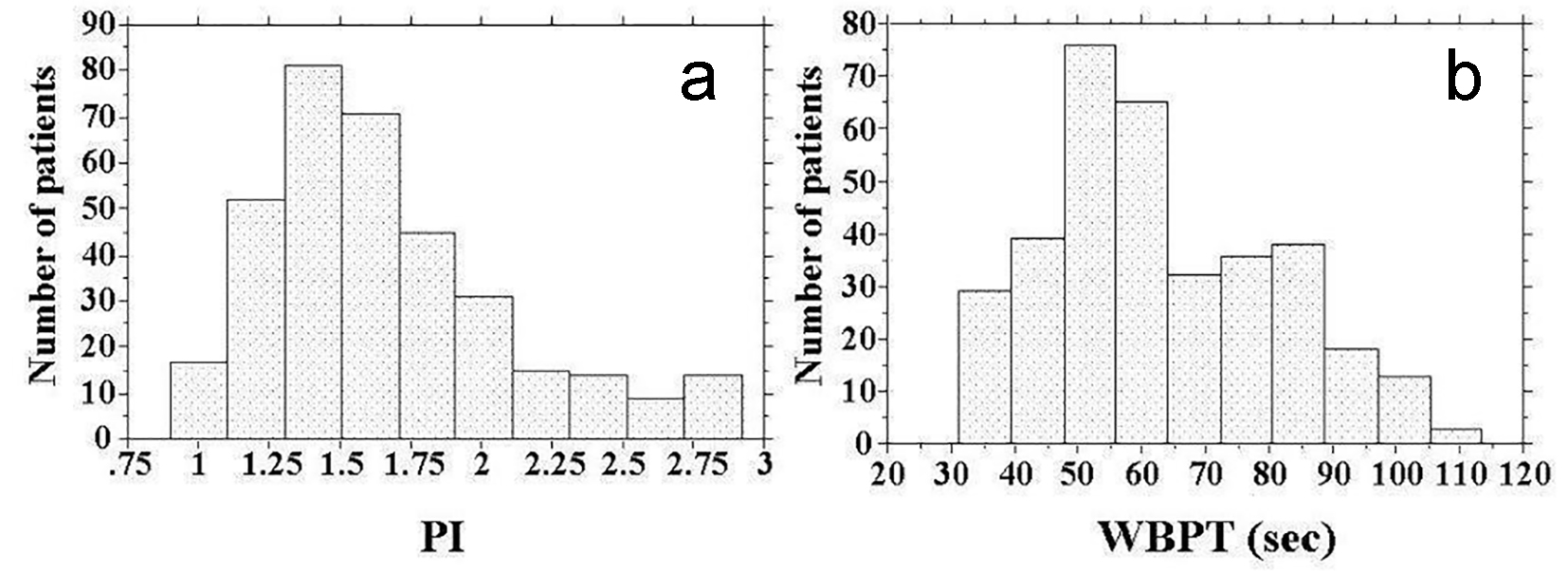
Figure 1. Histogram of PI and WBPT. (a) The mean and median values of PI were 1.69 (± 0.63; range, 0.69 - 2.92) and 1.61, respectively. (b) The mean and median values of WBPT were 62.9 (± 18.0; range, 31.2 - 113.50) s and 59.6 s, respectively. PI: pulsatility index; WBPT: whole blood passage time.
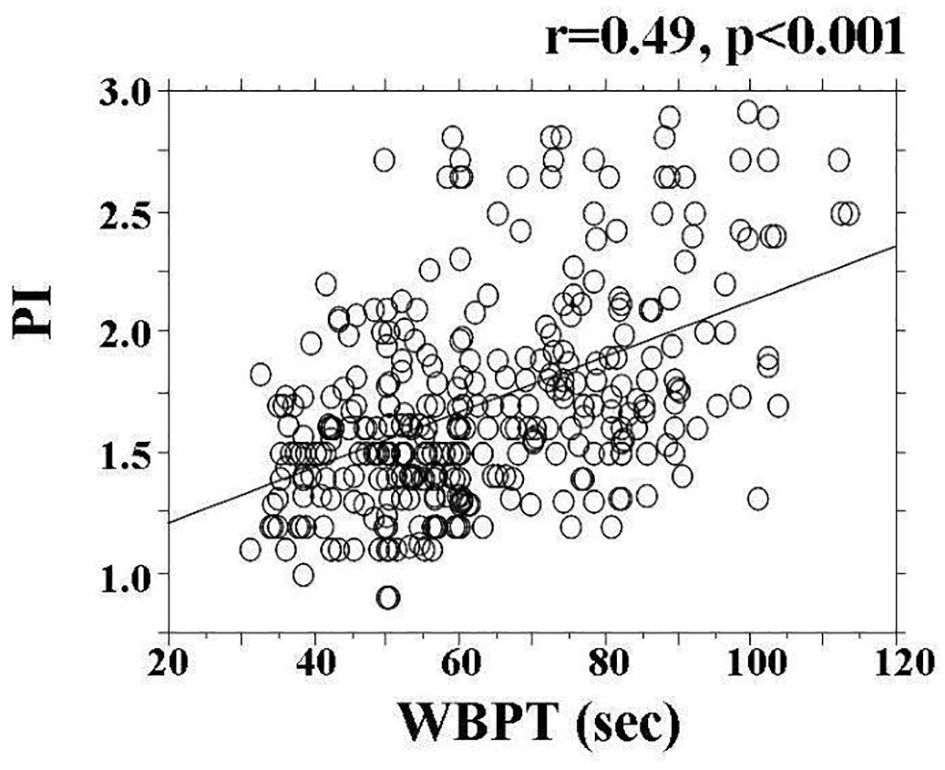
Figure 2. The correlation between PI and WBPT. A statistically significant positive correlation (r = 0.49, P < 0.001) was observed between PI and WBPT. PI: pulsatility index; WBPT: whole blood passage time.
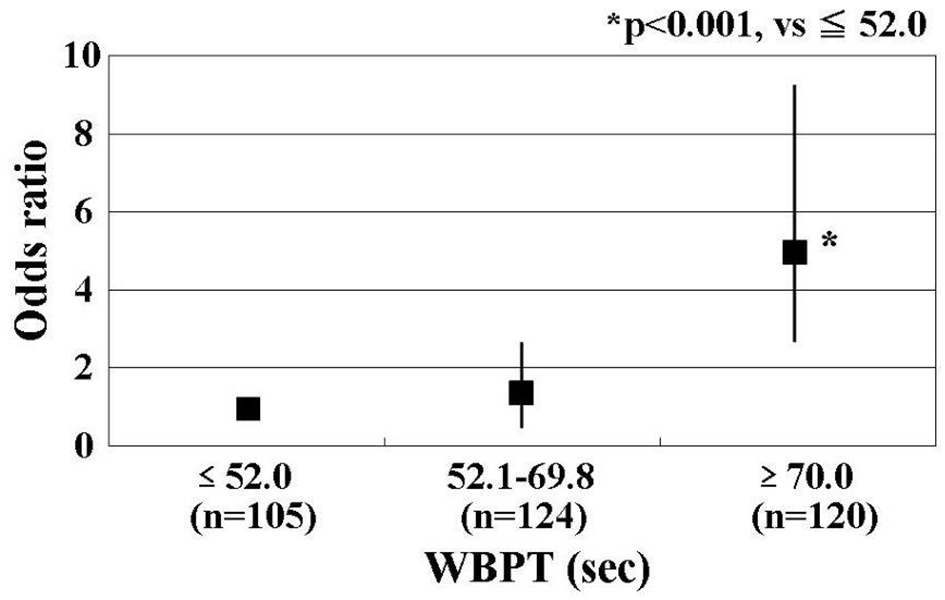
Figure 3. Results of multiple logistic regression analysis for high PI. Patients with high WBPT (≥ 70 s) had significantly higher risk (odds ratio, 5.2; 95% confidence interval, 2.4 - 9.2; P < 0.001) of being detected with a high PI of CCA than those with low WBPT (≤ 52.0 s). A high PI of CCA was defined as a PI of > 2. Adjustment factors: age, max-IMT, current smoker, d-ROMs test, and skin autofluorescence. PI: pulsatility index; WBPT: whole blood passage time.


