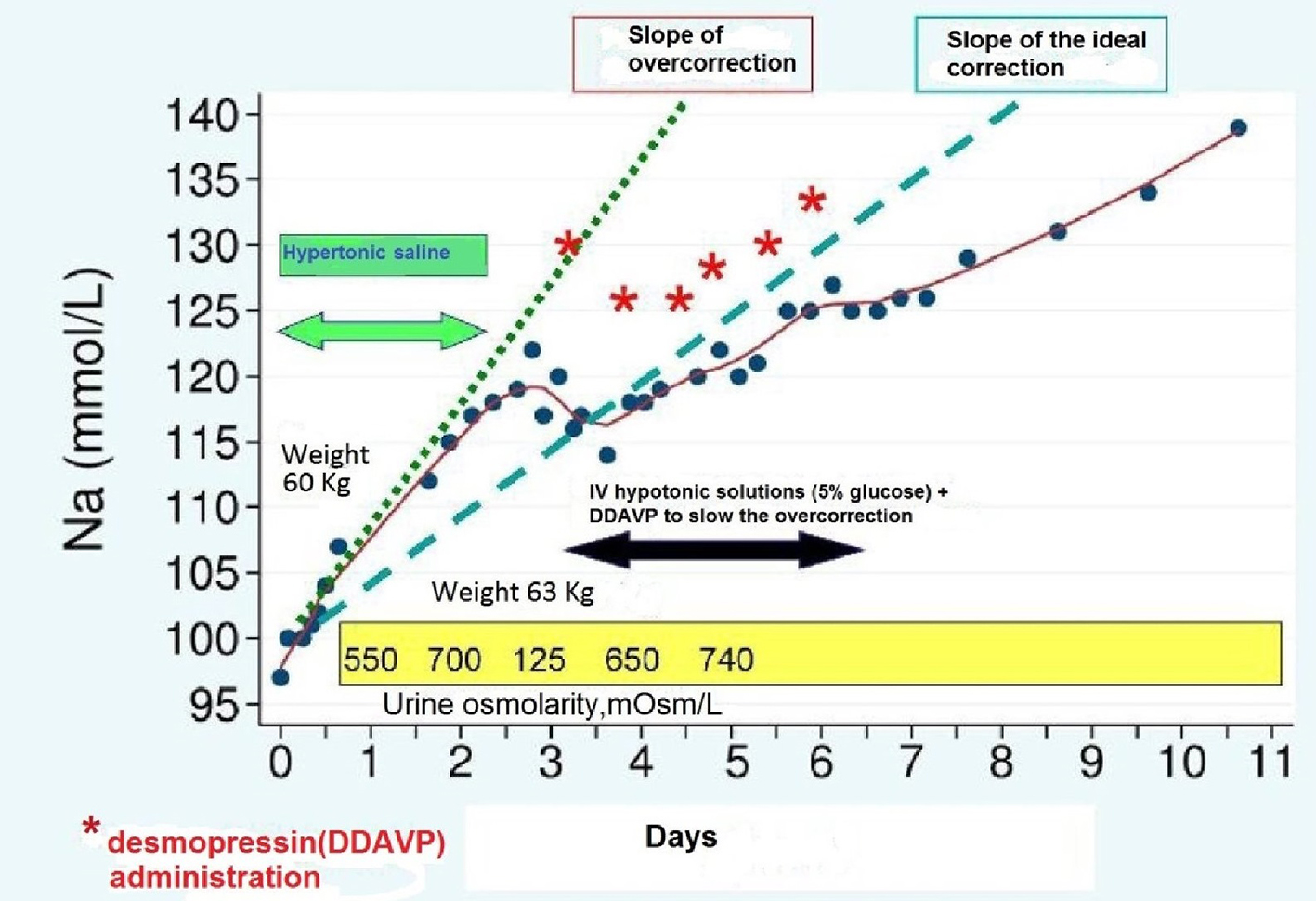
Figure 1. Symptoms of hyponatremia depend on the extent of the electrolytic disorder, but also on the rapidity with which it occurs.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 9, Number 4, April 2017, pages 266-272
Does Accidental Overcorrection of Symptomatic Hyponatremia in Chronic Heart Failure Require Specific Therapeutic Adjustments for Preventing Central Pontine Myelinolysis?
Figures

Table
| Possible observable immediate precursors | Frequently observed symptoms |
|---|---|
| Seizures | Acute para- or tetra-paresis |
| Disturbed consciousness | Dysphagia |
| Gait troubles | Dysarthria |
| Diplopia | |
| Loss of consciousness | |
| Other neurological symptoms associated with brainstem damage | |
| The patient may experience locked-in syndrome where cognitive function is intact, but all muscles are paralyzed with the exception of eye blinking. This severe clinical picture ensues from a rapid myelinolysis of the corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts in the brainstem. |