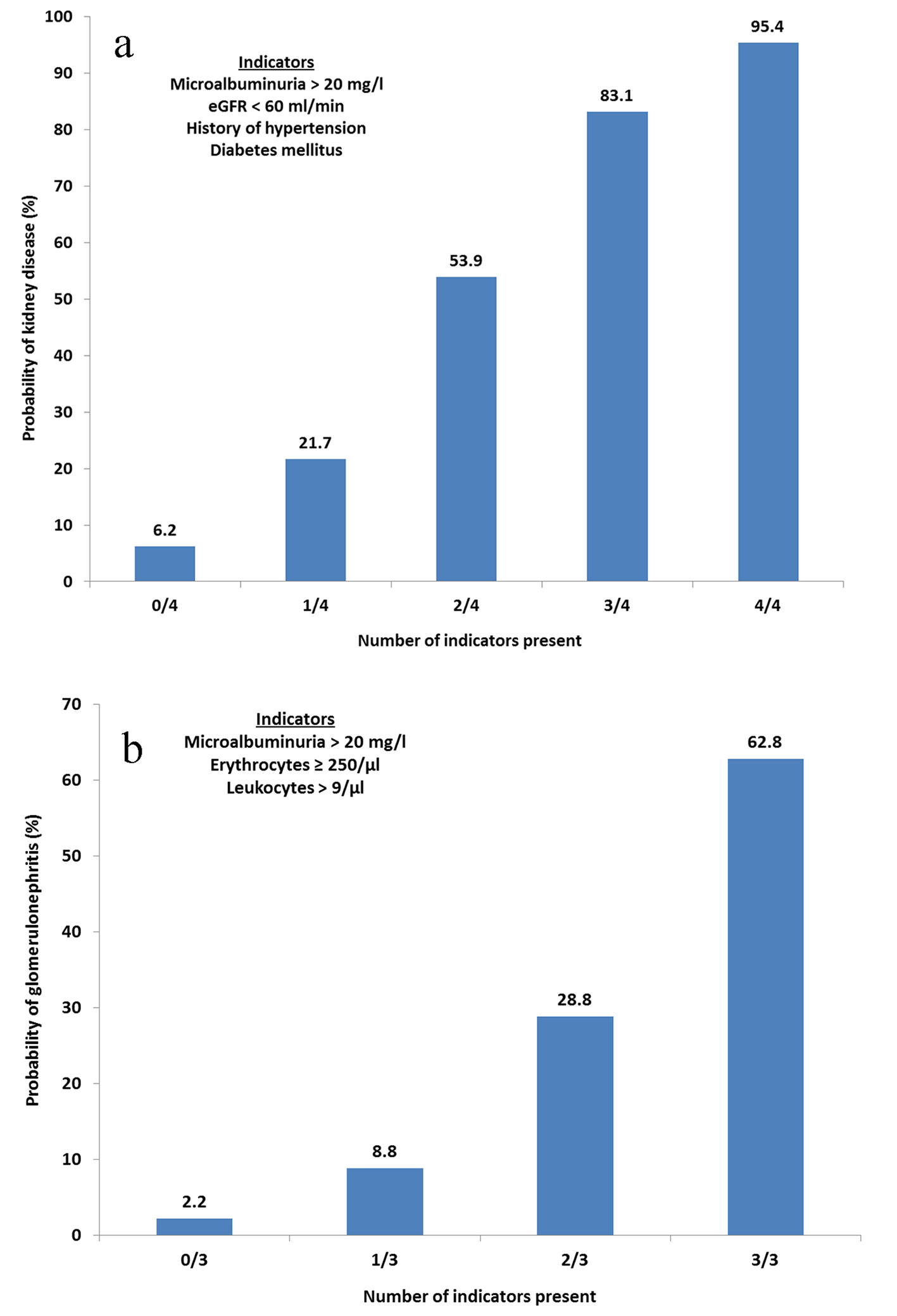
Figure 1. (a) Probability of kidney disease based on clinical findings. Calculated probabilities of kidney disease based on factors found to be significant in the multivariate logistic regression. Any combination of indicators can be present. eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate. (b) Probability of glomerulonephritis based on clinical findings. Calculated probabilities of glomerulonephritis based on factors found to be significant in the multivariate logistic regression. Any combination of indicators can be present. Erythrocyte concentration determined by urine stick analysis.