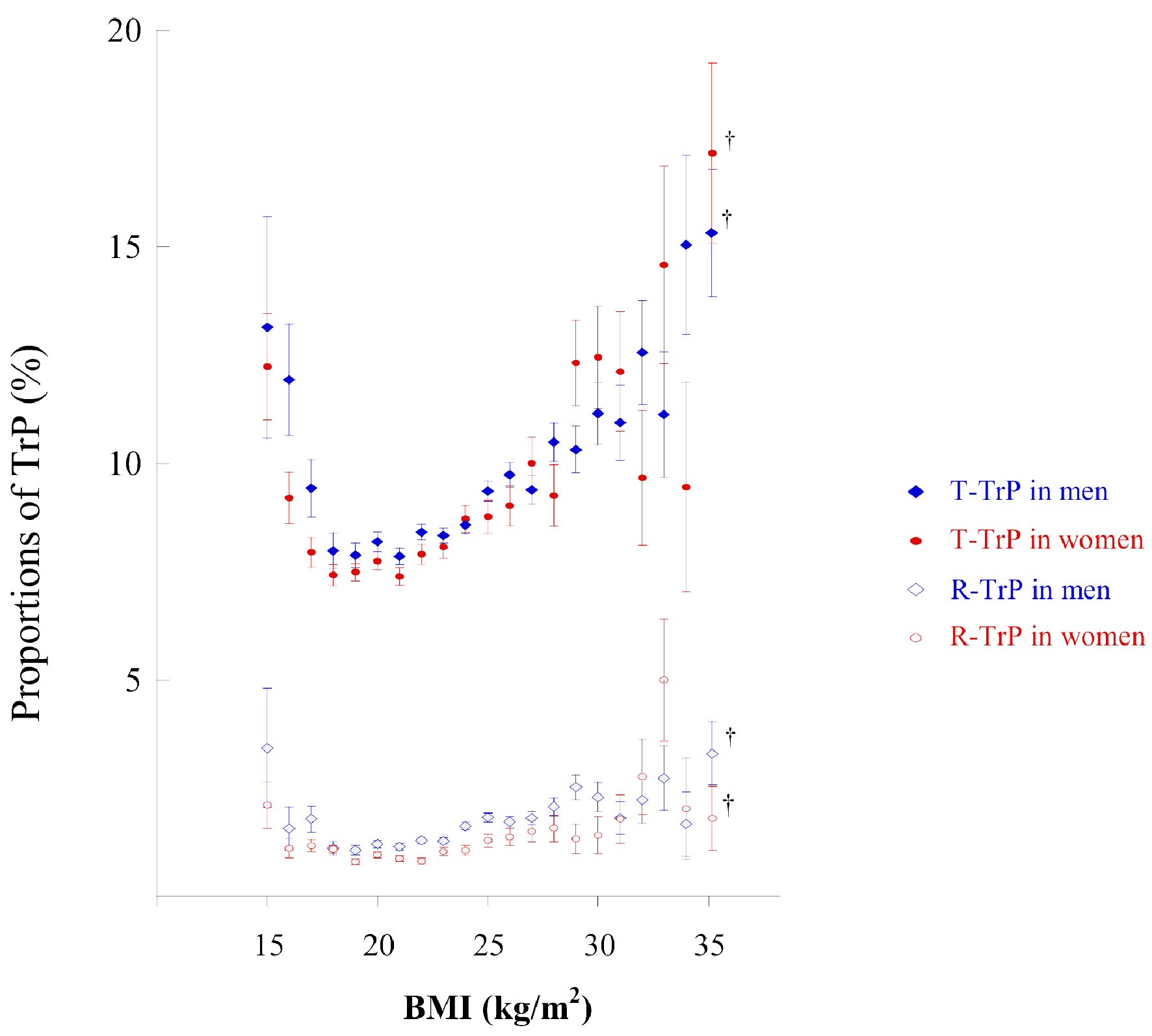
Figure 1. Proportion of subjects with TrP according to BMI categories. The circle in the middle of each bar shows the mean percentage of subjects with TrP (± on dipstick urinalysis) according to BMI intervals (1.0 kg/m2). This percentage was calculated as the number of subjects with TrP/number of subjects in each BMI group × 100 for each BMI interval (1.0 kg/m2 intervals). The vertical bar represents the standard error when TrP is 1 and non-TrP is 0. †BMI from 35.0 to 50.0 kg/m2. BMI: body mass index; TrP: trace proteinuria; T-TrP: transient TrP; R-TrP: recurrent TrP.