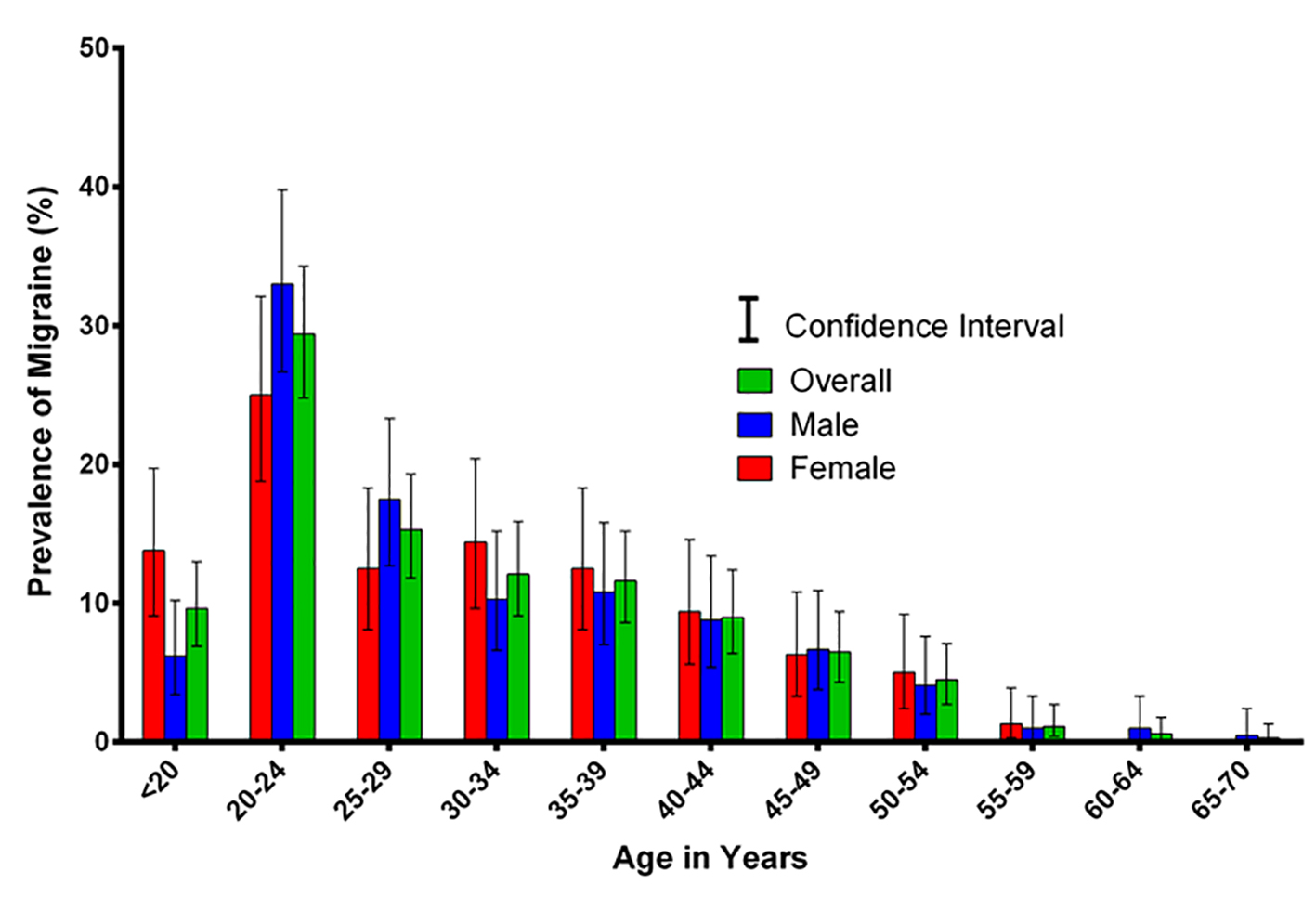
Figure 1. Sex-specific prevalence of migraine with associated CI sorted by age.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 10, Number 2, February 2018, pages 125-133
Prevalence of Migraine Headache in Taif City, Saudi Arabia
Figure

Tables
| Migraine without aura | |
| A. At least five attacks fulfilling criteria B-D. | |
| B. Headache attacks lasting 4 - 72 h (untreated or unsuccessfully treated) | |
| C. Headache has at least two of the following four characteristics: | |
| 1. Unilateral location | |
| 2. Pulsating quality | |
| 3. Moderate or severe pain intensity | |
| 4. Aggravation by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity (e.g., walking or climbing stairs) | |
| D. During headache at least one of the following: | |
| 1. Nausea and/or vomiting | |
| 2. Photophobia and phonophobia | |
| E. Not better accounted for by another ICHD-3 diagnosis. | |
| Migraine with aura | |
| A. At least two attacks fulfilling criteria B and C | |
| B. One or more of the following fully reversible aura symptoms: | |
| 1. Visual | |
| 2. Sensory | |
| 3. Speech and/or language | |
| 4. Motor | |
| 5. Brainstem | |
| 6. Retinal | |
| C. At least two of the following four characteristics: | |
| 1. At least one aura symptom spreads gradually over ≥ 5 min, and/or two or more symptoms occur in succession | |
| 2. Each individual aura symptom lasts 5 - 60 min | |
| 3. At least one aura symptom is unilateral | |
| 4. The aura is accompanied, or followed within 60 min, by headache | |
| D. Not better accounted for by another ICHD-3 diagnosis, and transient ischemic attack has been excluded |
| Diagnosis | Female | Male | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Prevalence (%) | N | Prevalence (%) | |
| Migraineurs with aura | 26 | 16.3 | 13 | 6.7 |
| Migraineurs without aura | 10 | 6.3 | 1 | 0.5 |
| Headachers | 103 | 64.4 | 125 | 64.4 |
| Non-headachers | 21 | 13.1 | 55 | 28.4 |
| Total | 160 | 100.0 | 194 | 100.0 |
| Female | Male | Total | P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| *The Chi-square statistic is significant (P < 0.05). †The Chi-square statistic is significant (P < 0.001). N: number of observations. | |||||||
| Habitat | |||||||
| City | 151 | 94.4% | 167 | 86.1% | 318 | 89.8% | 0.010* |
| Town/village | 9 | 5.6% | 27 | 13.9% | 36 | 10.2% | |
| Marital status | |||||||
| Divorced | 6 | 3.8% | 1 | 0.5% | 7 | 2.0% | 0.056 |
| Married | 74 | 46.3% | 88 | 45.4% | 162 | 45.8% | |
| Single | 78 | 48.8% | 105 | 54.1% | 183 | 51.7% | |
| Widow | 2 | 1.3% | 0 | 0.0% | 2 | 0.6% | |
| Employed | 47 | 29.4% | 95 | 49.0% | 142 | 40.1% | < 0.001† |
| Retired | 2 | 1.3% | 15 | 7.7% | 17 | 4.8% | |
| Employment status | |||||||
| Student “not working” | 53 | 33.1% | 46 | 23.7% | 99 | 28.0% | |
| Student “working” | 10 | 6.3% | 7 | 3.6% | 17 | 4.8% | |
| Unemployed | 48 | 30.0% | 31 | 16.0% | 79 | 22.3% | |
| Education Level | |||||||
| Bachelor’s | 101 | 63.1% | 104 | 53.6% | 205 | 57.9% | 0.232 |
| Diploma | 6 | 3.8% | 11 | 5.7% | 17 | 4.8% | |
| High school/or less | 43 | 26.9% | 69 | 35.6% | 112 | 31.6% | |
| Master | 7 | 4.4% | 9 | 4.6% | 16 | 4.5% | |
| PhD | 3 | 1.9% | 1 | 0.5% | 4 | 1.1% | |
| Smoking tobacco | |||||||
| No | 155 | 96.9% | 123 | 63.4% | 278 | 78.5% | < 0.001† |
| Yes | 5 | 3.1% | 71 | 36.6% | 76 | 21.5% | |
| Female | Male | Total | P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| The Chi-square statistic is significant (P < 0.05). †The Chi-square statistic is significant (P < 0.001). N: number of observations. | |||||||
| Headache | |||||||
| No | 21 | 13.1% | 55 | 28.4% | 76 | 21.5% | 0.002* |
| Yes | 139 | 86.9% | 139 | 71.6% | 278 | 78.5% | |
| Headache frequency | |||||||
| 2 - 4 | 29 | 20.9% | 36 | 25.9% | 65 | 23.4% | < 0.001† |
| Five times and more | 87 | 62.6% | 68 | 48.9% | 155 | 55.8% | |
| Less than 2 times | 23 | 16.5% | 35 | 25.2% | 58 | 20.9% | |
| Headache duration | |||||||
| 1 - 3 days | 25 | 18.0% | 9 | 6.5% | 34 | 12.2% | 0.108 |
| 13 - 24 h | 13 | 9.4% | 7 | 5.0% | 20 | 7.2% | |
| 6 - 4 h | 34 | 24.5% | 31 | 22.3% | 65 | 23.4% | |
| 7 - 12 h | 11 | 7.9% | 9 | 6.5% | 20 | 7.2% | |
| Less than 4 h | 48 | 34.5% | 81 | 58.3% | 129 | 46.4% | |
| More than 3 days | 8 | 5.8% | 2 | 1.4% | 10 | 3.6% | |
| Pain score | |||||||
| 1 - 3 | 20 | 14.4% | 25 | 18.0% | 45 | 16.2% | 0.002* |
| 4 - 6 | 52 | 37.4% | 76 | 54.7% | 128 | 46.0% | |
| 6 - 9 | 45 | 32.4% | 31 | 22.3% | 76 | 27.3% | |
| > 9 | 22 | 15.8% | 7 | 5.0% | 29 | 10.4% | |
| Pain type | |||||||
| Burning pain | 6 | 4.3% | 1 | 0.7% | 7 | 2.5% | 0.001* |
| Pressure pain | 64 | 46.0% | 59 | 42.4% | 123 | 44.2% | |
| Throbbing pain | 69 | 49.6% | 79 | 56.8% | 148 | 53.2% | |
| Examined by a doctor | |||||||
| No | 94 | 67.6% | 102 | 73.4% | 196 | 70.5% | < 0.001† |
| Yes | 45 | 32.4% | 37 | 26.6% | 82 | 29.5% | |
| Investigations done | |||||||
| Blood tests | 10 | 7.2% | 3 | 2.2% | 13 | 4.7% | 0.001* |
| CT | 10 | 7.2% | 6 | 4.3% | 16 | 5.8% | |
| EEG (electroencephalogram) | 4 | 2.9% | 6 | 4.3% | 10 | 3.6% | |
| MRI | 1 | 0.7% | 1 | 0.7% | 2 | 0.7% | |
| MRT | 5 | 3.6% | 0 | 0.0% | 5 | 1.8% | |
| None | 108 | 77.7% | 122 | 87.8% | 230 | 82.7% | |
| X-ray | 1 | 0.7% | 1 | 0.7% | 2 | 0.7% | |
| Headache medications | |||||||
| No | 61 | 43.9% | 57 | 41.0% | 118 | 42.4% | 0.009* |
| Yes | 78 | 56.1% | 82 | 59.0% | 160 | 57.6% | |
| Improvement by medications | |||||||
| Always | 28 | 35.9% | 31 | 37.8% | 59 | 36.9% | 0.003* |
| Never | 1 | 1.3% | 1 | 1.2% | 2 | 1.3% | |
| Sometimes | 49 | 62.8% | 50 | 61.0% | 99 | 61.9% | |
| Female | Male | Total | P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| *The Chi-square statistic is significant (P < 0.05). †The Chi-square statistic is significant (P < 0.001). N: number of observations. | |||||||
| Symptoms before attack | |||||||
| Muscle weakness | 3 | 1.9% | 7 | 3.6% | 10 | 2.8% | 0.002* |
| Nausea | 33 | 20.6% | 21 | 10.8% | 54 | 15.3% | |
| None | 58 | 36.3% | 63 | 32.5% | 121 | 34.2% | |
| Numbness in the skin | 2 | 1.3% | 4 | 2.1% | 6 | 1.7% | |
| Sensitivity to light | 16 | 10.0% | 6 | 3.1% | 22 | 6.2% | |
| Sensitivity to noise | 7 | 4.4% | 9 | 4.6% | 16 | 4.5% | |
| Sight disorders | 15 | 9.4% | 26 | 13.4% | 41 | 11.6% | |
| Speech defects | 2 | 1.3% | 3 | 1.5% | 5 | 1.4% | |
| Vomiting | 2 | 1.3% | 0 | 0.0% | 2 | 0.6% | |
| Symptoms during attack | |||||||
| Nausea | 58 | 36.3% | 21 | 10.8% | 79 | 22.3% | < 0.001† |
| None | 31 | 19.4% | 71 | 36.6% | 102 | 28.8% | |
| Sensitivity to light | 25 | 15.6% | 29 | 14.9% | 54 | 15.3% | |
| Sensitivity to noise | 19 | 11.9% | 17 | 8.8% | 36 | 10.2% | |
| Vomiting | 5 | 3.1% | 1 | 0.5% | 6 | 1.7% | |
| Symptoms after attack | |||||||
| Muscle weakness | 8 | 5.0% | 6 | 3.1% | 14 | 4.0% | 0.108* |
| Nausea | 9 | 5.6% | 10 | 5.2% | 19 | 5.4% | |
| None | 94 | 58.8% | 99 | 51.0% | 193 | 54.5% | |
| Numbness in the skin | 2 | 1.3% | 2 | 1.0% | 4 | 1.1% | |
| Sensitivity to light | 9 | 5.6% | 4 | 2.1% | 13 | 3.7% | |
| Sensitivity to noise | 6 | 3.8% | 6 | 3.1% | 12 | 3.4% | |
| Sight disorders | 5 | 3.1% | 8 | 4.1% | 13 | 3.7% | |
| Speech defects | 3 | 1.9% | 3 | 1.5% | 6 | 1.7% | |
| Vomiting | 2 | 1.3% | 1 | 0.5% | 3 | 0.8% | |
| Knowing the trigger | |||||||
| No | 80 | 50.0% | 87 | 44.8% | 167 | 47.2% | 0.002* |
| Yes | 59 | 36.9% | 52 | 26.8% | 111 | 31.4% | |
| Waking up by pain | |||||||
| Always | 16 | 10.0% | 7 | 3.6% | 23 | 6.5% | 0.001 |
| Never | 63 | 39.4% | 79 | 40.7% | 142 | 40.1% | |
| Sometimes | 59 | 36.9% | 52 | 26.8% | 111 | 31.4% | |
| Family history of headache | |||||||
| No | 42 | 30.2% | 58 | 41.7% | 100 | 36.0% | < 0.001† |
| Yes | 97 | 69.8% | 81 | 58.3% | 178 | 64.0% | |
| Predictors | B | SE | Adjusted OR (95% CI)† | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B: logistic regression coefficient; SE: standard error of logistic regression coefficient; OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval; P: probability value. *Statistically significant (< 0.05). †Adjusted relative odds are odds ratio for migraineur status relative to the reference group (= 1.0) for each covariate, after adjusting for all covariates by logistic regression. | ||||
| Age | -0.03 | 0.02 | 0.97 (0.93 - 1.02) | 0.219 |
| Gender | -1.28 | 0.42 | 0.28 (0.12 - 0.63) | 0.002* |
| Habitat | -0.77 | 0.77 | 0.46 (0.1 - 2.11) | 0.320 |
| Marital status | -0.46 | 0.37 | 0.63 (0.3 - 1.3) | 0.211 |
| Employment status | -0.22 | 0.12 | 0.8 (0.64 - 1.01) | 0.060 |
| Education level | 0.06 | 0.15 | 1.06 (0.79 - 1.42) | 0.694 |
| Smoking tobacco | 0.01 | 0.51 | 1.01 (0.37 - 2.76) | 0.978 |