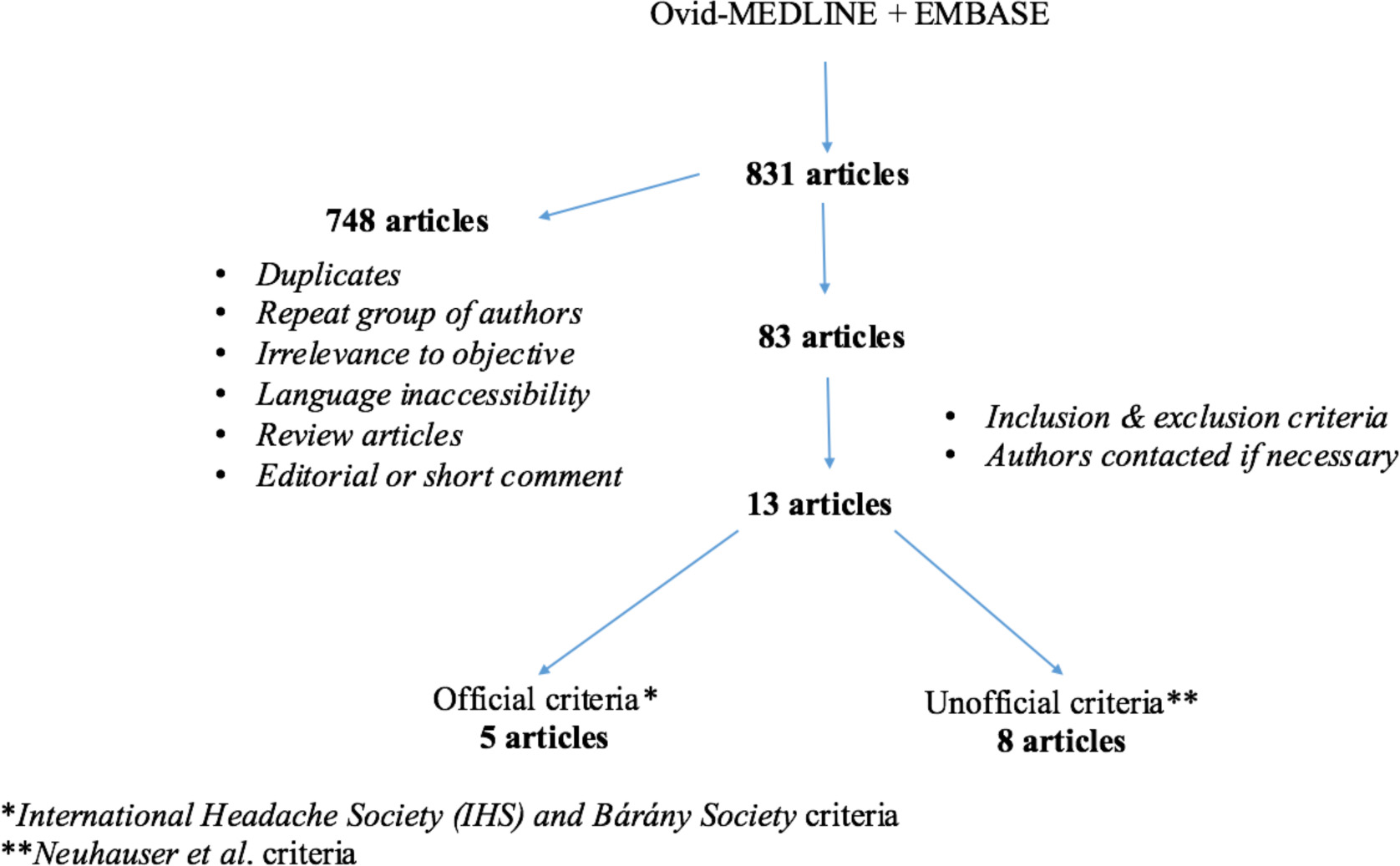
Figure 1. Study methodology - flow chart.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 9, Number 9, September 2017, pages 733-744
Meniere’s Disease and Vestibular Migraine: Updates and Review of the Literature
Figure

Tables
| Vestibular migraine, defined |
| 1) Vestibular symptoms at least of moderate intensity |
| 2) Current or past history of migraine, according to International Headache Society criteria |
| 3) One of the following migraine symptoms during at least two attacks of vertigo: migraine, photophobia, phonophobia, visual or other auras |
| 4) Other causes ruled out by an appropriate research |
| Probable vestibular migraine |
| 1) Vestibular symptoms of at least moderate intensity |
| 2) One of the following: |
| a) Current or past history of migraine according to 2004 criteria |
| b) Migraine symptoms during vestibular symptoms |
| c) Migraine precipitants of vertigo in more than 50% of attacks: food triggers, sleep problems, hormonal changes |
| d) Response to anti-migraine drugs in more than 50% of attacks |
| 3) Other causes ruled out by appropriate research |
| aUsually interfere with daily activities. bUsually prohibit daily activities. |
| Vestibular migraine |
| 1) At least five episodes with vestibular symptoms of moderatea or severeb intensity, lasting 5 min to 72 h |
| 2) Current or previous history of migraine with or without aura according to the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD) |
| 3) One or more migraine features with at least 50% of the vestibular episodes: a) headache with at least two of the following characteristics: one sided location, pulsating quality, moderatea or severeb pain intensity, aggravation of routine physical activity; b) photophobia and phonophobia; c) visual aura |
| 4) Not better accounted for by another vestibular or ICHD diagnosis |
| Probable vestibular migraine |
| 1) At least five episodes with vestibular symptoms of moderate or severe intensity, lasting 5 min to 72 h |
| 2) Only one of the criteria B and C for vestibular migraine is fulfilled (migraine history or migraine features during the episode) |
| 3) Not better accounted for by another vestibular or ICHD diagnosis |
| Certain Meniere’s disease | Definite Meniere’s disease plus histopathologic confirmation |
| Definite Meniere’s disease | Two or more definitive spontaneous episodes of vertigo 20 minutes or longer |
| Audiometrically documented hearing loss on at least one occasion | |
| Tinnitus or aural fullness in the treated ear | |
| Other causes excluded | |
| Probable Meniere’s disease | One definitive episode of vertigo |
| Audiometrically documented hearing loss on at least one occasion | |
| Tinnitus or aural fullness in the treated ear | |
| Other causes excluded | |
| Possible Meniere’s disease | Episodic vertigo of the Meniere’s type without documented hearing loss or sensorineural hearing loss, fluctuating or fixed, with disequilibrium but without definitive episodes |
| Other causes excluded |
| Findings | Article | Criteria | MD | VM | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nil: data not mentioned; ND: no difference noted but no P-value given; MSQ: motion sensitivity questionnaire; HL: hearing loss; HA: headache; Mod: moderate; Hx: history. Official: International Headache Society and Barany Society criteria (2012); Unofficial: Neuhauser criteria (2001). | |||||
| Sex (female %) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 35 | 83 | < 0.0001 |
| Martin-Sanz et al [20] | Official | Nil | Nil | ND | |
| Age (years) | Hong et al [19] | Unofficial | 49 | 43 | ND |
| Martin-Sanz et al [20] | Official | 46 | 37 | ND | |
| Age of onset (years) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 51 | 41 | 0.0007 |
| Lopez-Escamez et al [18] | Official | 48 | 43 | 0.007 | |
| Evolution | Martin-Sanz et al [20] | Official | Nil | Nil | ND |
| Vertigo Duration (hours) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 47 | 19 | < 0.0001 |
| Illness duration (months) | 12 | 6 | < 0.0001 | ||
| Non-vertiginous dizziness (%) | 50 | 78 | < 0.0001 | ||
| Fluctuating HL (%) | 78 | 14 | < 0.0001 | ||
| Progressive HL (%) | 93 | 22 | < 0.0001 | ||
| HL related to vertigo (%) | 43 | 44 | 0.91 | ||
| Tinnitus (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 96 | 55 | < 0.0001 |
| Lopez-Escamez et al [18] | Official | 83 | 46 | < 0.001 | |
| Tinnitus related to vertigo (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 59 | 50 | 0.47 |
| Aural Fullness (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 78 | 51 | 0.0026 |
| Lopez-Escamez et al [18] | Official | 80 | 34 | < 0.001 | |
| Aural Fullness related to vertigo (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 65 | 70 | 0.71 |
| Otalgia (%) | 17 | 27 | 0.09 | ||
| Palpitations (%) | Lopez-Escamez et al [18] | Official | 34 | 50 | 0.008 |
| Anxiety (%) | 78 | 91 | 0.024 | ||
| Headache (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 81 | 99 | 0.0026 |
| Lopez-Escamez et al [18] | Official | 41 | 95 | < 0.001 | |
| Frequent headache (daily or weekly) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 19 | 67 | < 0.0001 |
| Headache duration (> day) | 8 | 43 | 0.0012 | ||
| Headache severity (mod/severe) (%) | 26 | 96 | < 0.0001 | ||
| HA age of onset (years) | 23 | 28 | 0.44 | ||
| Migraine-type headache (%) | Lopez-Escamez et al [18] | Official | 8 | 69 | < 0.001 |
| Phonophobia (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 63 | 82 | 0.1 |
| Lopez-Escamez et al [18] | Official | 62 | 80 | < 0.001 | |
| Photophobia (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 40 | 86 | < 0.0001 |
| Lopez-Escamez et al [18] | Official | 41 | 80 | < 0.001 | |
| Nausea or vomiting with HA (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 20 | 72 | < 0.0001 |
| Vomiting (%) | Lopez-Escamez et al [18] | Official | 84 | 69 | 0.002 |
| Headache triggers (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 11 | 69 | < 0.0001 |
| Balance symptoms with HA | 31 | 81 | 0.07 | ||
| Frequency of balance symptoms with HA | 29 | 80 | < 0.0001 | ||
| Aura (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 22 | 62 | < 0.0001 |
| Lopez-Escamez et al [18] | Official | 11 | 32 | < 0.001 | |
| Family Hx of vertigo or dizziness (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 17 | 30 | 0.16 |
| Family Hx of HL (%) | 33 | 25 | 0.74 | ||
| Family Hx of Migraine (%) | 26 | 61 | 0.0017 | ||
| History of motion sickness (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 20 | 51 | 0.0023 |
| MSQ score to riding in a car | Sharon et al [17] | Unofficial | 0.5 | 1.07 | 0.048 |
| Findings (unit) | Article | Criteria | MD | VM | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD: Meniere’s disease; VM: vestibular Migraine; dMD: definite Meniere’s disease; dVM: definite vestibular migraine; pMD: probable Meniere’s disease; pVM: probable vestibular migraine; PTA: pure tone average; ELH: endolymphatic hydrops; ECOG: electrocochleography; dB: decibels; Nil: data not mentioned; D: difference noted but no P-value given; official: International Headache Society and Barany Society criteria (2012); unofficial: Neuhauser criteria (2001). Hearing class according to AAO-HNS hearing preservation reporting guidelines (view Table 7). SP: summating potential; AP: action potential. | |||||
| Abnormal head-shaking nystagmus (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 62 | 15 | < 0.0001 |
| Shin et al [21] | 71 | 50 | < 0.05 | ||
| Abnormal head-thrust (%) | Neff et al [16] | 37 | 3 | < 0.0001 | |
| Abnormal vibration induced nystagmus (%) | Neff et al [16] | 60 | 12 | < 0.0001 | |
| Shin et al [21] | 42 | 32 | < 0.05 | ||
| Abnormal smooth pursuit (%) | Neff et al [16] | 5 | 8 | 0.09 | |
| Abnormal saccades (%) | 5 | 0 | 0.46 | ||
| Initial PTA ≥ 25 dB (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 83 | 7 | 0.0011 |
| Worst PTA ≥ 25 dB (%) | 100 | 9 | < 0.0001 | ||
| Initial discrimination ≥ 25 dB (%) | 68 | 2 | < 0.0001 | ||
| Change in discrimination (%/month) | 86 | 2 | < 0.0001 | ||
| Initial hearing class B-D (%) | 71 | 5 | < 0.0001 | ||
| Worst hearing class B-D (%) | 95 | 6 | < 0.0001 | ||
| Low tone hearing loss pattern (%) | 40 | 0 | < 0.0001 | ||
| PTA for dMD vs. dVM (dB) | Martin-Sanz et al [20] | Official | Nil | Nil | > 0.05 |
| PTA for pMD vs. pVM (dB) | 35 | 16 | D | ||
| Significant vestibular ELH (%) | Nakada et al [22] | Official | 79 | 14 | < 0.01 |
| Significant Cochlear ELH (%) | 30 | 0 | < 0.05 | ||
| ELH on ECOG (%) (SP/AP amplitude ratio) | Martin-Sanz et al [20] | 82 | 24 | < 0.05 | |
| Findings | Article | Criteria | MD | VM | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hz: Hertz; TB: tone burst; vHIT: video head impulse test; hVOR: horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex; CAQEM: covert anti-compensatory quick eye movements; nil: data not mentioned; official: International Headache Society and Barany Society criteria (2012); unofficial: Neuhauser criteria (2001). oVEMP: ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential; cVEMP: cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potential; µV: microvolt; ms: millisecond; mV: millivolt; ND: no difference noted but no P-value given. | |||||
| Mean caloric asymmetry (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 33 | 13 | < 0.0001 |
| Blodow et al [23] | Official | 38 | 16 | 0.005 | |
| Sharon et al [17] | Unofficial | 40 | 24 | 0.0007 | |
| Abnormal caloric asymmetry (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 63 | 17 | < 0.0001 |
| Blodow et al [23] | Official | 67 | 22 | 0.002 | |
| Hong et al [19] | Unofficial | 48 | 23 | < 0.05 | |
| Shin et al [21] | Unofficial | 47 | 25 | < 0.05 | |
| Taylor et al [24] | Unofficial | OR = 26.36 for MD vs. VM | < 0.001 | ||
| Sensitivity = 74.5% | |||||
| Martin-Sanz et al [20] | Official | Nil | Nil | > 0.05 | |
| Mean directional preponderance (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 19 | 13 | 0.09 |
| Abnormal directional preponderance (%) | 29 | 15 | 0.15 | ||
| Abnormal rotary chair phase (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 68 | 18 | < 0.0001 |
| Rotary chair gain towards affected ear (Hz) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 25 | 36 | < 0.0001 |
| Taylor et al [24] | Unofficial | 16 | 25 | 0.014 | |
| Rotary chair gain towards unaffected ear (Hz) | Taylor et al [24] | Unofficial | 18 | 23 | 0.165 |
| Abnormal rotary chair TC towards affected ear (Hz) | 16 | 25 | 0.009 | ||
| Abnormal rotary chair TC towards un affected ear (Hz) | 17 | 24 | 0.033 | ||
| Abnormal rotary chair symmetry (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 35 | 29 | 0.02 |
| Abnormal vHIT hVOR gain (%) | Blodow et al [23] | Official | 37 | 9 | 0.025 |
| Presence of vHIT CAQEM (%) | Heuberger et al [28] | Official | Nil | Nil | 0.01 |
| Abnormal VEMP (%) | Neff et al [16] | Unofficial | 45 | 16 | 0.0068 |
| cVEMP 250 Hz TB amplitude asymmetry ratios (%) | Taylor et al [24] | Unofficial | 40 | 5 | < 0.001 - 0.024 |
| cVEMP 500 Hz TB amplitude asymmetry ratios (%) | 60 | 10 | < 0.001 - 0.024 | ||
| cVEMP 1 kHz TB amplitude asymmetry ratios (%) | 40 | 15 | < 0.001 - 0.024 | ||
| cVEMP 2 kHz TB amplitude asymmetry ratios (%) | 30 | 15 | < 0.001 - 0.024 | ||
| cVEMP 500 Hz/1kHz TB amplitude ratio | 0.89 | 1.11 | 0.007 | ||
| cVEMP 500 Hz TB detection rate (%) | Murofushi et al [25] | Unofficial | 63 | 100 | 0.0003 |
| cVEMP mean corrected amplitudes | 0.59 | 1.49 | 0.001 | ||
| cVEMP click amplitudes (µV) | Zuniga et al [26] | Unofficial | Nil | Nil | ND |
| cVEMP click peak-to-peak amplitudes (µV) | 29 | 38 | 0.625 | ||
| cVEMP click latencies (ms) | Nil | Nil | ND | ||
| cVEMP click amplitudes for right side | Baier et al [27] | Unofficial | Nil | Nil | 0.22 |
| cVEMP click amplitudes for left side (ms) | Nil | Nil | 0.744 | ||
| cVEMP click latencies p13 right side (ms) | 16 | 16 | > 0.01 | ||
| cVEMP click latencies p13 left side (ms) | 16 | 16 | > 0.01 | ||
| cVEMP click latencies n23 right side (ms) | 25 | 25 | > 0.01 | ||
| cVEMP click latencies n23 left side (ms) | 26 | 25 | > 0.01 | ||
| oVEMP click reflex latencies (ms) | Zuniga et al [26] | Unofficial | 11.1 | 9.8 | 0.028 |
| oVEMP 500 Hz TB reflex latencies (ms) | 11.1 | 10.4 | 0.041 | ||
| oVEMP 500 Hz TB reflex amplitudes | 0.98 | 3.4 | 0.007 | ||
| oVEMP reflex hammer midline tap amplitudes (mV) | 4.6 | 5.45 | 0.21 | ||
| oVEMP mini-shaker tap amplitudes (mV) | 3.9 | 5 | 0.217 | ||
| oVEMP reflex hammer midline tap latencies (ms) | 8 | 7.5 | 0.879 | ||
| oVEMP reflex mini-shaker tap latencies (ms) | 9.8 | 9.8 | 0.597 | ||
| Class | Pure-tone thresholds | Speech discrimination (%) |
|---|---|---|
| A | ≤ 30 dB | ≥ 70 |
| B | > 30 dB, ≤ 50 dB | ≥ 50 |
| C | > 50 dB | ≥ 50 |
| D | Any level | < 50 |
| Definite | Two or more spontaneous episodes of vertigo, each lasting 20 min to 12h |
| Audiometrically documented low to midfrequency sensorineural hearing loss in one ear, defining the ear on one occasion before, during or after one episode of vertigo | |
| Fluctuating aural symptoms (hearing, tinnitus, or fullness) in the affected ear | |
| Not better accounted for by another vestibular diagnosis | |
| Probable | Two or more episodes of vertigo or dizziness, each lasting 20 min to 24 h |
| Fluctuating aural symptoms (hearing, tinnitus, or fullness) in the affected ear | |
| Not better accounted for by another vestibular diagnosis |