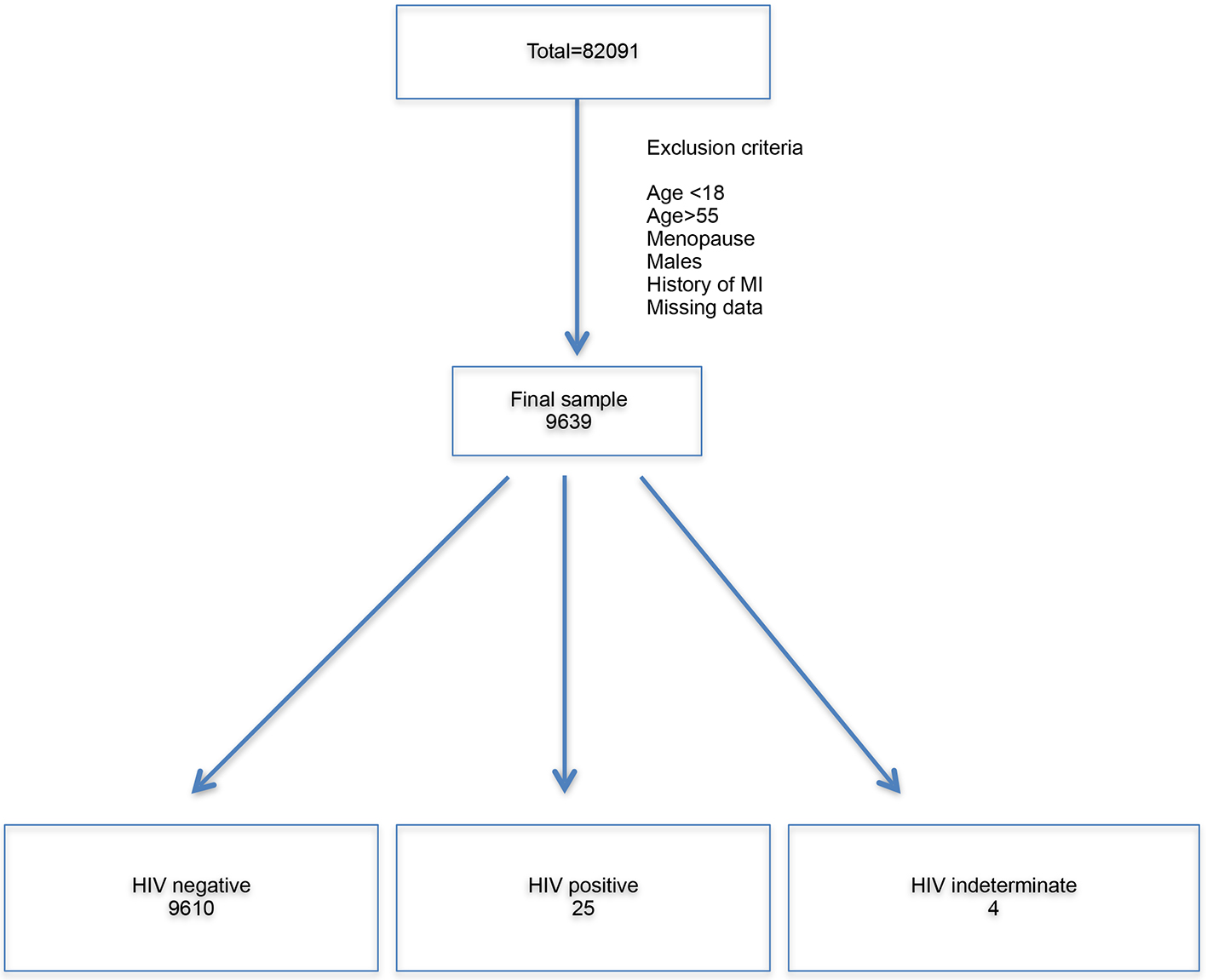
Figure 1. Flow chart illustrating derivation of final sample. The total sample was 82,091. All the exclusion criteria were applied. The final sample was 9,639. Overall, 9,610 people were HIV-negative, four were HIV-indeterminate and 25 were HIV-positive. HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; MI: myocardial infarction.