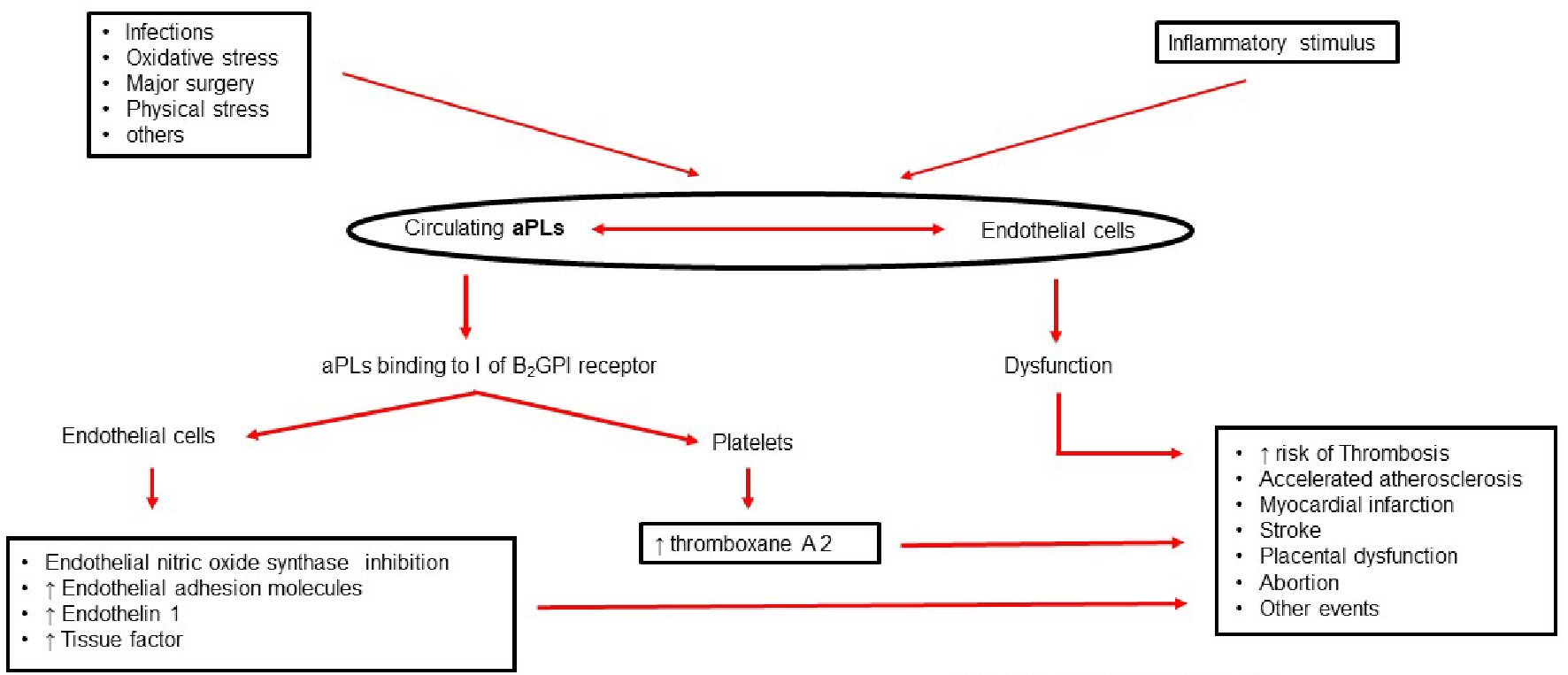
Figure 1. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: pathophysiology. aPLs: antiphospholipid antibodies.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 12, Number 5, May 2020, pages 286-292
The Issue of the Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome
Figure

Tables
| *According to red blood count. |
| Deep vein thrombosis |
| Arterial thrombosis of limbs |
| Subclavian and jugular vein thrombosis |
| Pulmonary embolism |
| Pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| Valvulopathy |
| Acute myocardial infarction |
| Mesenteric ischemia |
| Migraine |
| Stroke |
| Transient ischemic attack |
| Renal infarction |
| Renal vein thrombosis |
| Ulcers |
| Cutaneous necrosis |
| Livedo reticularis |
| Arthralgia |
| Arthritis |
| Anemia* |
| Thrombocytopenia |
| Eclampsia |
| Placental detachment |
| Abortions |
| Prematures |
| IgM: immunoglobulin M; IgG: immunoglobulin G. |
| Serum dosages of antiphospholipid antibodies with intermediate or elevated titers on two occasions with an interval of at least 12 weeks |
| Lupic anticoagulante |
| Anticardiolipin antibody IgM and/or IgG |
| Anti-β2 glycoprotein |