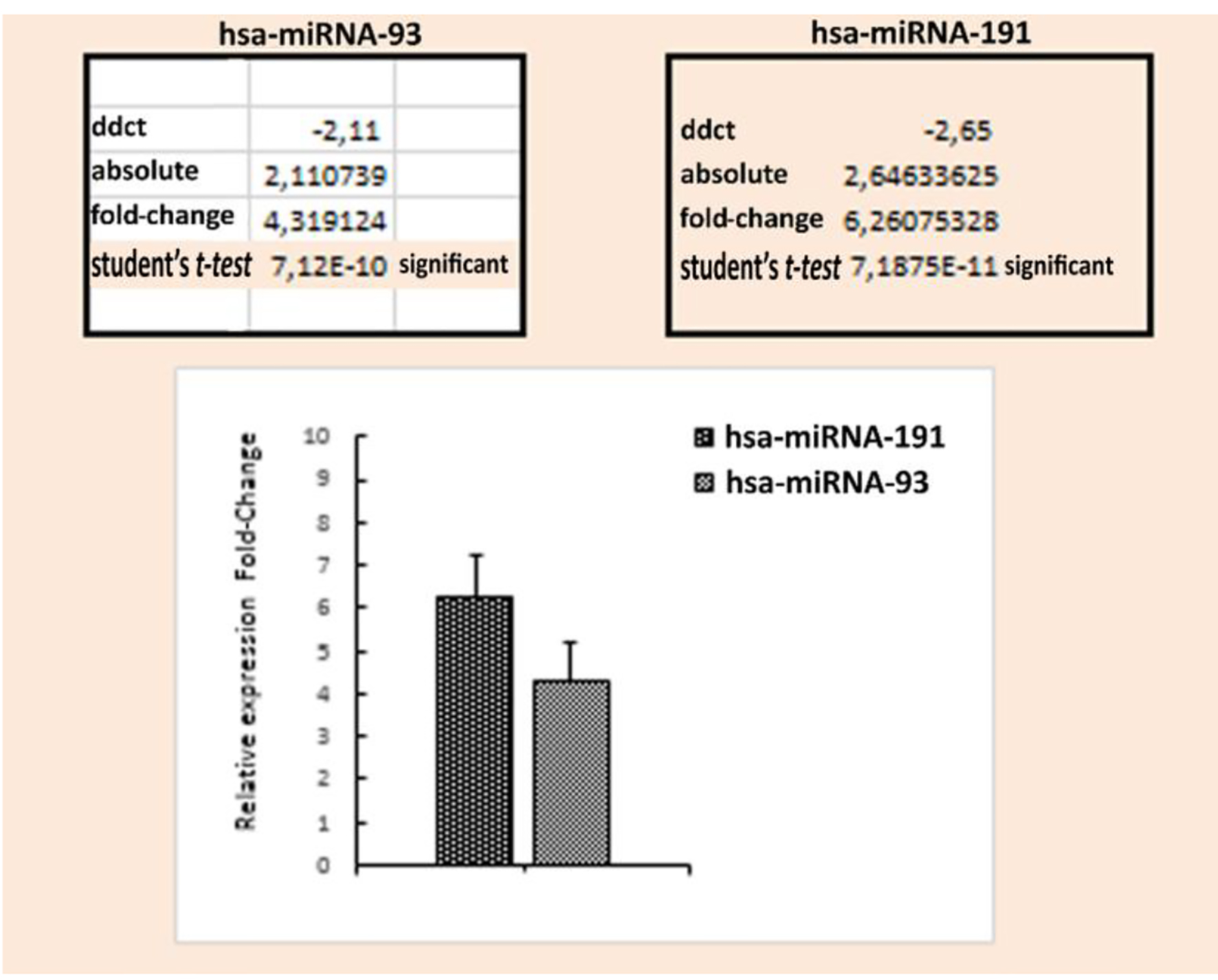
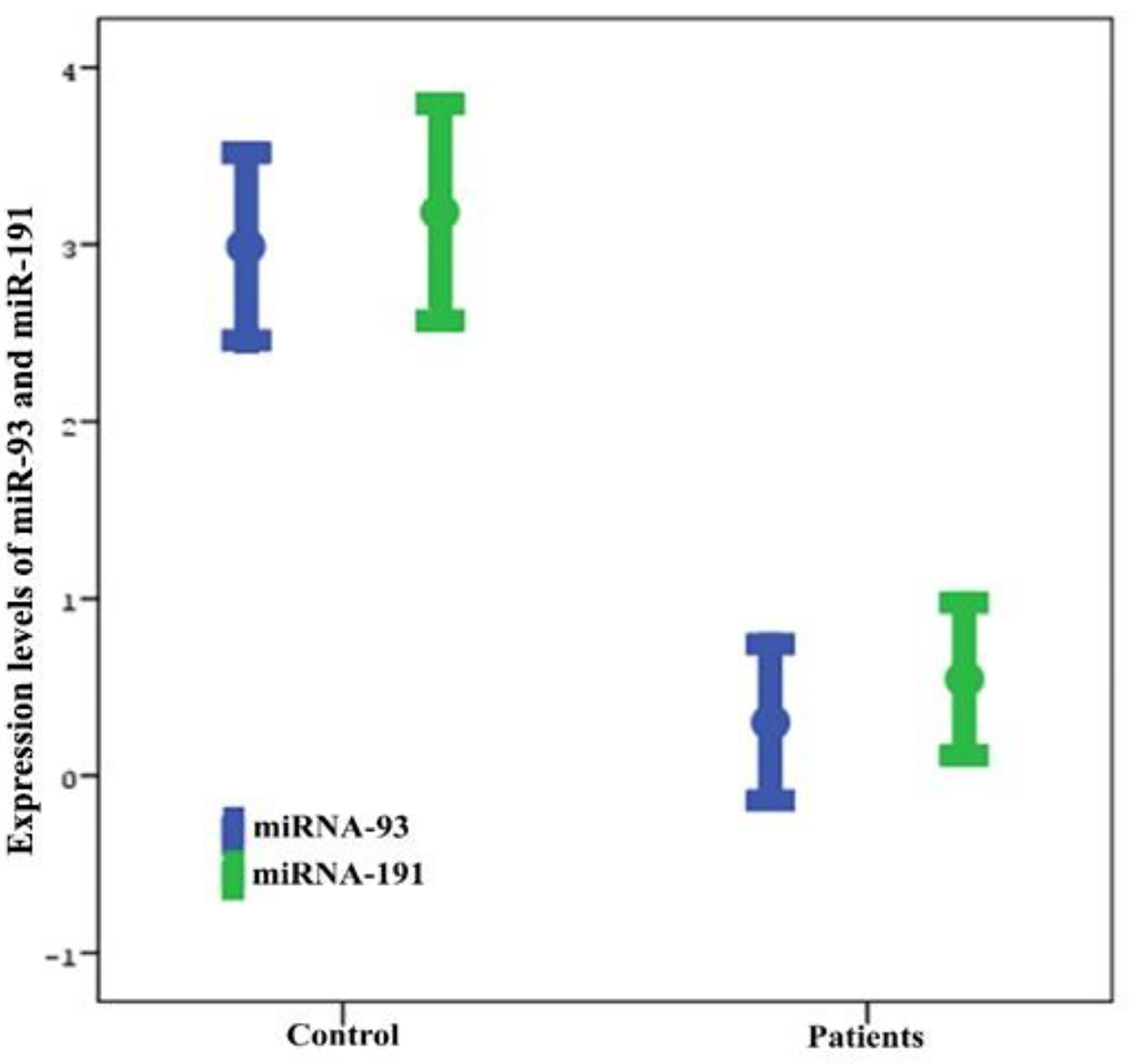
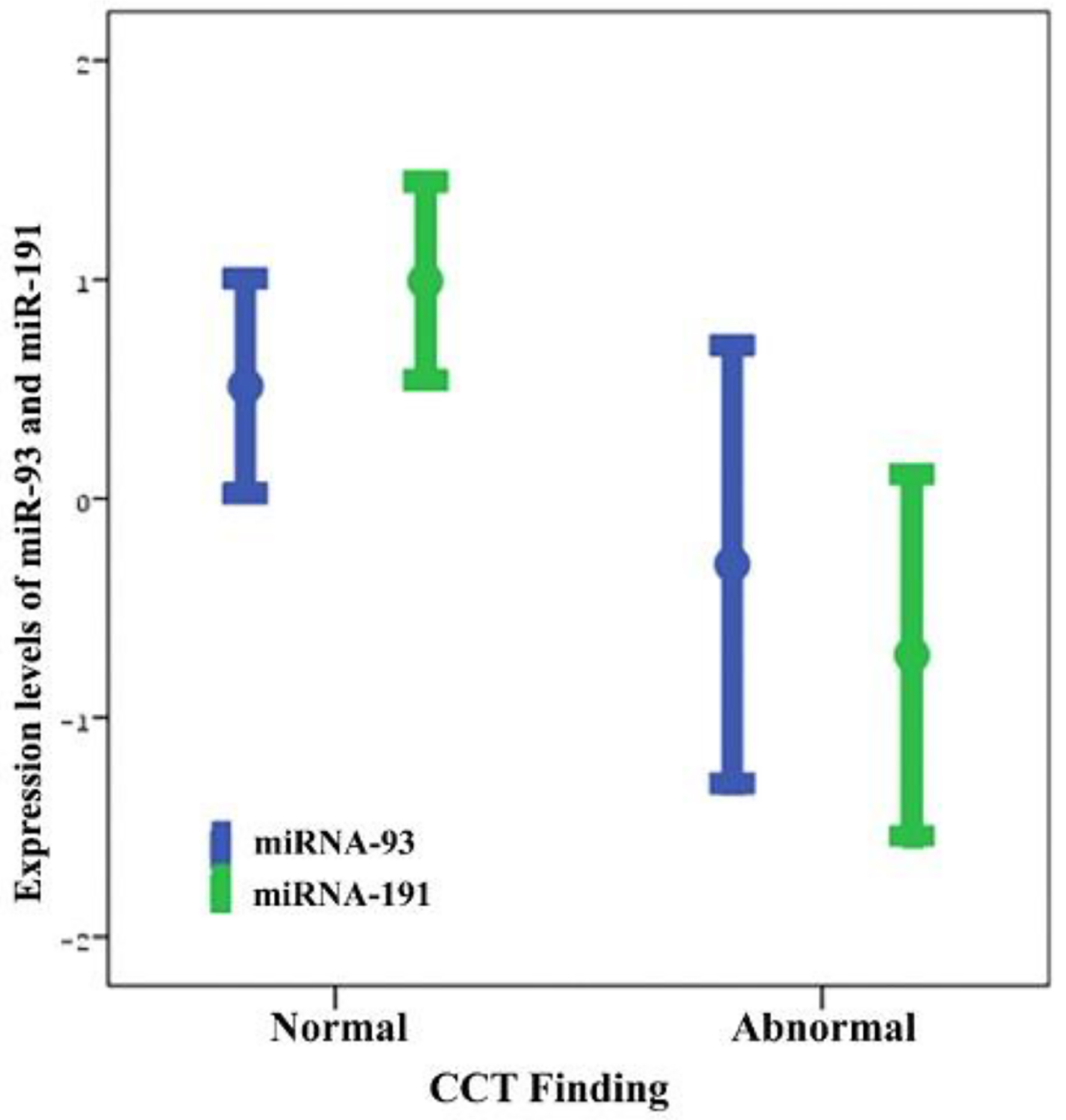
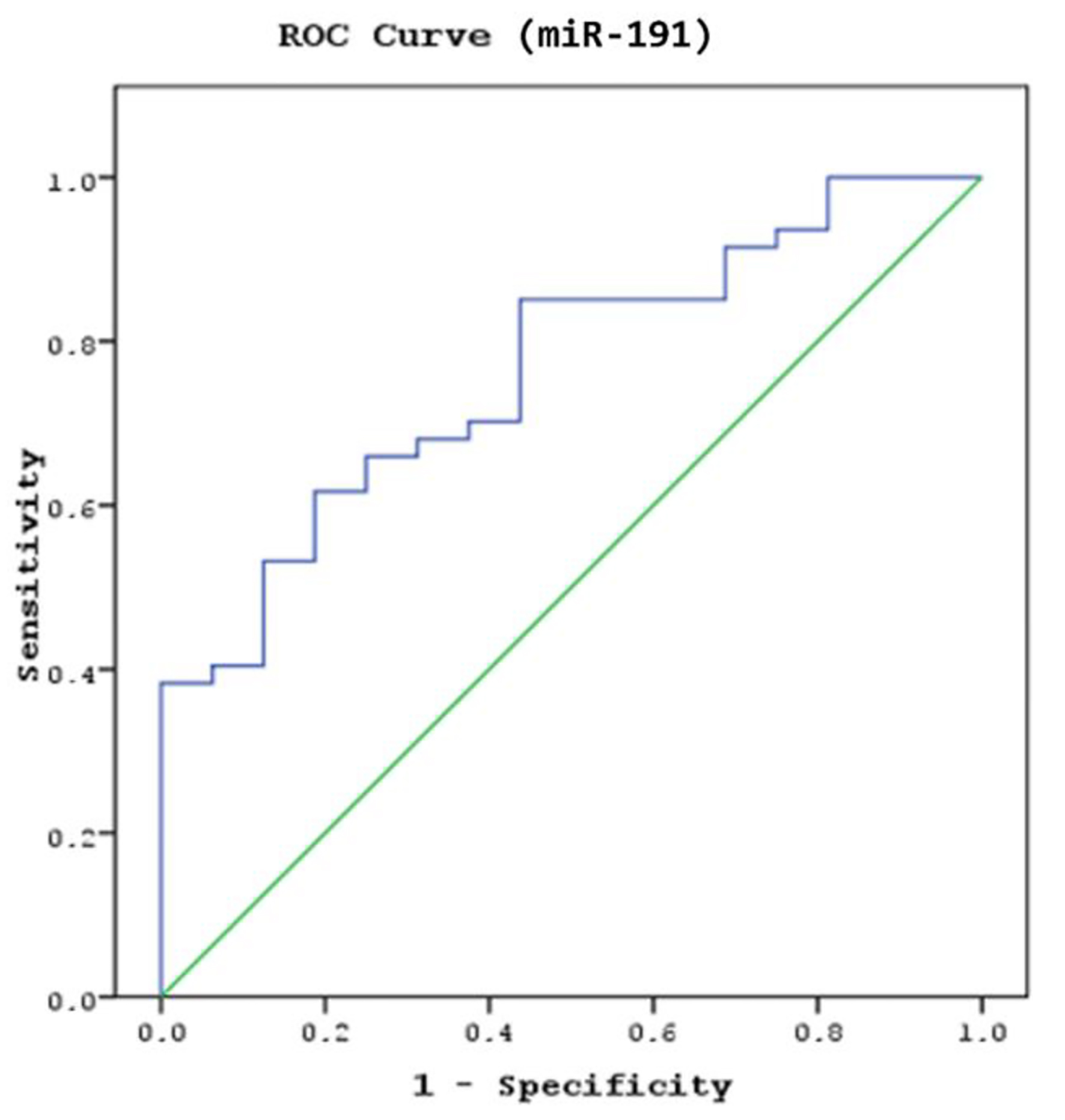
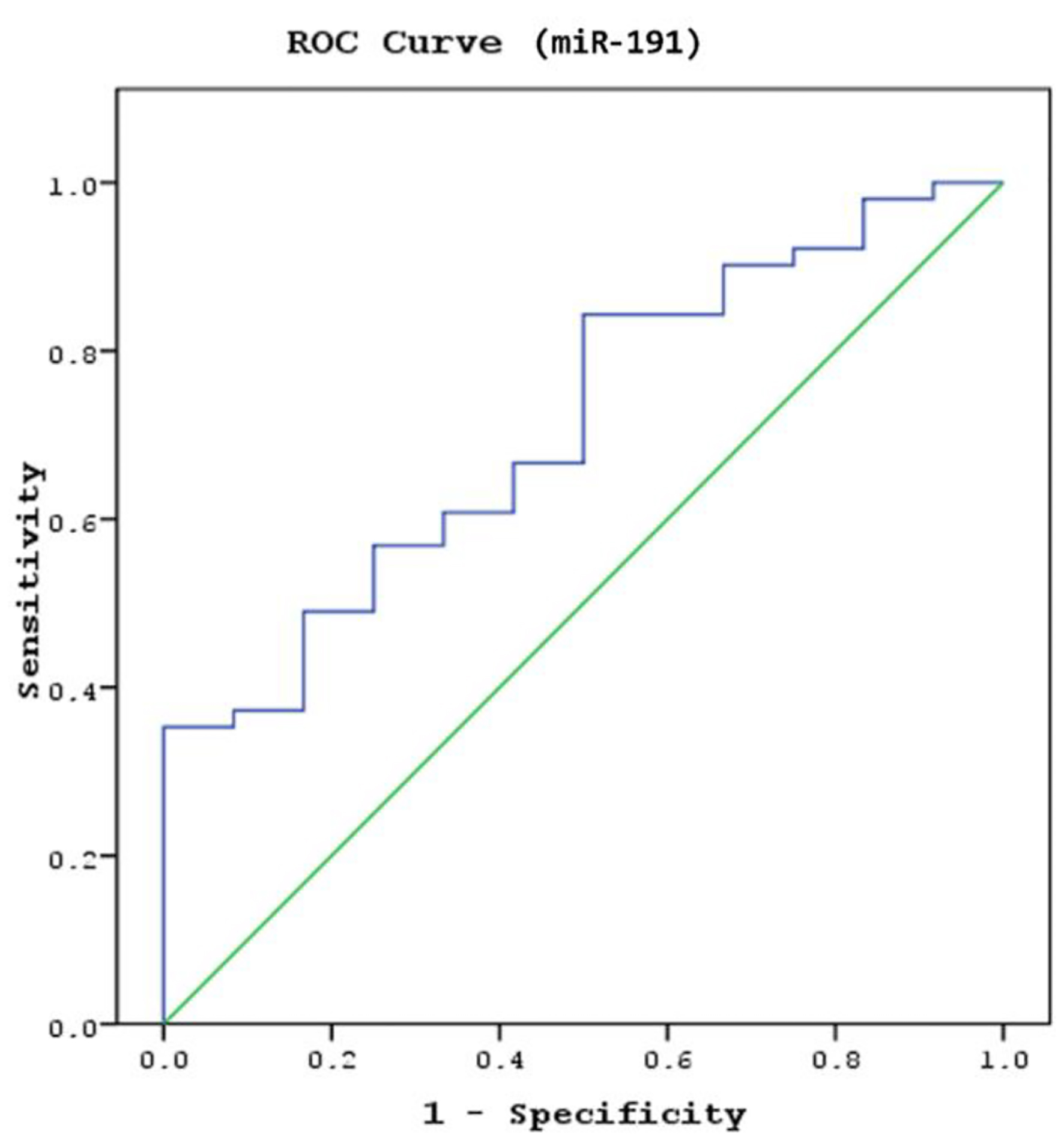
| Data are presented as numbers, percentages, mean ± standard deviation (SD) and minimum and maximum values. *The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare serum miR93 and miR191 levels between groups. Normal CT scan findings, including patients in the absence of traumatic intracranial or extracranial lesions (e.g., skull fracture, brain swelling, cerebral contusion and intracerebral hematoma). Abnormal CT scan findings, including linear fractures, collapse fractures, or traumatic brain injury (TBI). TBI, traumatic parenchymal lesions including epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, cerebral contusion and pneumocephalus. |