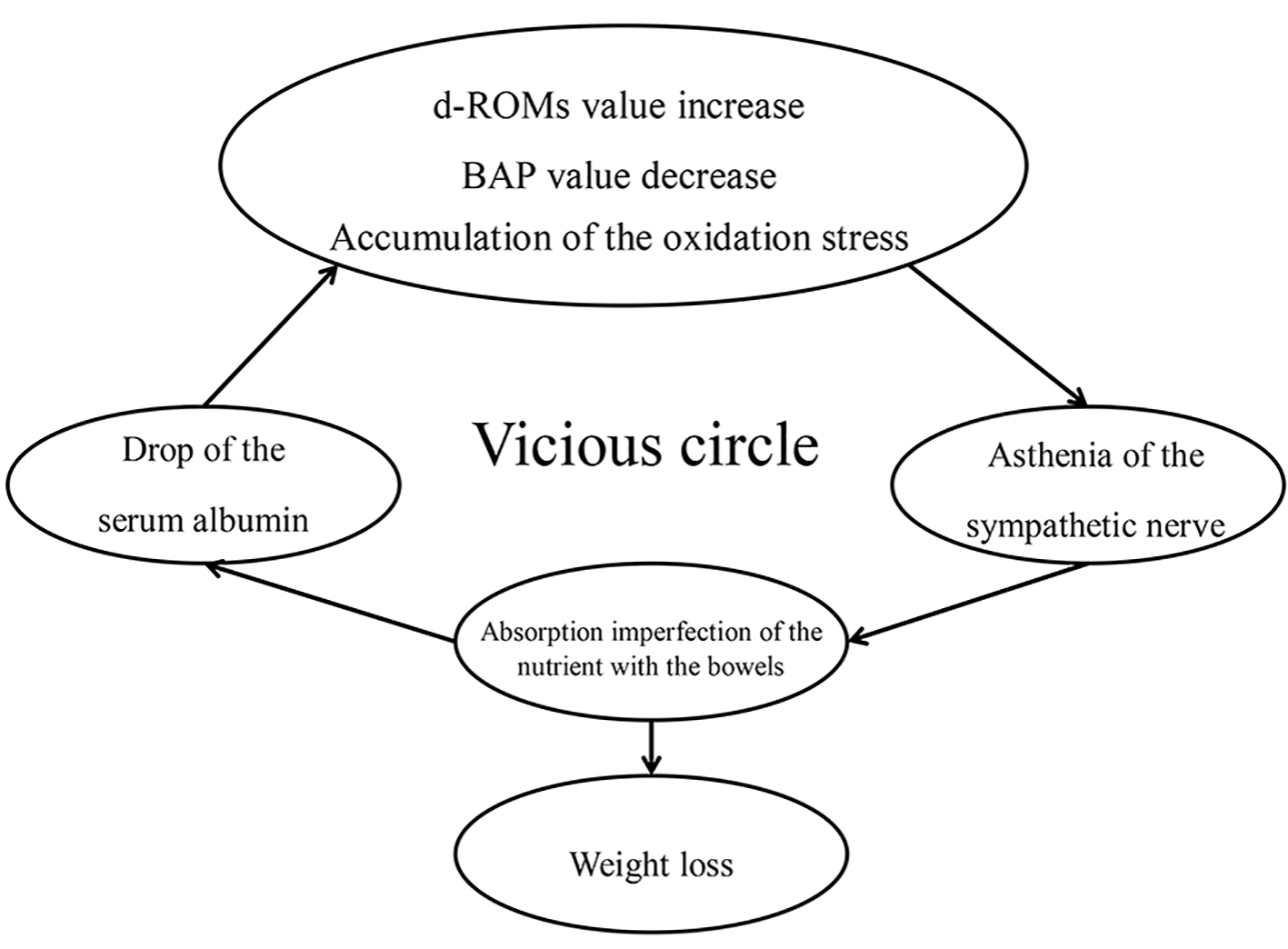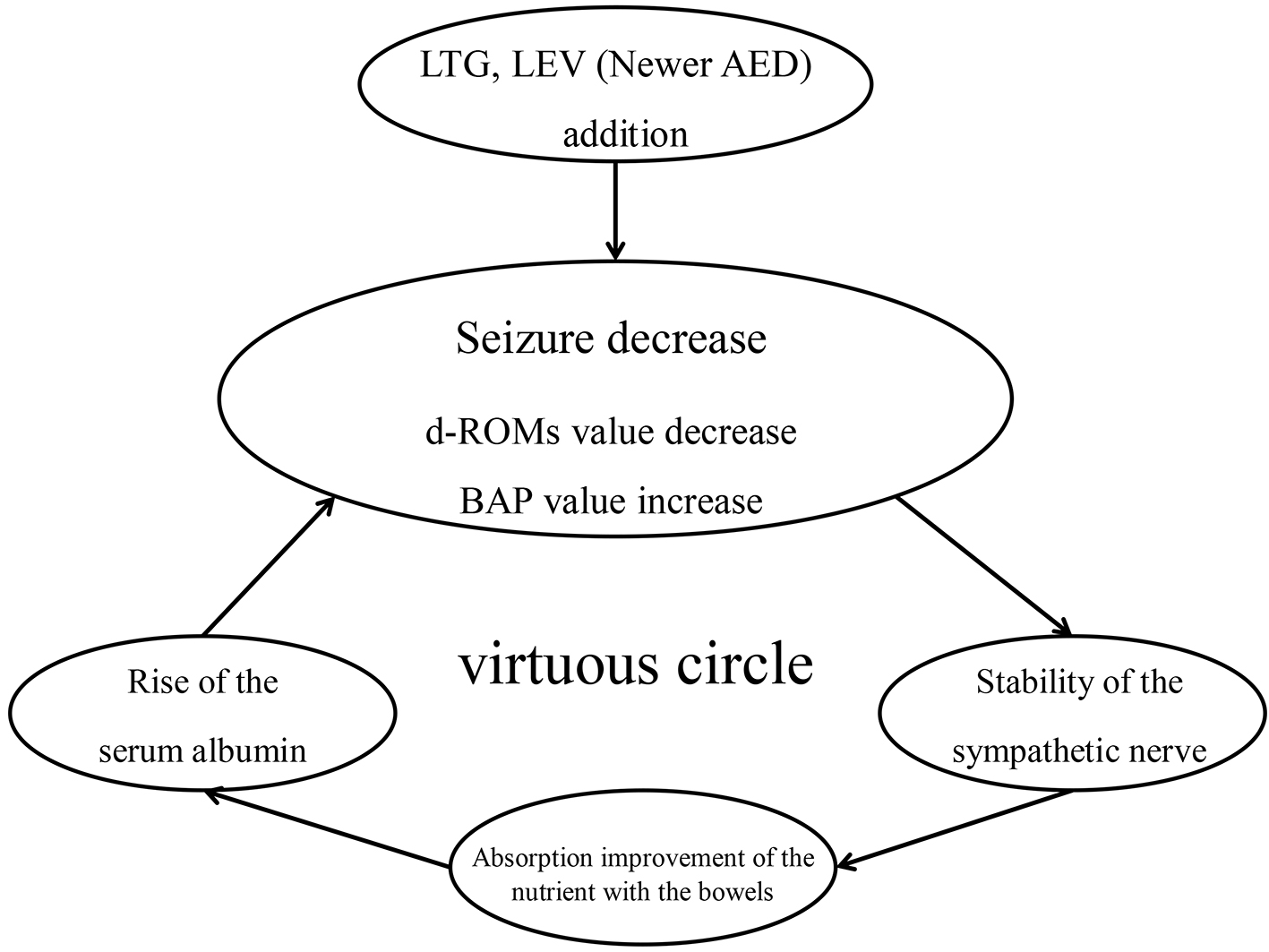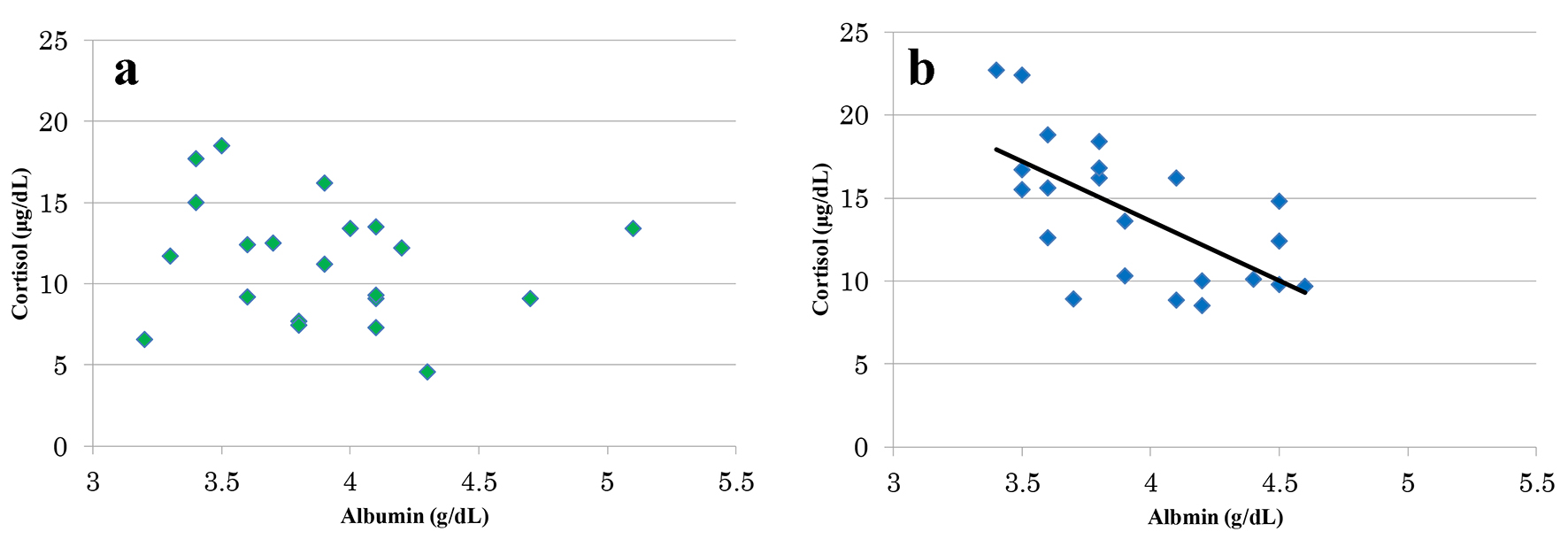
Figure 1. Relations of albumin level and the cortisol level. There was no significant correlation between albumin value and cortisol value in old AED group (r = -0.195, P = 0.39) (a). For the newer AED group, a significant correlation was found between the albumin value and the cortisol value (r = -0.641, P < 0.01) (b).