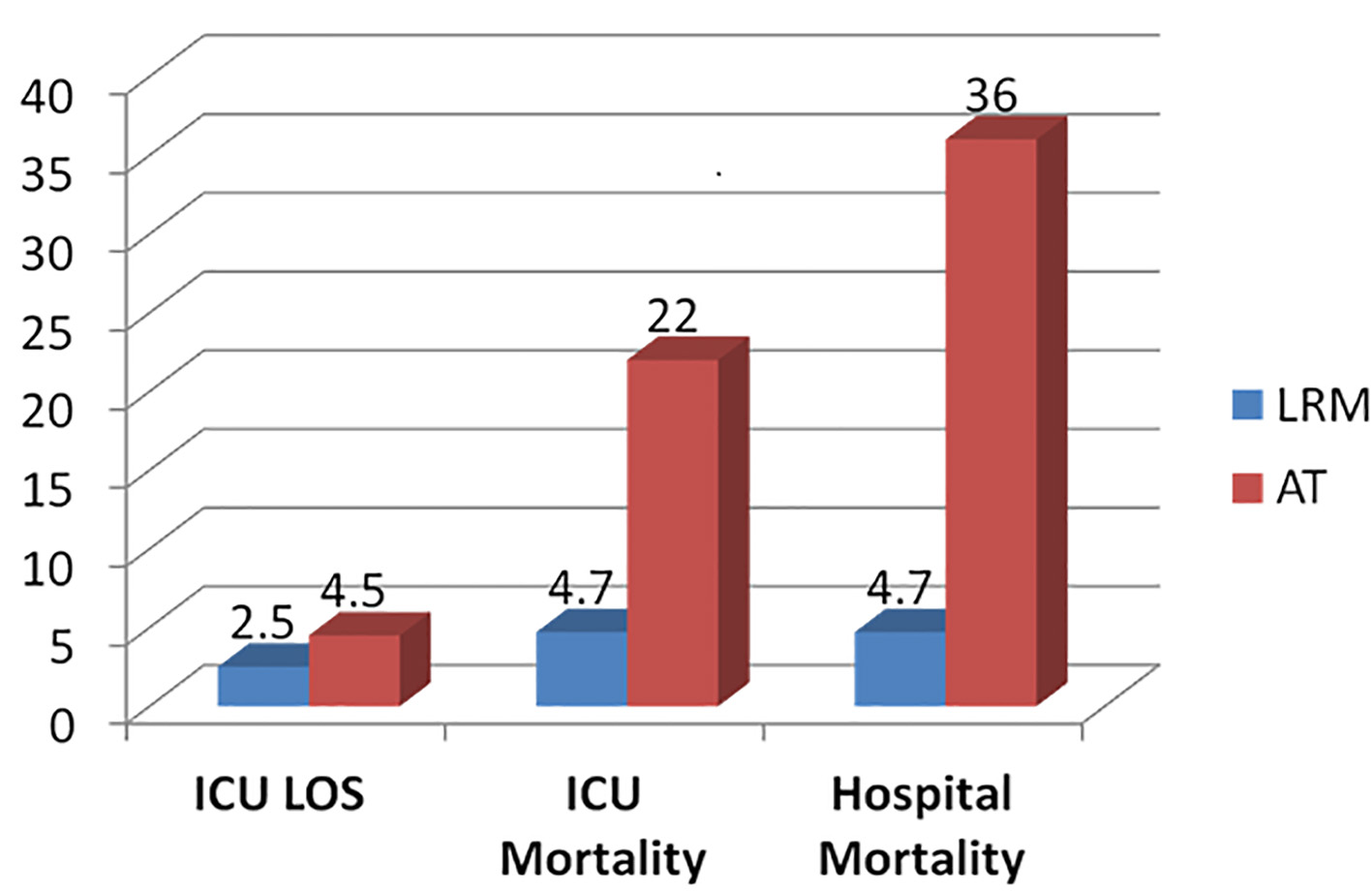
Figure 1. Outcome comparisons between the low risk monitor (LRM) and active treatment (AT) groups.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 10, Number 3, March 2018, pages 174-177
Do All Acute Stroke Patients Receiving tPA Require ICU Admission?
Figure

Tables
| AV pacing | Endoscopies | PA catheter |
|---|---|---|
| AV: atrioventricular; CRRT: continuous renal replacement therapy; ECMO: extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; HFOV: high frequency oscillatory ventilation; IPPV: intermittent positive pressure ventilation; IRRT/HD: intermittent renal replacement therapy/hemodialysis; IV: intravenous; NIPPV (BiPAP): non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (Bilevel positive airway pressure); PA: pulmonary artery; Tx: treatment; VAD: ventricular assist device. | ||
| Barbiturate anesthesia | HFOV | Post-arrest |
| Cardioversion | Induced hypothermia | Prone positioning |
| Continuous antiarrythmic | IABP | Rapid blood transfusion |
| Continuous arterial drug infusion | IPPV | Reintubation within 24 h |
| Continuous neuromuscular blockade | IRRT/HD | Vasoactive drug infusion |
| CRRT | IV replacement excessive fluid loss | Tx of status epilepticus |
| ECMO | IV vasopressin | VAD |
| Emergency procedure inside ICU | Intubation in ICU | Vasoactive > one |
| Emergency procedure outside ICU | NIPPV (BiPAP) | Ventriculostomy |
| Age | Continuous measure plus five spline terms |
|---|---|
| *The APS is a sum of weights assigned to 17 physiologic variables. The weights are determined by the most abnormal value for a measurement within first day in intensive care unit. Variables include pulse rate, mean blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, PaO2/FiO2 ratio (or P(Aa)O2) for intubated patients with FiO2 N.5), hematocrit, white blood cell count, creatinine, urine output, blood urea nitrogen, sodium, albumin, bilirubin, glucose, acid base status, and neurological abnormalities based on Glasgow coma score. | |
| Chronic health variables | Y/N for the following variables: AIDS, hepatic failure, lymphoma, metastatic tumor, immunosuppression, leukemia or myeloma, and cirrhosis. Not used for elective surgery patients. |
| ICU admission source | Floor, emergency room, operating/recovery room, step down unit, direct admission, other ICU, other hospital, other admission source |
| ICU admission diagnosis | 116 categories, leading to 115 indicator variables (“acute myocardial infarction, other location” is the reference category). |
| Length of stay before ICU admission | Square root of time in minutes between hospital admission and ICU admission. This is a continuous measure, and four spline terms are added. |
| Unable to assess Glasgow coma score due to sedation or paralysis | Y/N |
| Emergency surgery | Y/N |
| Mechanical ventilation on first ICU day | Y/N |
| Thrombolytic therapy | Y/N (for patients with acute myocardial infarction) |
| ICU readmission | Y/N |
| Glasgow coma score rescaled | 15 minus measured Glasgow coma score |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio rescaled | |
| APS* | Continuous measure plus five spline terms |
| Active treatment | LRM | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of ICU admissions | 59 | 21 | |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 75 ± 13 | 72 ± 17 | 0.4 |
| APACHE III (mean ± SD) | 62 ± 26 | 41 ± 15 | 0.0008 |
| Pre-tPA-NIHSS (mean ± SD) | 16 ± 9 | 14 ± 8 | 0.4 |
| Hospital mortality, n (%) | 21 (36) | 1 (4.7) | 0.006 |
| ICU mortality, n (%) | 13 (22) | 1 (4.7) | 0.07 |
| ICU LOS (mean days ± SD) | 4.5 ± 4.4 | 2.5 ± 1.3 | 0.04 |