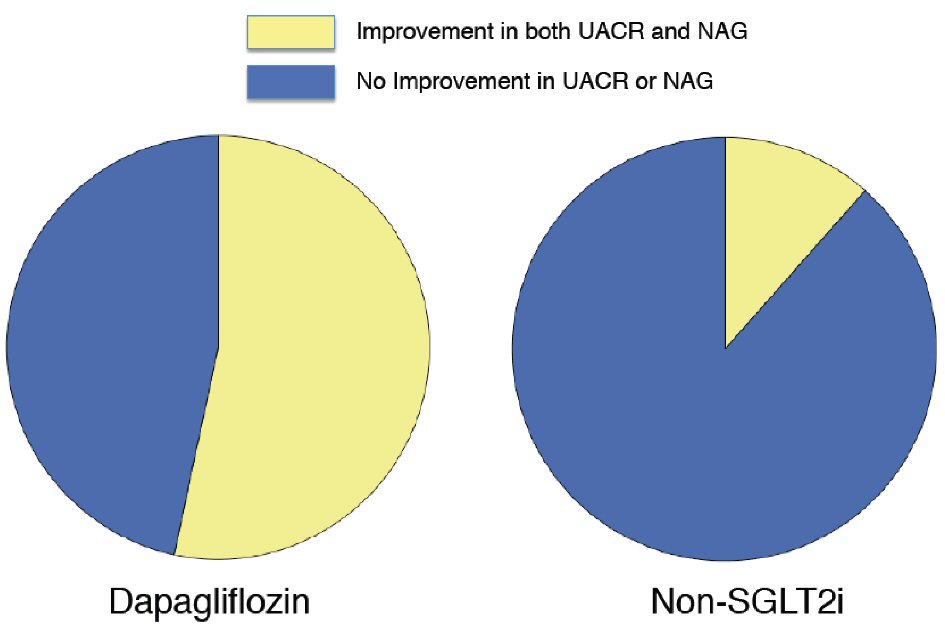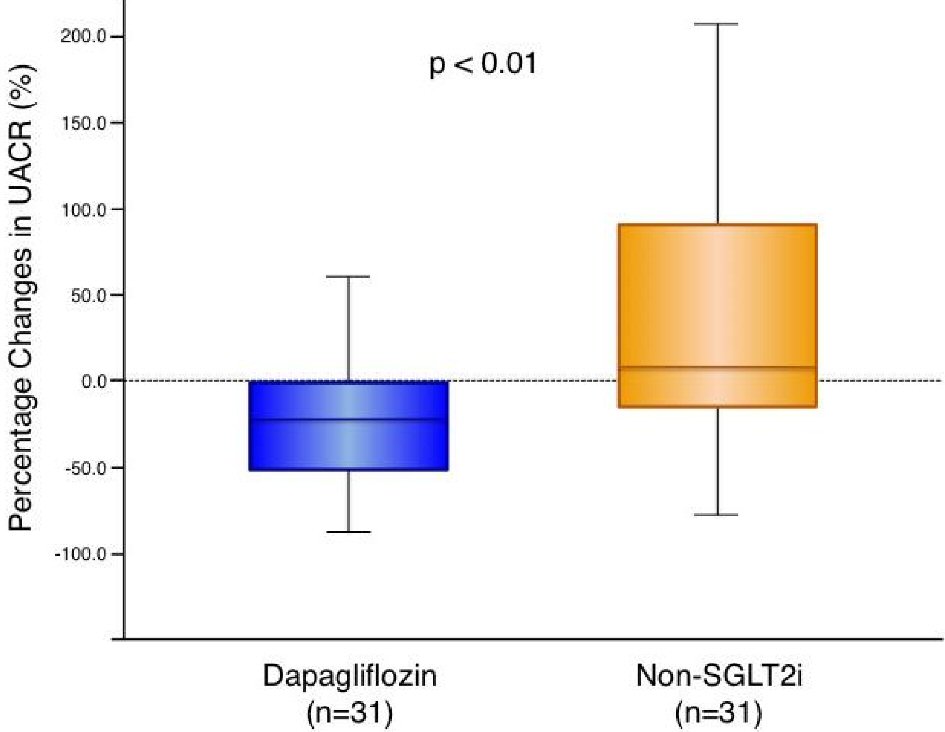
Figure 1. Change in urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio with dapagliflozin therapy and non-SGLT2 inhibitor therapy. Dapagliflozin (n = 31): -21.2 (-52.5 to -1.1) % vs. non-SGLT2i (n = 31): 7.8 (-18.4 to 91.3) %, P = 0.004. Box-and-whisker plots indicate the percentage changes in urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) in patients with dapagliflozin therapy (n = 31) or non-sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor therapy (n = 31). In the box-and-whisker plots, lines within boxes represent median values; the top and bottom edges of the boxes represent the 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively; the top and bottom bars outside the boxes represent the 10th and 90th percentiles, respectively. Percentage change in UACR = ((UACR after 6 months of therapy) – (UACR at enrollment)) × 100/(UACR at enrollment). Notably, upon inter-group comparison, the percentage changes in UACR in patients with dapagliflozin therapy were significantly greater than those in the patients with non-SGLT2 inhibitor therapy.