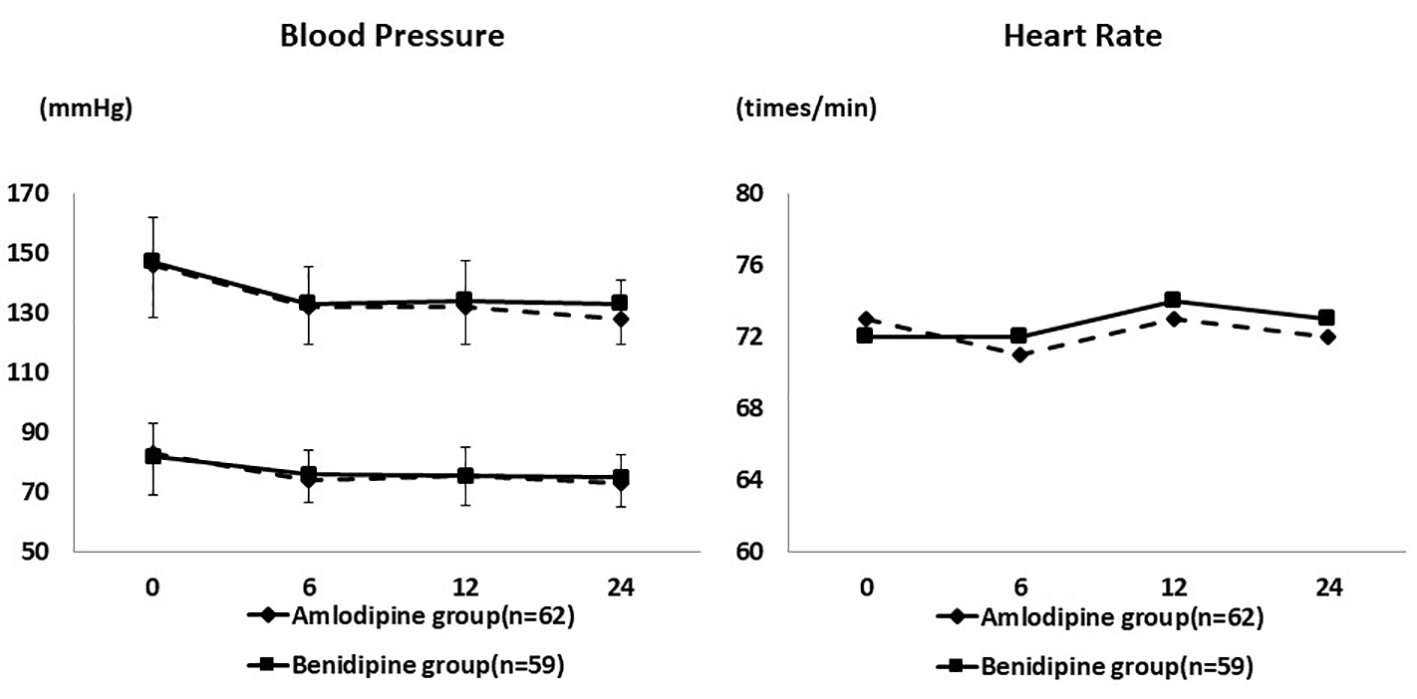
Figure 1. Changes of blood pressure and heart rate during the study period. Systolic and diastolic blood pressure decreased significantly in both groups. The heart rate remained at approximately the same level.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 10, Number 2, February 2018, pages 117-124
Effect of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor/Calcium Antagonist Combination Therapy on Renal Function in Hypertensive Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: Chikushi Anti-Hypertension Trial - Benidipine and Perindopril
Figures

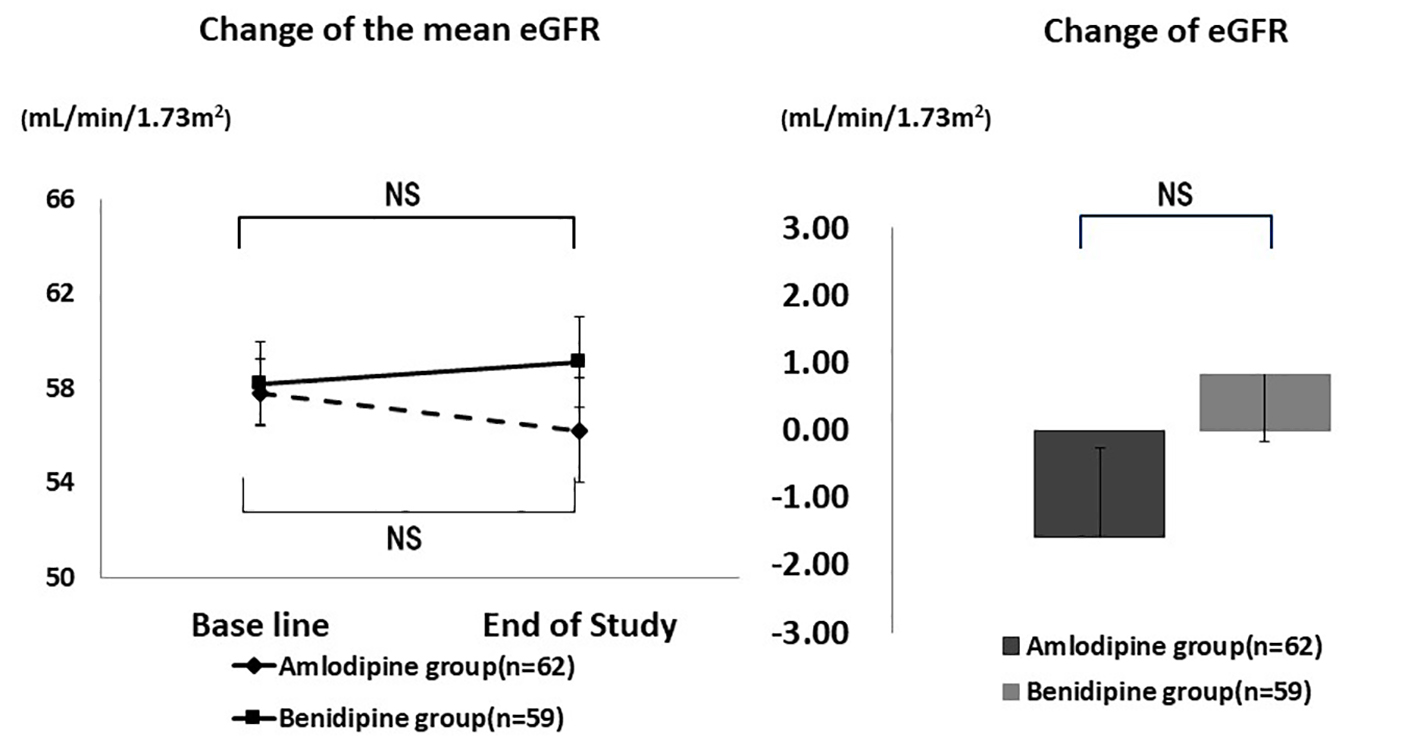
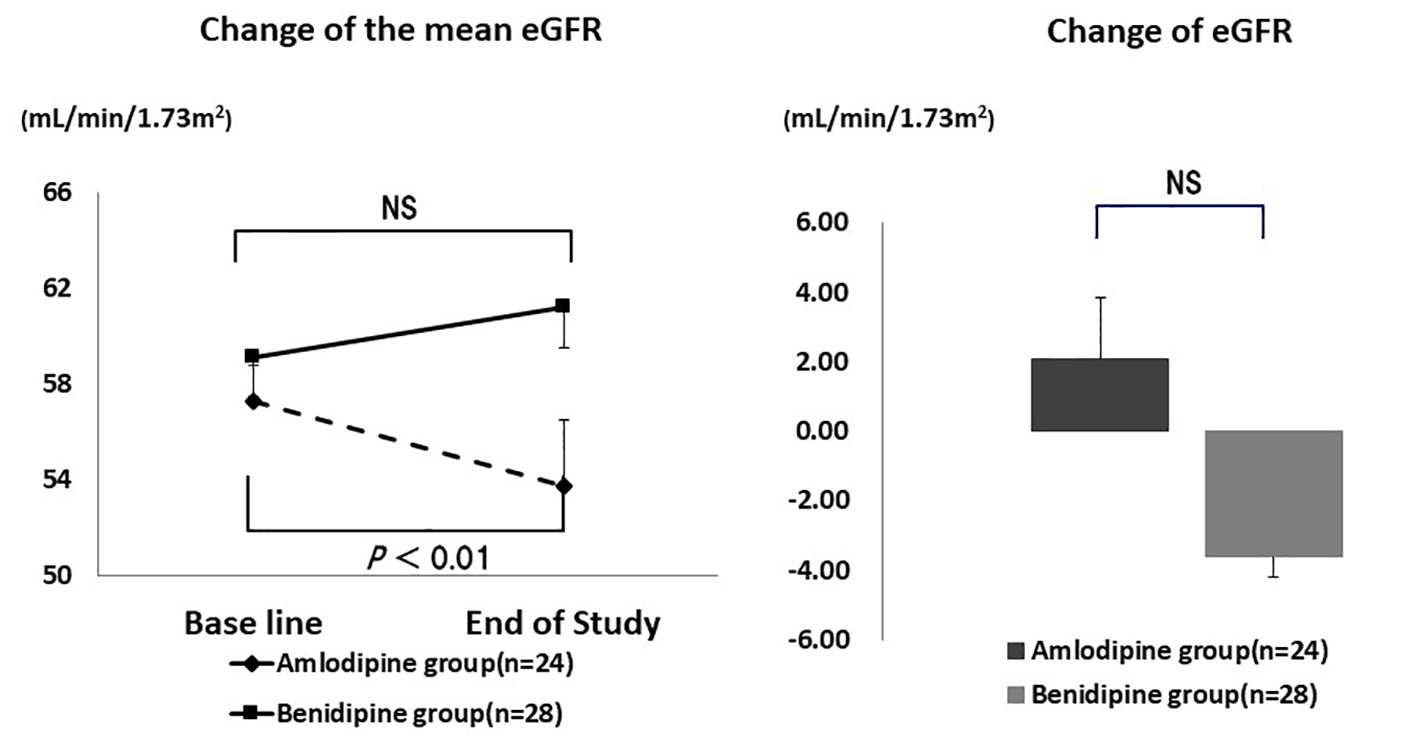
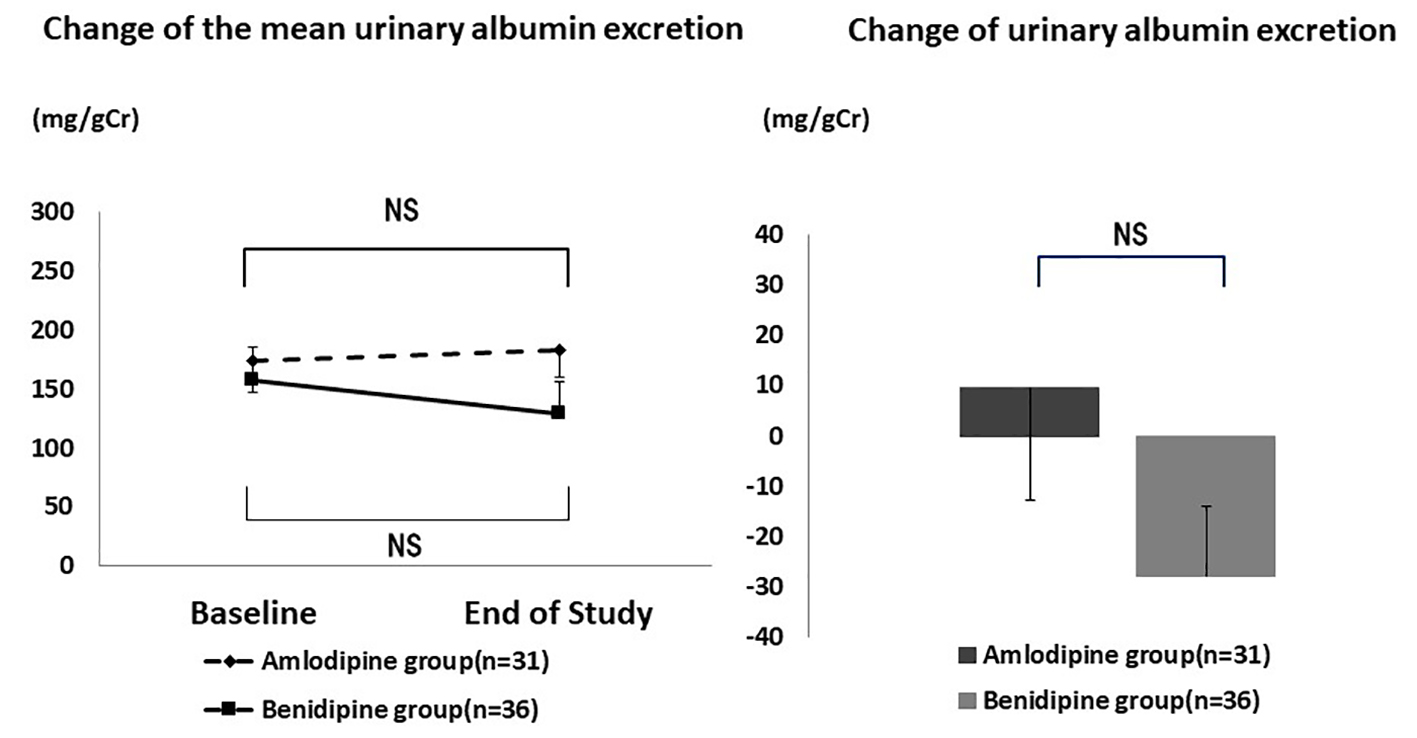
Table
| Amlopidine group (n = 62) | Benidipine group (n = 59) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI: body mass index; Cr: creatinine; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate. | |||
| Gender (male/female) | 38/24 | 37/21 | NS |
| Age (years) | 68.9 ± 10.2 | 69.0 ± 9.1 | NS |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.4 ± 3.7 | 25.2 ± 3.5 | NS |
| Smoking (yes/past/no) | 15/19/28 | 13/15/31 | NS |
| Drinking (yes/no) | 43/37 | 46/30 | NS |
| Perindopril (mg/day) | 4.2 ± 1.2 | 4.2 ± 0.9 | NS |
| Complications (n (%)) | 57 (91) | 54 (91) | NS |
| Diabetes mellitus (n (%)) | 24 (39) | 28 (47) | NS |
| Dyslipidemia (n (%)) | 33 (53) | 31 (52) | NS |
| Hyperuricemia (n (%)) | 16 (25) | 12 (21) | NS |
| Coronary artery disease (n (%)) | 10 (16) | 11 (19) | NS |
| Heart failure (n (%)) | 9 (10) | 14 (16) | NS |
| Cerebrovascular disease (n (%)) | 5 (8) | 4 (7) | NS |
| Renal failure (n (%)) | 2 (3) | 0(0) | NS |