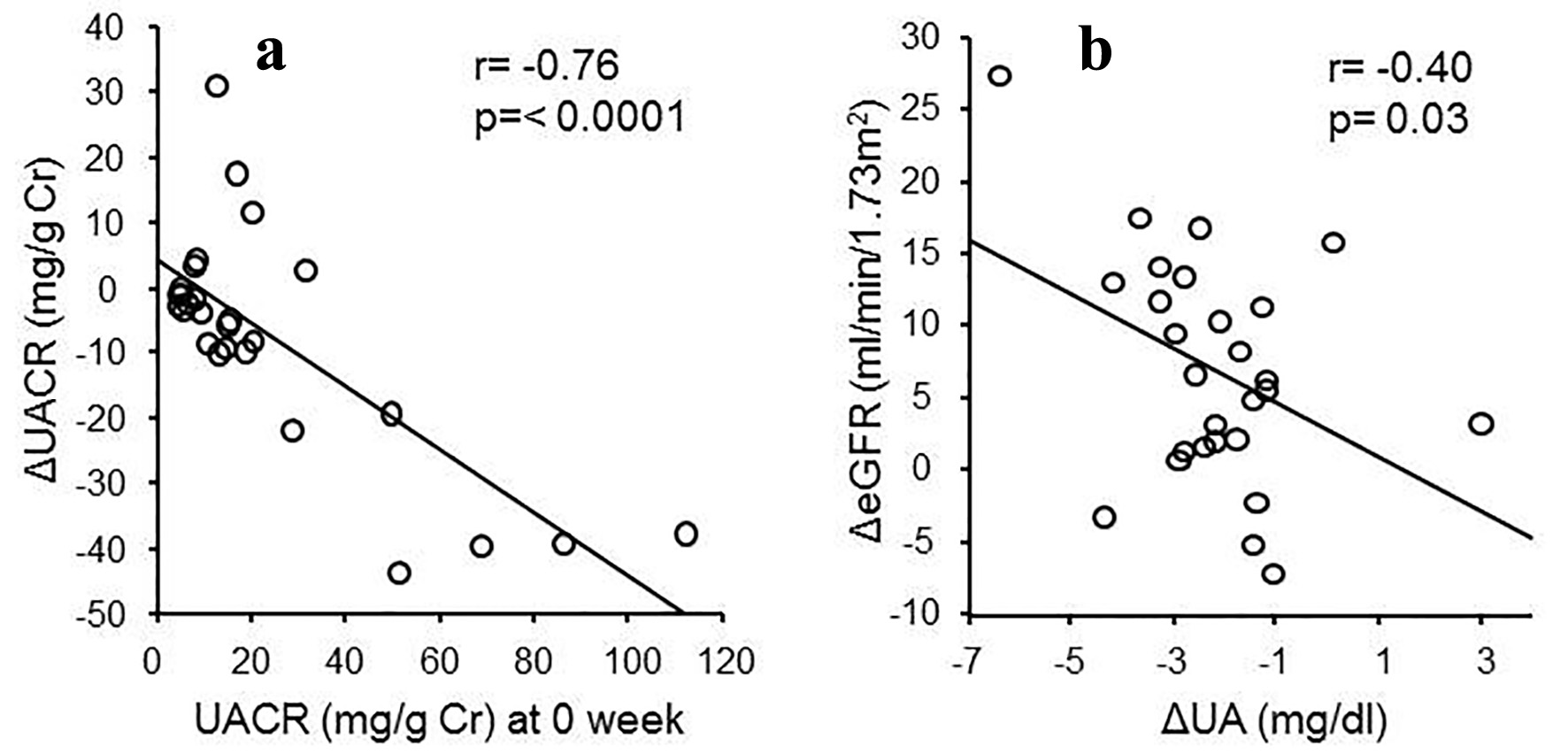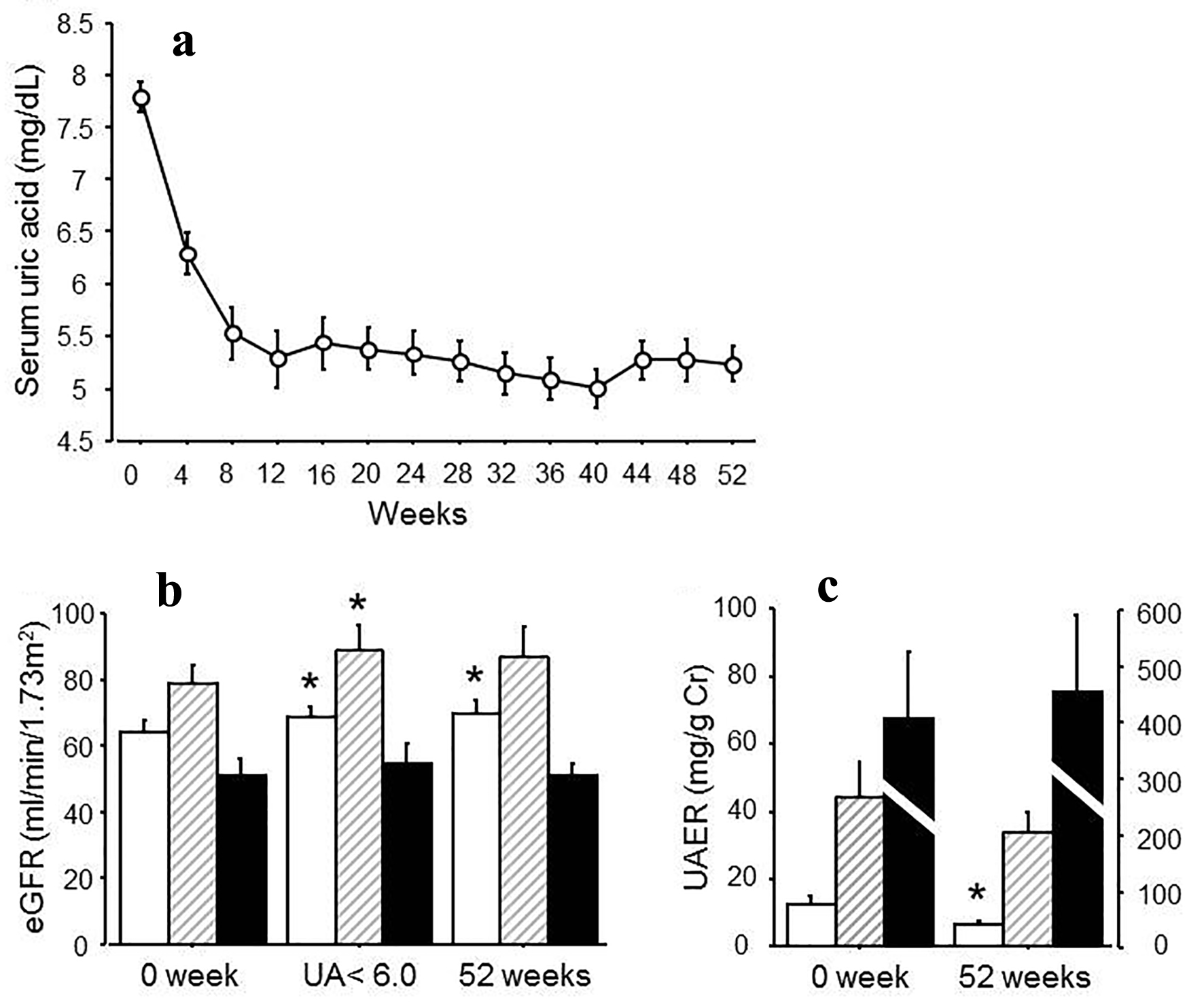
Figure 1. (a) Changes in serum urate levels after the treatment for 52 weeks. (b) eGFR at 0 week, at the point when uric acid reached under 6.0 mg/dL and at 52 weeks after the treatment. White bars: no albuminuria; shaded bars: microalbuminuria; black bars: macroalbuminuria. (c) UAER at 0 and 52 weeks after the treatment. White bars: no albuminuria; stripe bars: microalbuminuria; black bars: macroalbuminuria. *P < 0.05 vs. 0 week.