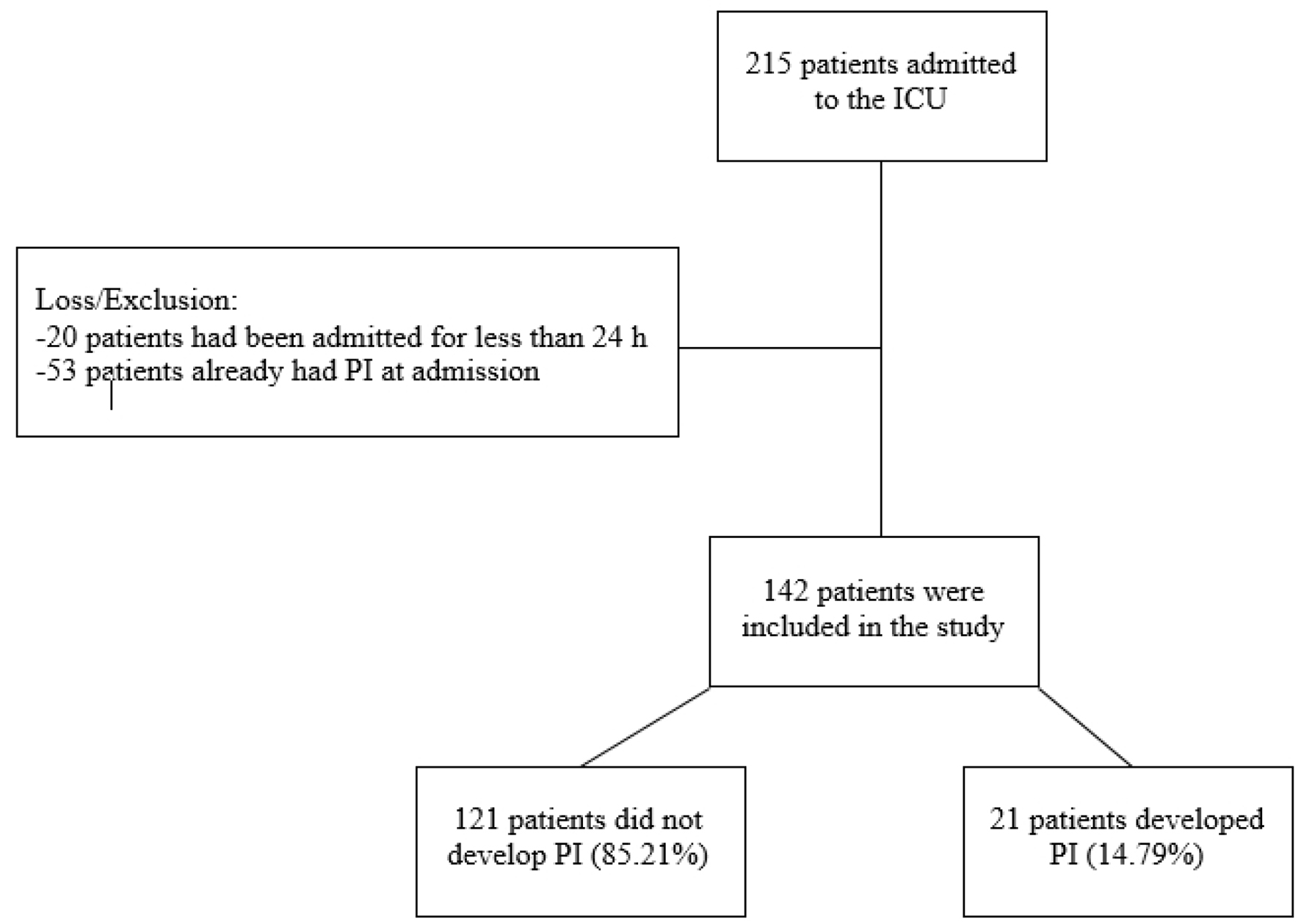
Figure 1. Study screening process.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 10, Number 12, December 2018, pages 898-903
APACHE II Death Risk and Length of Stay in the ICU Are Associated With Pressure Injury in Critically Ill Patients
Figure

Tables
| Variables | Patients without PI (n = 121) | Patients with PI (n = 21) | P value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| PI: pressure injury; P value: univariate analysis by Fisher’s exact test. | |||||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 61 | 52 | 13 | 62 | 0.23 |
| Female | 60 | 48 | 8 | 38 | |
| Reason for ICU admission | |||||
| Clinical | 82 | 68 | 18 | 86 | 0.07 |
| Surgical | 39 | 32 | 3 | 14 | |
| Variables | Patients without PI | Patients with PI | P value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | (min - max) | Median | (min - max) | ||
| LOS: length of stay in the ICU; PI: pressure injury; P value: univariate analysis by Wilcoxon test. | |||||
| Age (years) | 58 | 18 - 101 | 62 | 21 - 86 | 0.09 |
| Braden scale risk score (per point increase) | 13 | 8 - 20 | 10 | 8 - 14 | 0.0003 |
| APACHE II death risk (%) | 39 | 2 - 97 | 75 | 26 - 96 | < 0.0001 |
| LOS (days) | 4 | 2 - 36 | 16 | 5 - 29 | < 0.0001 |
| Variable | Odds ratio (OR) | Confidence interval (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOS: length of stay in the ICU. | |||
| Age | 1.02 | 0.98 - 1.06 | 0.34 |
| Braden scale risk score (per point increase) | 0.84 | 0.61 - 1.14 | 0.26 |
| Reason for ICU admission | 0.22 | 0.03 - 1.79 | 0.16 |
| APACHE II death risk (%) | 1.05 | 1.01 - 1.09 | 0.008 |
| LOS (days) | 1.25 | 1.12 - 1.39 | 0.000 |