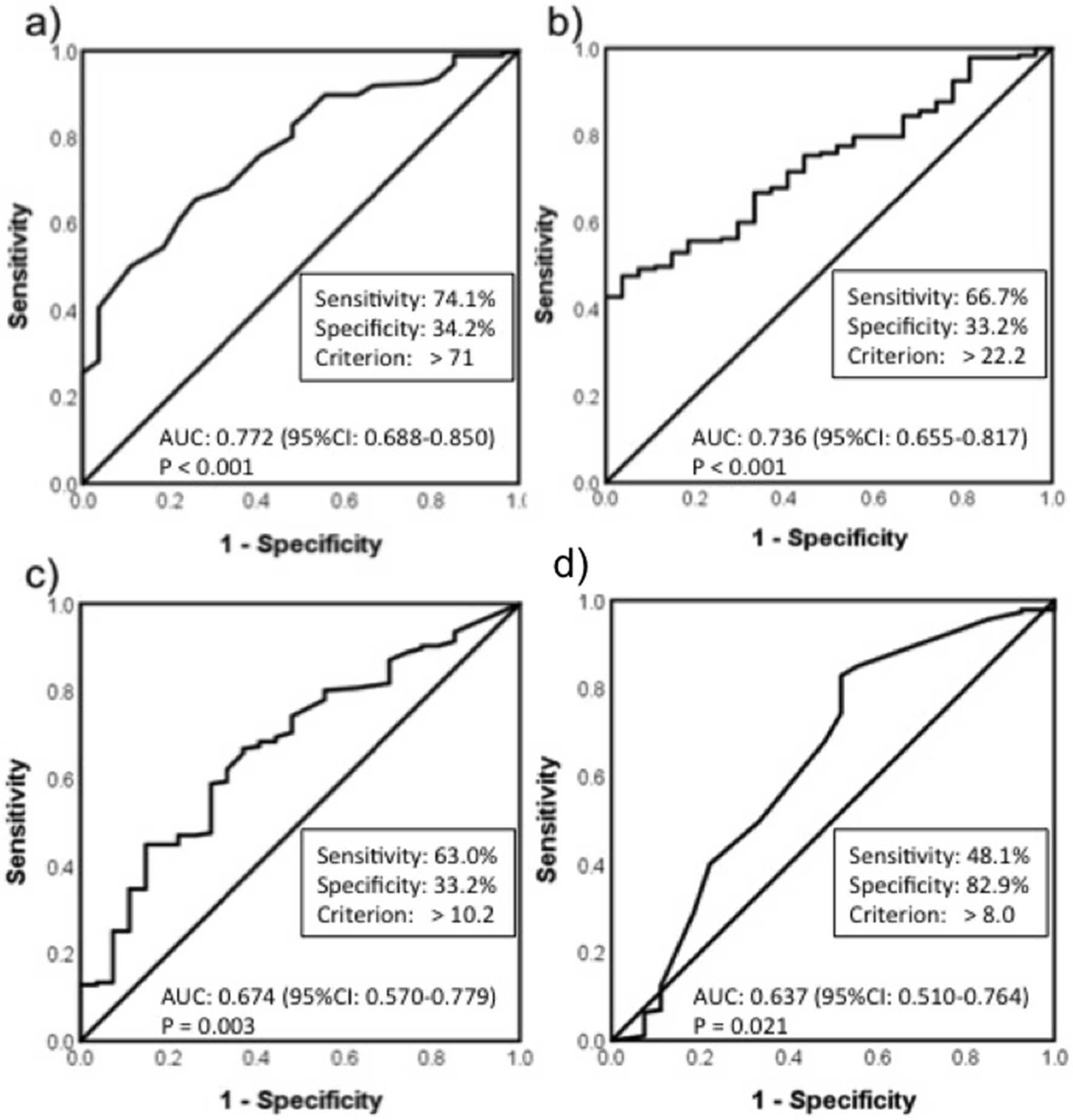
Figure 1. ROC analysis. (a) age; (b) body mass index; (c) physical activity; (d) total time of sitting and lying on the day. AUC: area under the curve; CI: confidence interval; BMI: body mass index.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 10, Number 12, December 2018, pages 920-927
Relationship Between Sarcopenia and Both Physical Activity and Lifestyle in Patients With Chronic Liver Disease
Figure

Tables
| All patients (n = 214) | Sarcopenia (n = 27) | Non-sarcopenia (n = 187) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data were expressed as means ± standard deviation or as median (interquartile range) or as n (%). P < 0.05 was considered significant. Categorical variables were compared by Fisher’s exact test and continuous variables were compared by Student’s t-tests or Mann-Whitney U test. BMI, body mass index. | ||||
| Age (years) | 68.17 ± 11.17 | 76.48 ± 6.69 | 66.97 ± 11.19 | < 0.01 |
| Sex, male (%) | 122 (57%) | 13 (48.1%) | 109 (58.3%) | 0.41 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.4 ± 3.7 | 20.8 ± 2.4 | 23.8 ± 3.7 | < 0.01 |
| Etiology of liver disease (%) | < 0.01 | |||
| Hepatitis B | 54 (25.2%) | 1 (3.7%) | 54 (29%) | |
| Hepatitis C | 78 (36.4%) | 12 (44.4%) | 68 (36%) | |
| Alcoholic hepatitis | 25 (11.7%) | 6 (22.2%) | 19 (10.2%) | |
| Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis | 28 (13.1%) | 2 (7.4%) | 26 (13.9%) | |
| Autoimmune hepatitis | 1 (0.5%) | 0 | 1 (0.5%) | |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis | 6 (2.8%) | 0 | 6 (3.2%) | |
| Others | 22 (10.3%) | 6 (22.2%) | 16 (8.6%) | |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma, yes (%) | 55 (25.7%) | 10 (37%) | 45 (24.1%) | 0.16 |
| ALBI-grade (%) | 0.03 | |||
| 1 | 168 (78.5%) | 16 (64%) | 152 (81.3%) | |
| 2 | 45 (21%) | 9 (36%) | 34 (18.2%) | |
| 3 | 1 (0.5%) | 0 | 1 (0.5%) | |
| Branched chain amino acids, yes (%) | 84 (39.3%) | 15 (60%) | 72 (38%) | 0.09 |
| Physical activity (METs-h/week) | 15.55 (6.6 - 34.46) | 6.6 (2.34 - 19.90) | 16.50 (6.6 - 41.23) | < 0.01 |
| Total time sitting and lying (h/day) | 5.90 ± 3.34 | 7.43 ± 4.09 | 5.68 ± 3.17 | 0.01 |
| Living alone, yes (%) | 40 (18.7%) | 7 (25.9%) | 33 (17.6%) | 0.29 |
| Currently smoking, yes (%) | 35 (16.4%) | 1 (3.7%) | 34 (18.2%) | 0.09 |
| Currently drinking, yes (%) | 43 (20.1%) | 5 (18.5%) | 38 (20.3%) | > 0.99 |
| Driving of cars (%) | 172 (80.4%) | 17 (63.0%) | 155 (82.9%) | 0.02 |
| Employment status, retired (%) | 112 (52.3%) | 22 (81.5%) | 90 (48.1%) | < 0.01 |
| Do home tasks, yes (%) | 121 (56.5%) | 20 (74.1%) | 101 (54%) | 0.06 |
| Healthy eating, yes (%) | 185 (86.4%) | 25 (92.6%) | 160 (85.6%) | 0.54 |
| Exercise habits, yes (%) | 151 (70.6%) | 19 (70.4%) | 132 (70.6%) | > 0.99 |
| Variable | Sarcopenia (n = 27) | Non-sarcopenia (n = 187) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data were expressed as median (interquartile range) or as n (%). P < 0.05 was considered significant. Categorical variables were compared by Fisher’s exact test and continuous variables were compared by Mann-Whitney U test. Alb: serum albumin; ALP: alkaline phosphatase; ALT: alanine transaminase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; CK: creatine kinase; Cre: creatinine; ChE: cholinesterase; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; Hb: hemoglobin; HbA1c: hemogobinA1c; AFP: α-fetoprotein; K: potassium; Na: sodium; PT-INR: prothrombin time-international normalized ratio; T-bil: total bilirubin; T-cho: total cholesterol; TP: total protein; TG: triglyceride; RBC: red blood cell count; WBC: white blood cell count; TLC: total lymphocyte count; Plt: platelet count; CONUT-score: controlling nutritional status index score; Fib4-index: fibrosis 4 index. | |||
| Alb (g/dL) | 3.9 (3.4 - 4.3) | 4.2 (4.0 - 4.45) | < 0.01 |
| ALP (U/L) | 254.0 (197.5 - 353.5) | 245.0 (197.0 - 323.8) | 0.68 |
| ALT (U/L) | 13.0 (10.5 - 18.0) | 18.0 (14.0 - 26.0) | 0.01 |
| AST (U/L) | 23.0 (18.5 - 36.0) | 26.0 (22.0 - 32.0) | 0.38 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 17.2 (13.4 - 22.1) | 15.1 (13.0 - 17.3) | 0.05 |
| CK (U/L) | 88.0 (59.0 - 109.50) | 102.5 (77.0 - 159.5) | 0.01 |
| Cre (mg/dL) | 0.72 (0.51 - 0.92) | 0.72 (0.59 - 0.82) | 0.92 |
| ChE (U/L) | 228.0 (173.0 - 301.5) | 289.5 (244.0 - 356.8) | < 0.01 |
| eGFR (mL/m/1.73 m2) | 68.8 (59.0 - 87.1) | 74.8 (66.3 - 86.6) | 0.23 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 12.4 (11.2 - 13.4) | 13.5 (12.6 - 14.7) | < 0.01 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.8 (5.4 - 6.3) | 5.80 (5.5 - 6.2) | 0.79 |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 3.30 (2.3 - 4.3) | 3.10 (2.1 - 4.7) | 0.62 |
| K (mmol) | 4.1 (3.9 - 4.4) | 4.09 (4.0 - 4.3) | 0.56 |
| Na (mmol) | 141.0 (138.5 - 142.0) | 140.00 (139.00 - 142.00) | 0.49 |
| PT-INR | 1.02 (0.97 - 1.05) | 1.00 (0.97 - 1.05) | 0.87 |
| T-bil (mg/dL) | 0.52 (0.42 - 0.71) | 0.65 (0.49 - 0.80) | 0.02 |
| T-cho (mg/dL) | 181.0 (167.5 - 203.0) | 174.0 (157.5 - 199.0) | 0.26 |
| TP (g/dL) | 7.5 (6.9 - 7.7) | 7.4 (7.1 - 7.7) | 0.94 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 102.0 (76.5 - 141.5) | 90.5 (65.0 - 130.5) | 0.36 |
| RBC (× 104/µL) | 400.0 (371.5 - 437.5) | 437.0 (405.0 - 477.5) | < 0.01 |
| WBC (× 102/µL) | 54.0 (40.0 - 64.0) | 53.0 (42.0 - 64. 0) | 0.67 |
| TLC | 1,361.1 (930.6 - 1,626.1) | 1,522.80 (1,160.8 - 2,136.70) | < 0.01 |
| Plt (× 104) | 18.10 (11.7 - 21.3) | 19.30 (15.9 - 24.2) | 0.11 |
| CONUT-score | 2.0 (1.5 - 4.0) | 1.0 (1.0 - 2.5) | 0.02 |
| CONUT-grade | 0.01 | ||
| Normal | 7 (25.9%) | 99 (52.9%) | |
| Light | 16 (59.3%) | 80 (42.8%) | |
| Moderate | 4 (14.8%) | 7 (3.7%) | |
| Severe malnutrition | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.5%) | |
| Fib4-index | 2.7 (2.0 - 4.9) | 2.1 (1.6 - 3.0) | < 0.01 |
| Variable | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | P value | OR | 95% CI | P value | |
| Data were analyzed by logistic regression analysis model. OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval; BMI: body mass index. | ||||||
| Age (≥ 71/< 71 years) | 5.42 | 2.00 - 17.22 | < 0.01 | 5.89 | 2.15 - 16.20 | < 0.01 |
| Employment status (retired/employed) | 4.22 | 1.52 - 11.70 | < 0.01 | |||
| BMI (< 22.2/≥ 22.2) | 3.91 | 1.56 - 1048 | < 0.01 | 4.77 | 1.87 - 12.10 | < 0.01 |
| Low frequency of driving (yes/no) | 2.83 | 1.06 - 7.28 | 0.02 | |||
| Physical activity (< 10.2/≥ 10.2) | 3.40 | 1.38 - 8.85. | < 0.01 | 3.65 | 2.15 - 16.20 | < 0.01 |
| Total time sitting and lying (≥ 8/< 8) | 2.67 | 1.07 - 6.63 | 0.02 | |||