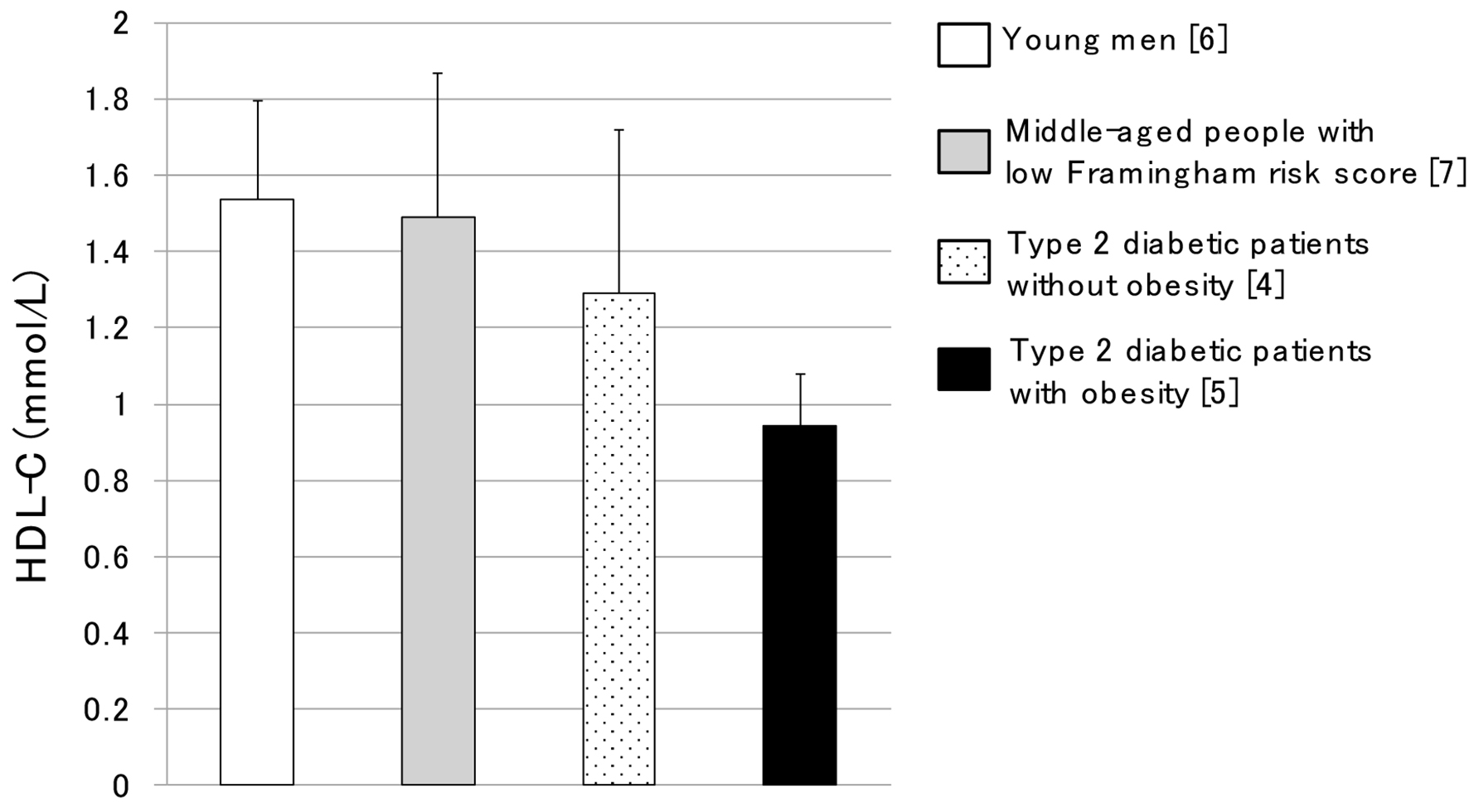
Figure 1. Serum HDL-C levels in young men, middle-aged people with low Framingham risk score, type 2 diabetic patients without obesity and type 2 diabetic patients with obesity. This figure was made by modification of data in our previous report [3].
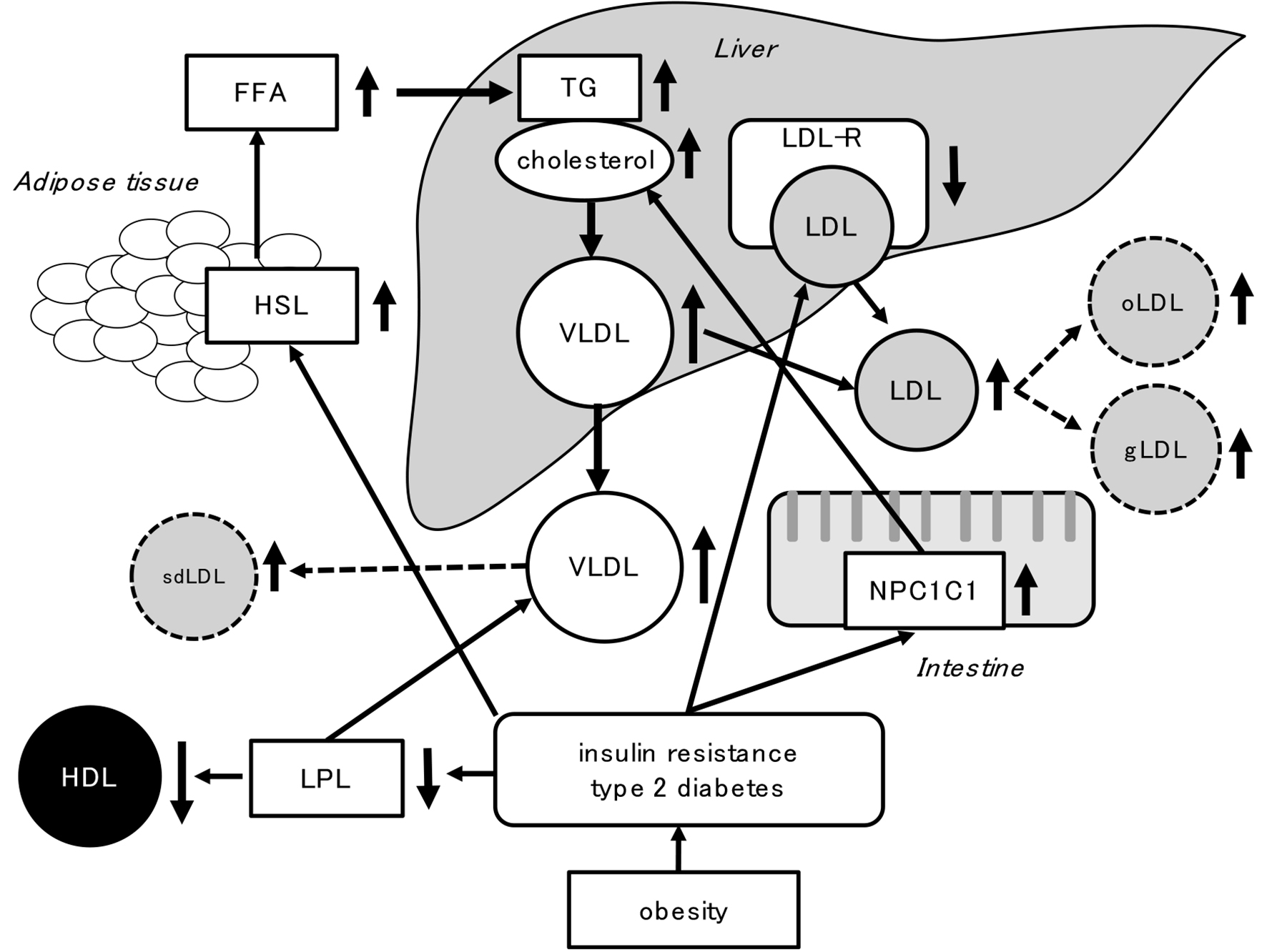
Figure 2. Abnormal lipid metabolism induced by obesity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. FFA: free fatty acid; gLDL: glycated LDL: HSL: hormone-sensitive lipase; LDL-R: LDL-receptor; LPL: lipoprotein lipase; NPC1L1: Niemann-Pick C1-like 1; oLDL: oxidized LDL; sdLDL: small dense LDL; VLDL: very low-density lipoprotein.

