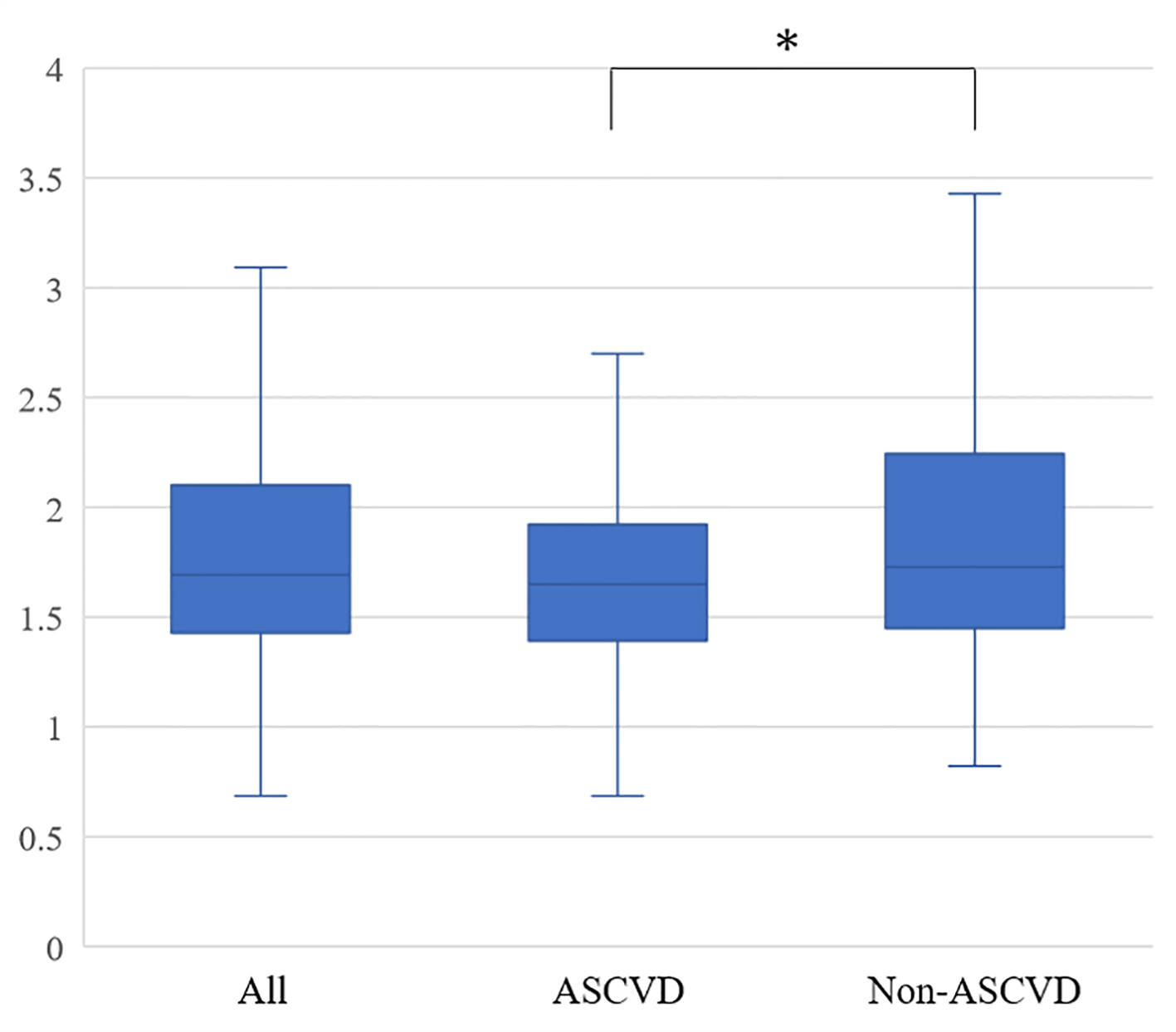
Figure 1. Reactive hyperemia indexes in all patients, the ASCVD and non-ASCVD groups. ASCVD: atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. *P < 0.05.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 12, Number 5, May 2020, pages 293-299
Reactive Hyperemia Index Associated With Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Under Treatment for Lifestyle Diseases
Figures

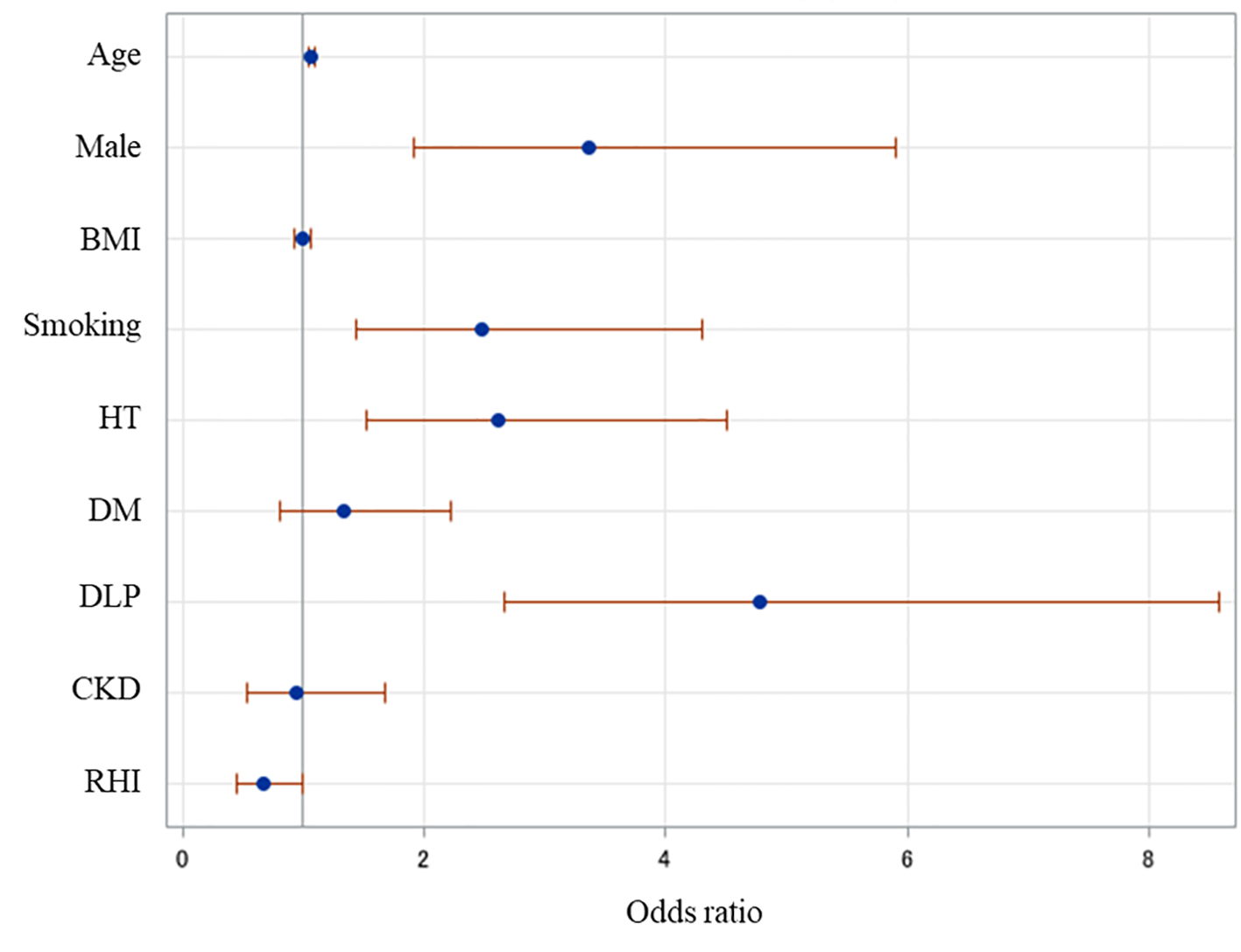
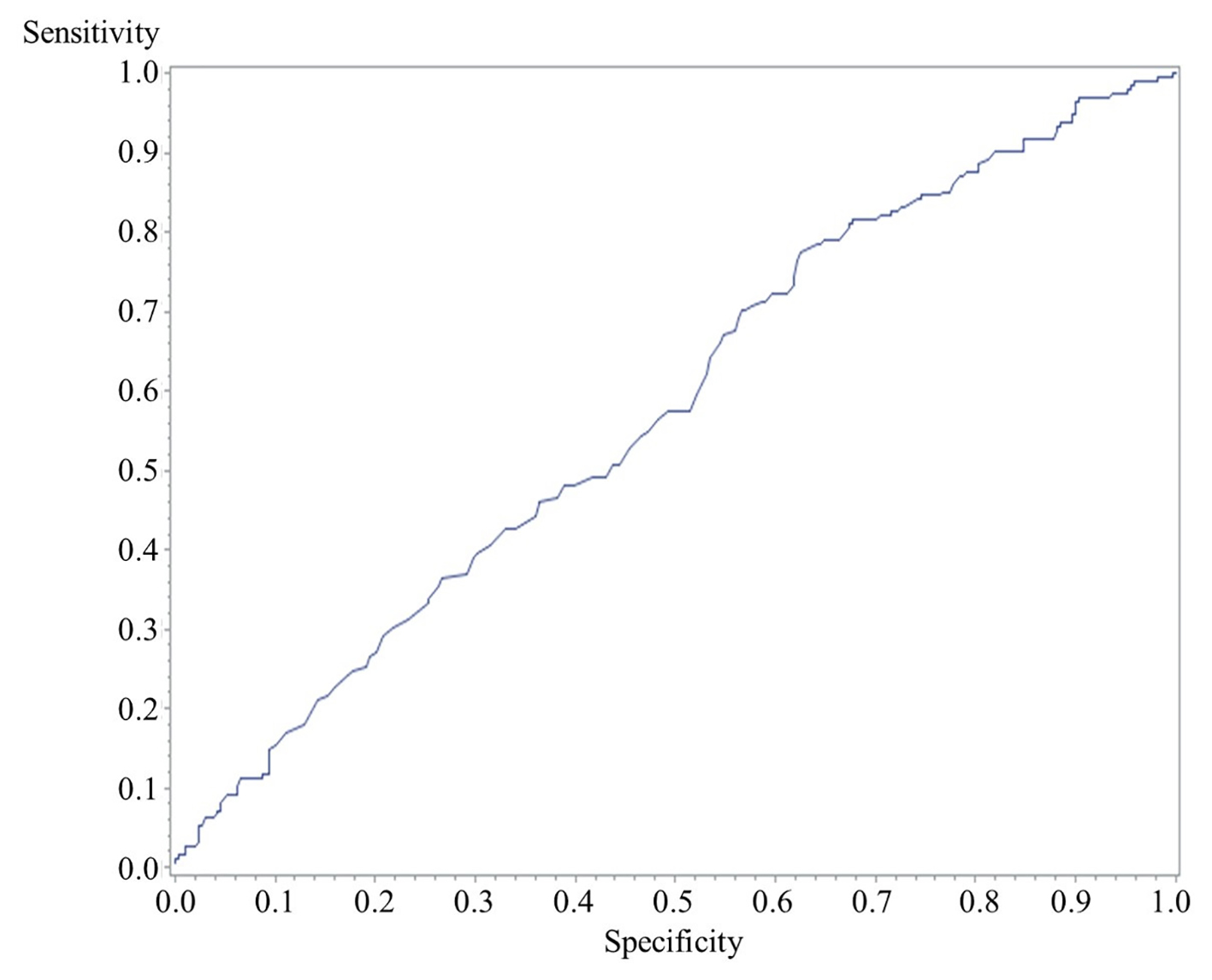
Tables
| Variables | All (n = 483) | ASCVD (n = 195) | Non-ASCVD (n = 288) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P value shows the comparison with ASCVD vs. non-ASCVD. ASCVD: atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; BMI: body mass index; HT: hypertension; DM: diabetes mellitus; DLP: dyslipidemia; MetS: metabolic syndrome; WBC: white blood cell; CRP: C-reactive protein. | ||||
| Age, years | 69 (62 - 76) | 72 (65 - 77) | 67 (61 - 75) | < 0.001 |
| Male, n (%) | 265 (55) | 147 (75) | 118 (41) | < 0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24 (22 - 26) | 24.3 ± 3.1 | 24 (22 - 26) | 0.047 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 208 (43) | 124 (64) | 84 (29) | < 0.001 |
| HT, n (%) | 357 (73.9) | 171 (87.7) | 186 (64.6) | < 0.001 |
| DM, n (%) | 116 (24) | 61 (31.3) | 55 (19.1) | 0.003 |
| DLP, n (%) | 366 (75.8) | 170 (87.2) | 196 (68.1) | < 0.001 |
| MetS, n (%) | 172 (35.6) | 102 (52.3) | 70 (24.3) | < 0.001 |
| WBC, 103/µL | 5,400 (4,500 - 6,700) | 5,900 (4,800 - 7,100) | 5,200 (4,400 - 6,300) | < 0.001 |
| CRP, mg/dL | 0.06 (0.03 - 0.12) | 0.07 (0.04 - 0.16) | 0.05 (0.03 - 0.10) | 0.003 |
| Variables | All (n = 483) | ASCVD (n = 195) | Non-ASCVD (n = 288) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P value shows the comparison with ASCVD vs. non-ASCVD. ASCVD: atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; ARB: angiotensin II receptor blocker; ACE-I: angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; CCB: calcium channel blocker; EPA: eicosapentaenoic acid; DPP-4I: dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor. | ||||
| Anti-hypertension | ||||
| ARB/ACE-I, n (%) | 237 (49) | 125 (64) | 112 (39) | < 0.001 |
| CCB, n (%) | 233 (48) | 114 (59) | 119 (41) | < 0.001 |
| Beta-blocker, n (%) | 61 (13) | 35 (18) | 26 (9) | 0.004 |
| Others, n (%) | 74 (15) | 40 (21) | 34 (12) | 0.01 |
| Anti-diabetes | ||||
| DPP-4I, n (%) | 77 (16) | 40 (21) | 37 (13) | 0.02 |
| Others, n (%) | 60 (12) | 34 (17) | 26 (9) | 0.006 |
| Anti-dyslipidemia | ||||
| Statin, n (%) | 239 (50) | 128 (66) | 111 (39) | < 0.001 |
| EPA, n (%) | 57 (12) | 35 (18) | 22 (8) | < 0.001 |
| Others, n (%) | 29 (6) | 12 (6) | 17 (6) | 0.9 |