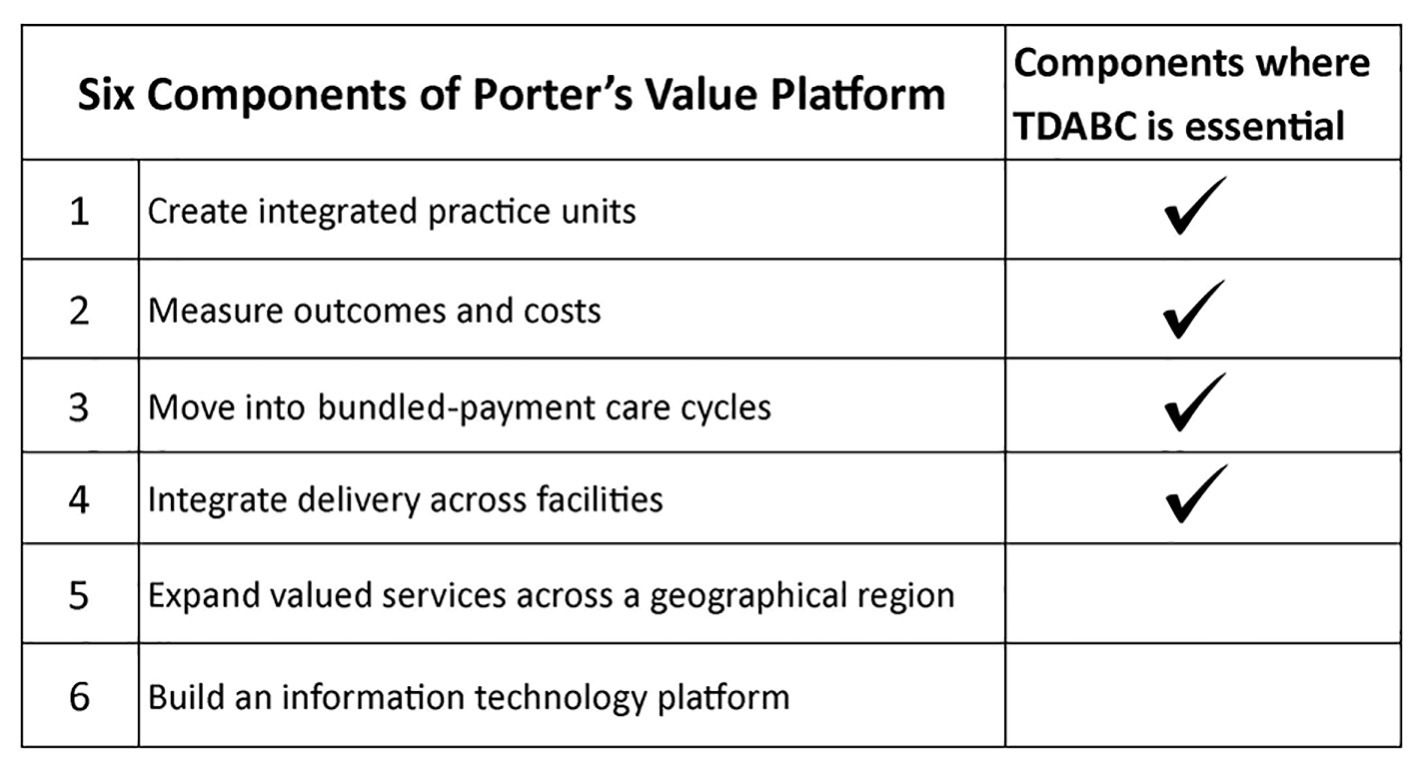
Figure 1. The six components of Michael Porter’s value platform delivered at the American Society of Anesthesiologists Annual Meeting in 2016. TDABC is essential to creating integrated practice units, measuring costs and outcomes, moving into bundled payment care cycles and integrating delivery across facilities. TDABC: time-driven activity-based costing.
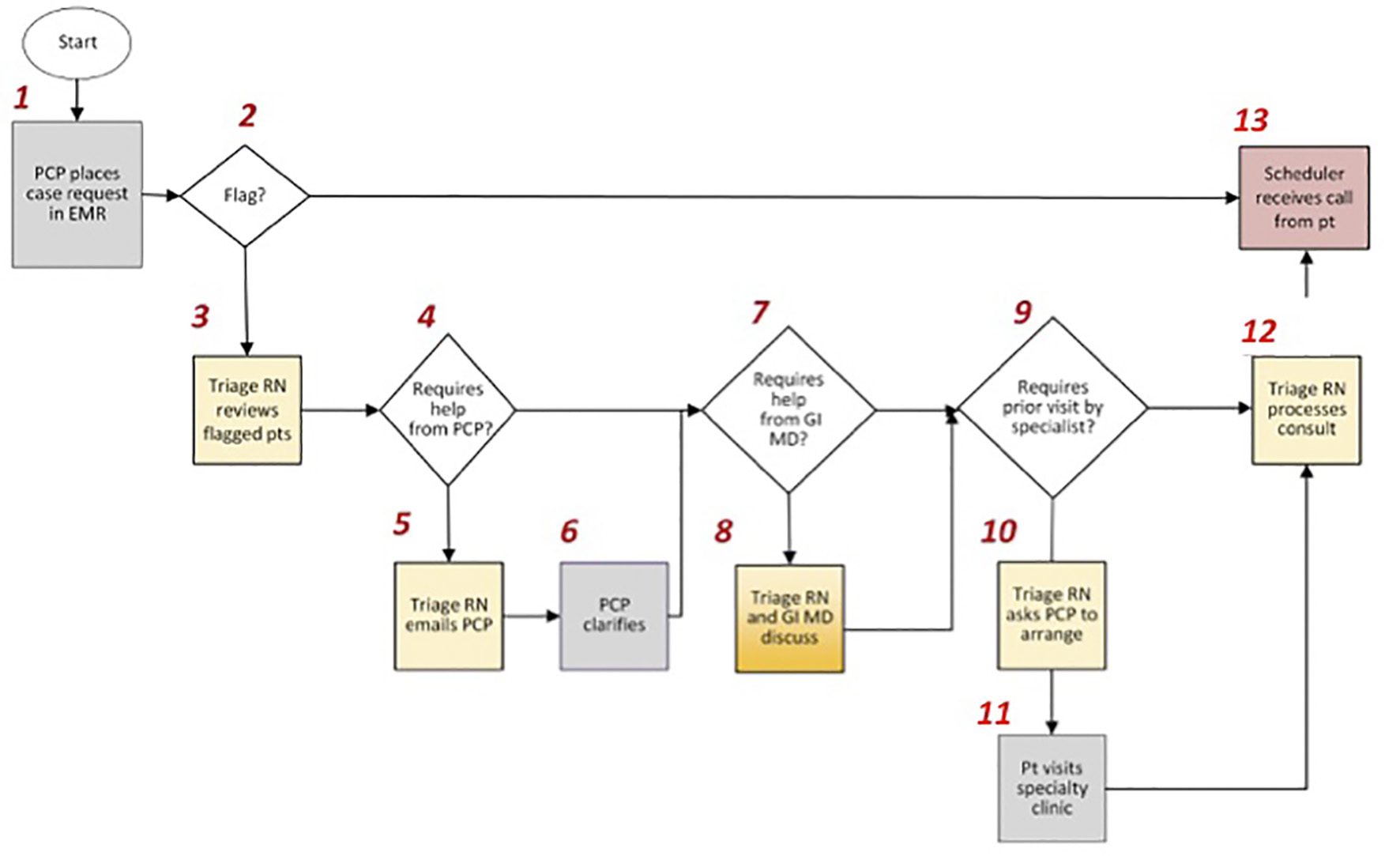
Figure 2. Referral process for patients requiring a gastroenterology procedure at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. After a request is made by the patient’s primary care provider, it is determined whether or not the patient’s medical history includes any of the following flag criteria: anticoagulation, pacemaker or defibrillator, cardiac disease, supplemental oxygen, obstructive sleep apnea, body mass index > 40, renal disease, insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, difficulty with sedation, airway issues, and chronic opioid use. Those patients not meeting flag criteria are eligible to bypass the pre-operative evaluation clinic and proceed to scheduling at the ambulatory facility. PCP: primary care provider; EMR: electronic medical record; RN: registered nurse; pts: patients; GI: gastrointestinal; MD: Medical Doctor.

