Figures
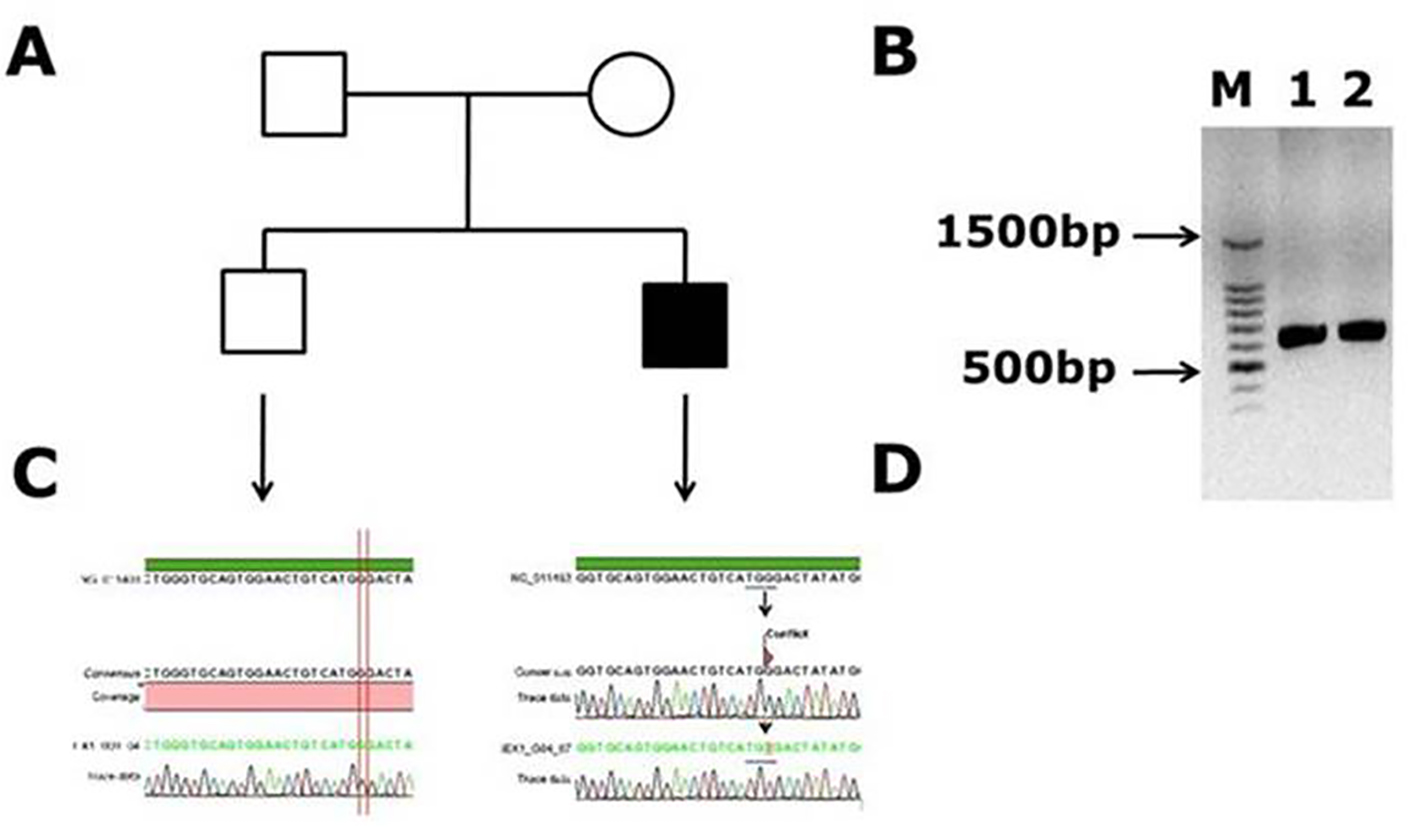
Figure 1. Novel missense mutation identified in exon 1 of the factor VIII gene. (A) Family pedigree. (B) PCR gel image of exon 1 in factor VIII showing single specific band of exon 1 product size 638 bp in patient and WT (lanes 1 and 2). (C) Representative electrophoregram showing WT genotype. (D) Representative electrophoregram showing the mutation (conflict) in exon 1.
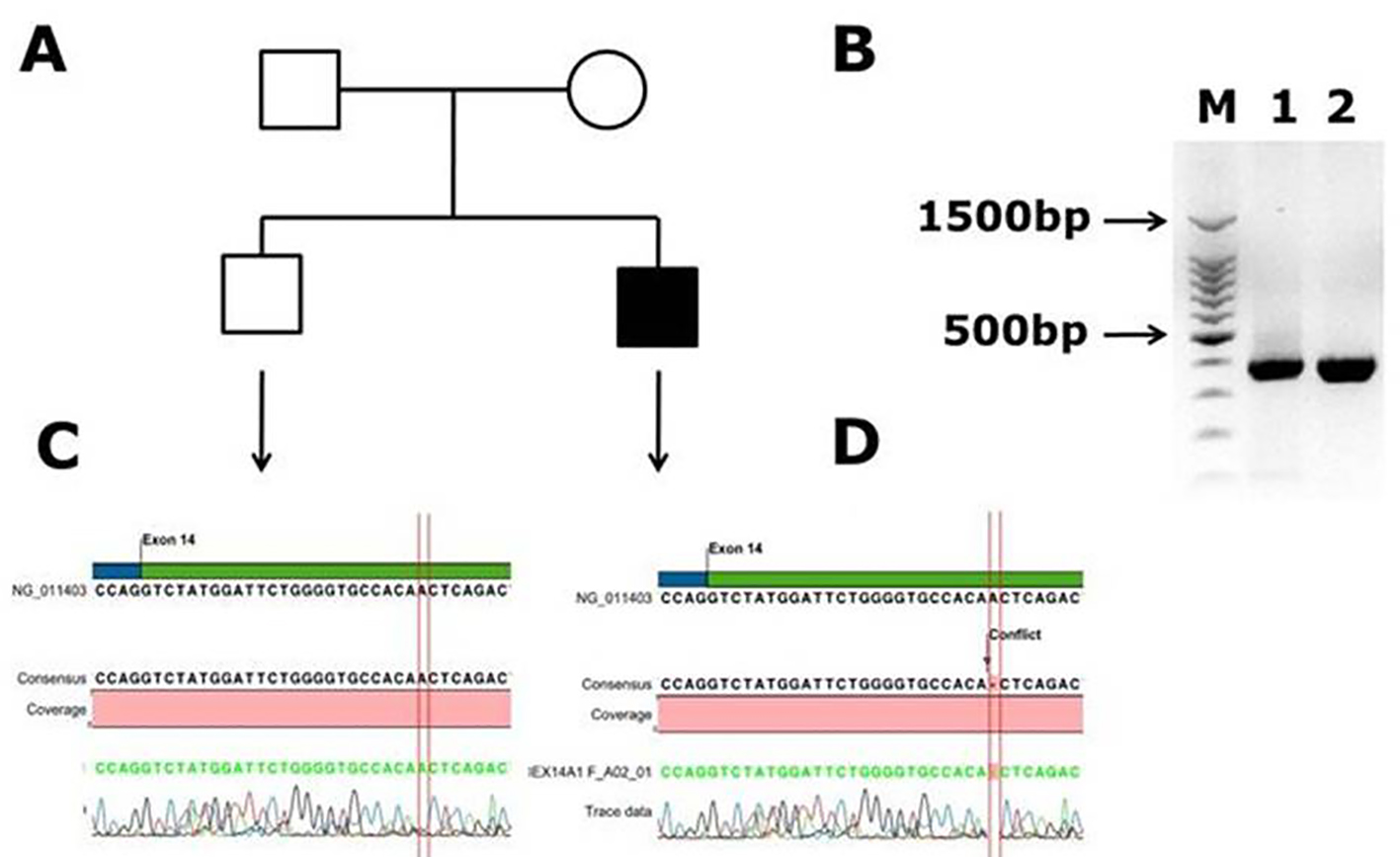
Figure 2. Identification of novel frame shift mutation in coagulation factor VIII c.2138 delA, p. (N713Tfs*9) causing hemophilia A in Saudi Arabian patient. (A) Family pedigree. (B) PCR gel image of exon 14 of factor VIII showing single specific band of product size 352 bp in patient and WT (lanes 1 and 2). As exon 14 is very large, we have designed primers of small fragments of exon 14. (C) Representative electrophoregram showing WT genotype. (D) Representative electrophoregram showing the mutation (conflict) in exon 14 of factor VIII gene.
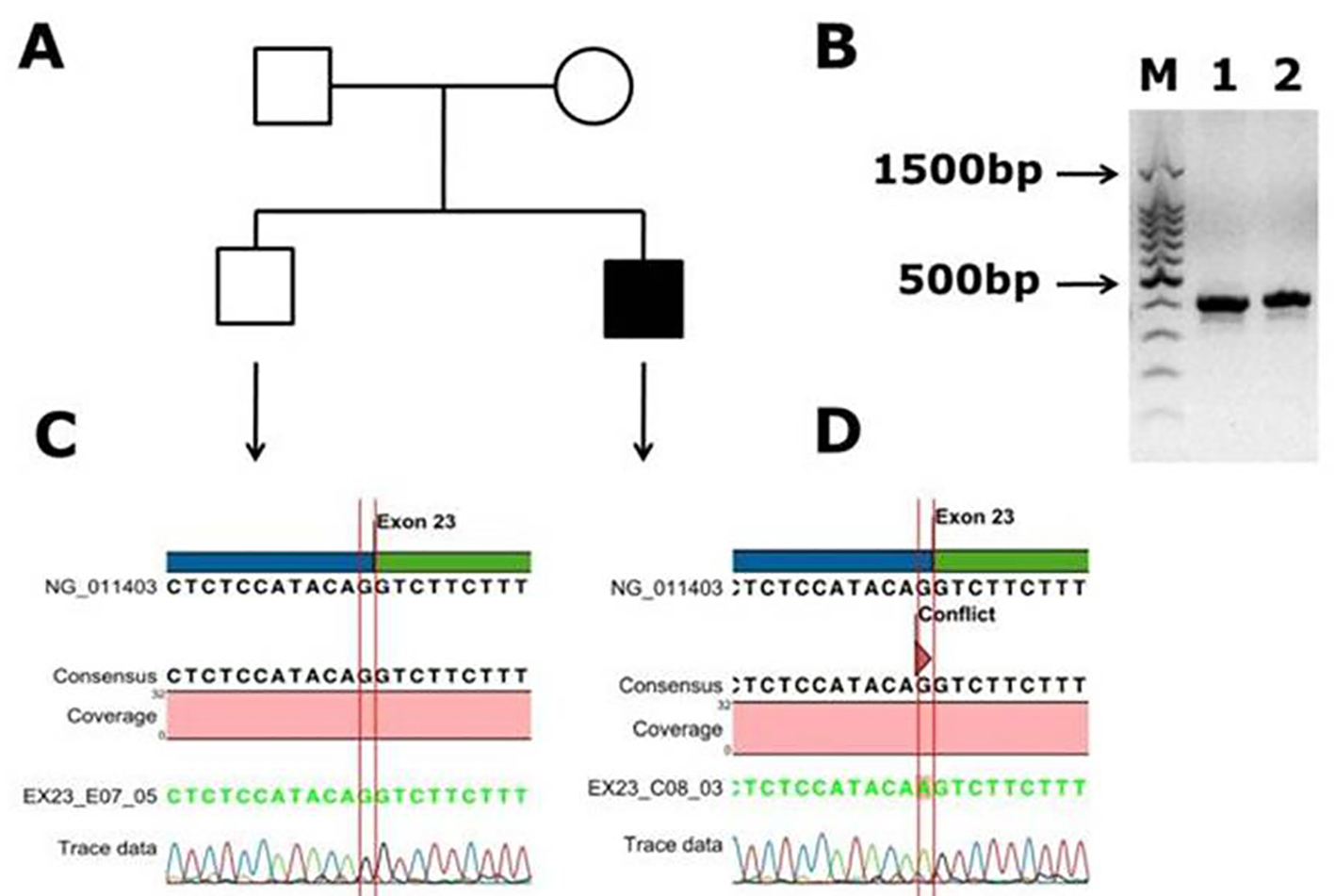
Figure 3. Identification of a novel splicing mutation c.6430 -1 G>A (splicing acceptor site) of factor VIII in a Saudi Arabian patient. (A) Family pedigree. (B) PCR gel image of exon 23 of factor VIII showing single specific band of product size 416 bp in patient and WT (lanes 1 and 2). (C) Representative electrophoregram showing WT genotype. (D) Representative electrophoregram showing the mutation (conflict) at exon intron junction in exon 23 of factor VIII gene.
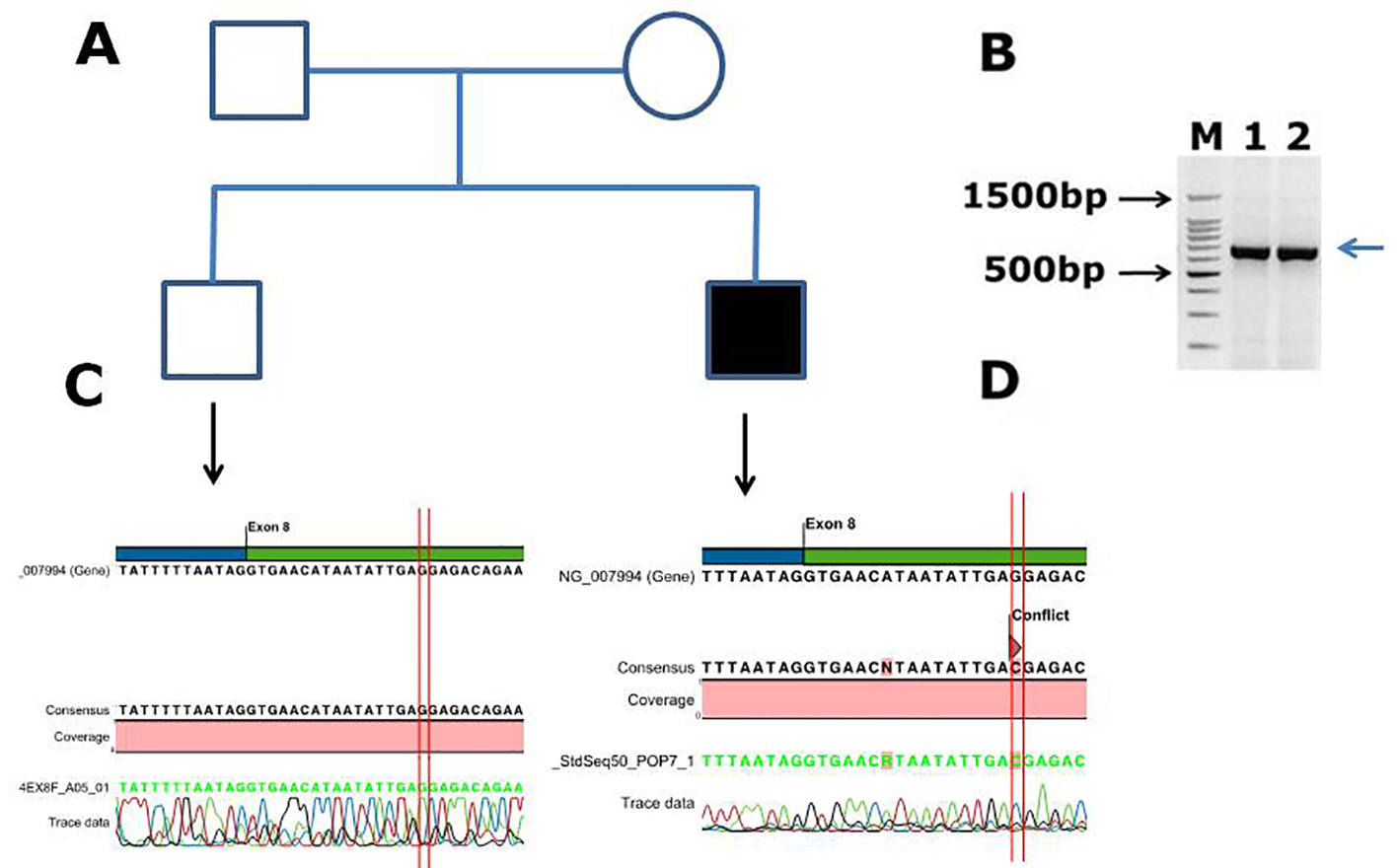
Figure 4. Identification of a novel missense mutation in coagulation factor IX c.855G>C, p. (E285D) causing hemophilia B in Saudi Arabian patient. (A) Family pedigree. (B) PCR gel image of factor IX exon 8, showing single specific band of product size 707 bp in two patients (lanes 1 and 2). (C) Representative electrophoregram showing WT genotype. (D) Representative electrophoregram showing the missense mutation (conflict) in exon 8 of factor IX.
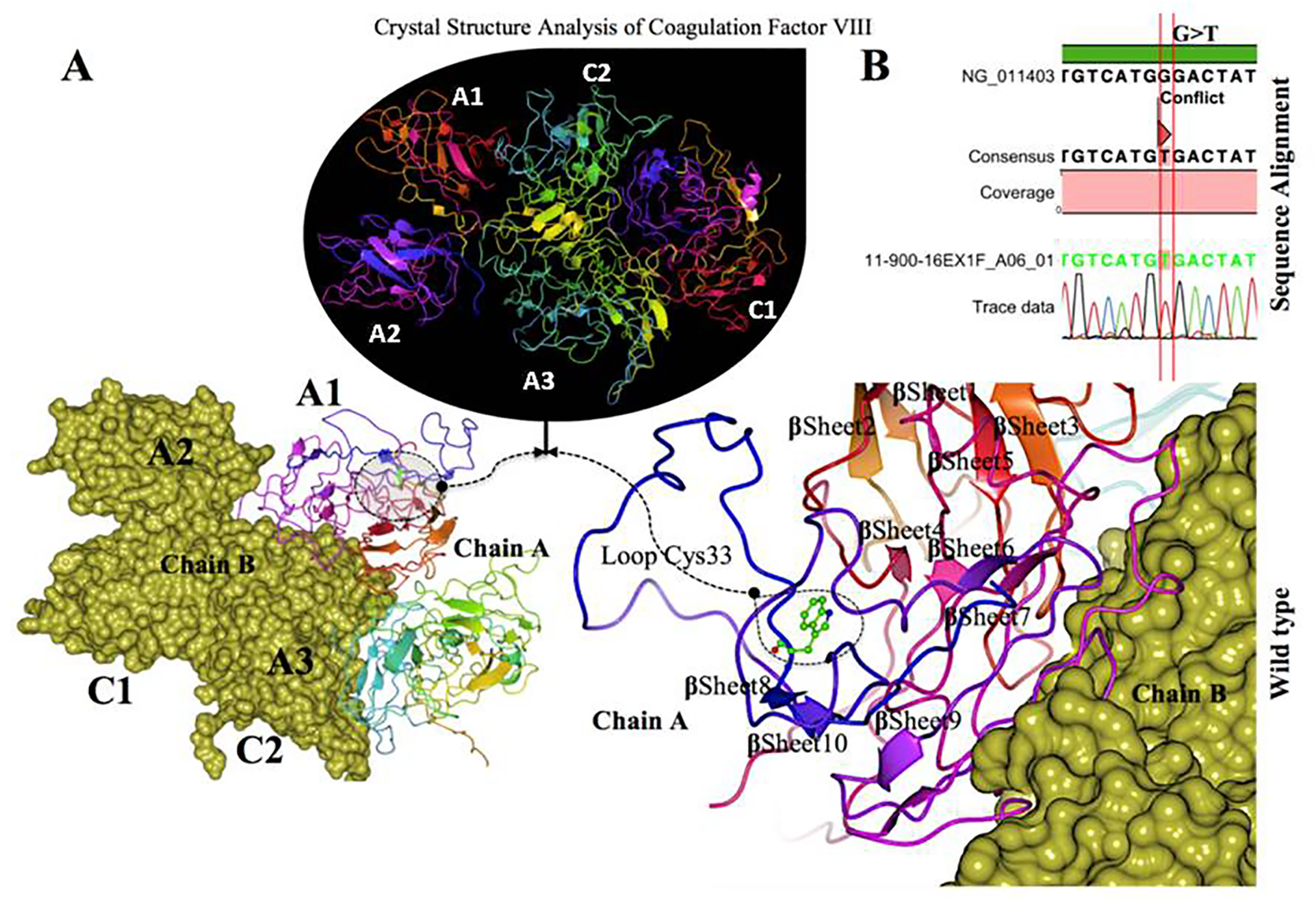
Figure 5. Crystal structure of coagulation domains of hemophilia factor VIII protein and MD simulation. (A) The crystal structure of the domains of factor VIII (PDB ID 2R7E), the individual domains are labeled and also in different colors (A1) in magenta, (A2) shown in blue, (A3) shown in yellowish green, (C1) shown in pink, and (C2) shown in bluish green. The molecular surface of factor VIII domains (A2) and (A3) are in chain B (yellow). Overview views positions of mutation with nearby residues shown as ball and stick models in dashed circle. The (Try33Cys) mutation located in the interface of (A1) domain, a tertiary structure of the wild type chain A of factor VIII protein showing the mutation (W 33 C) green on a loop region near with alpha helix 10. (B) The electrophoregram showing the sequence alignment the patient sample with the wild type for this mutation G>T.
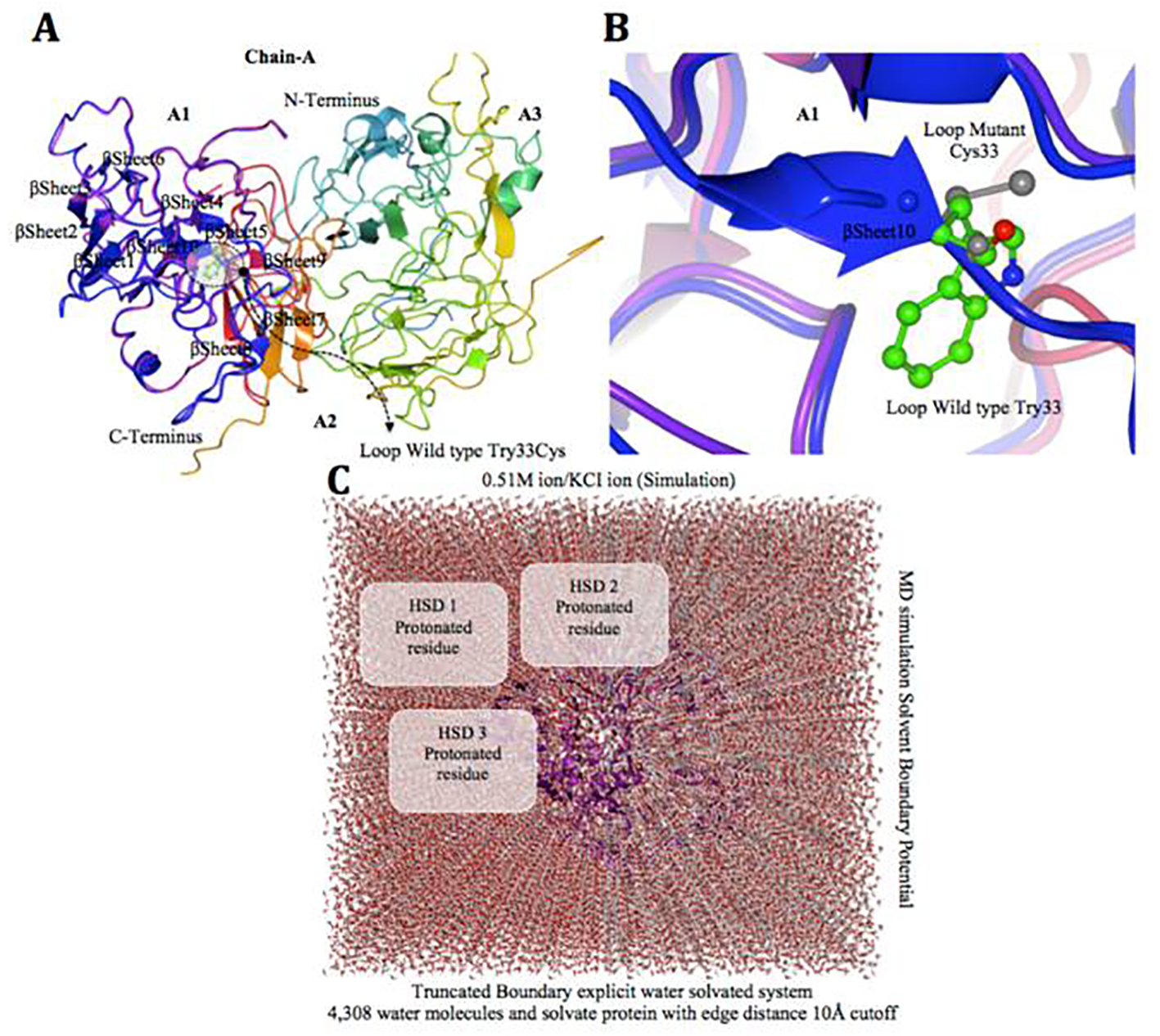
Figure 6. Factor VIII protein MD simulation showing truncated boundary explicit water solvated and hydrogen atoms. (A and B) Tertiary structure of the factor VIII protein showing amino acid mutation, i.e. gray cysteine (C 33), wild type green tryptophan (W 33), on loop region near with alpha helix 10 modeling. (C) The visual inspection also allow to identify the side chain of a histidine residue involved in the hydrogen bonding with surrounding molecules and the δ nitrogen of the histidine (HSD) is protonated. The MD simulation system used in calculations is: water box surrounding the entire protein (middle).
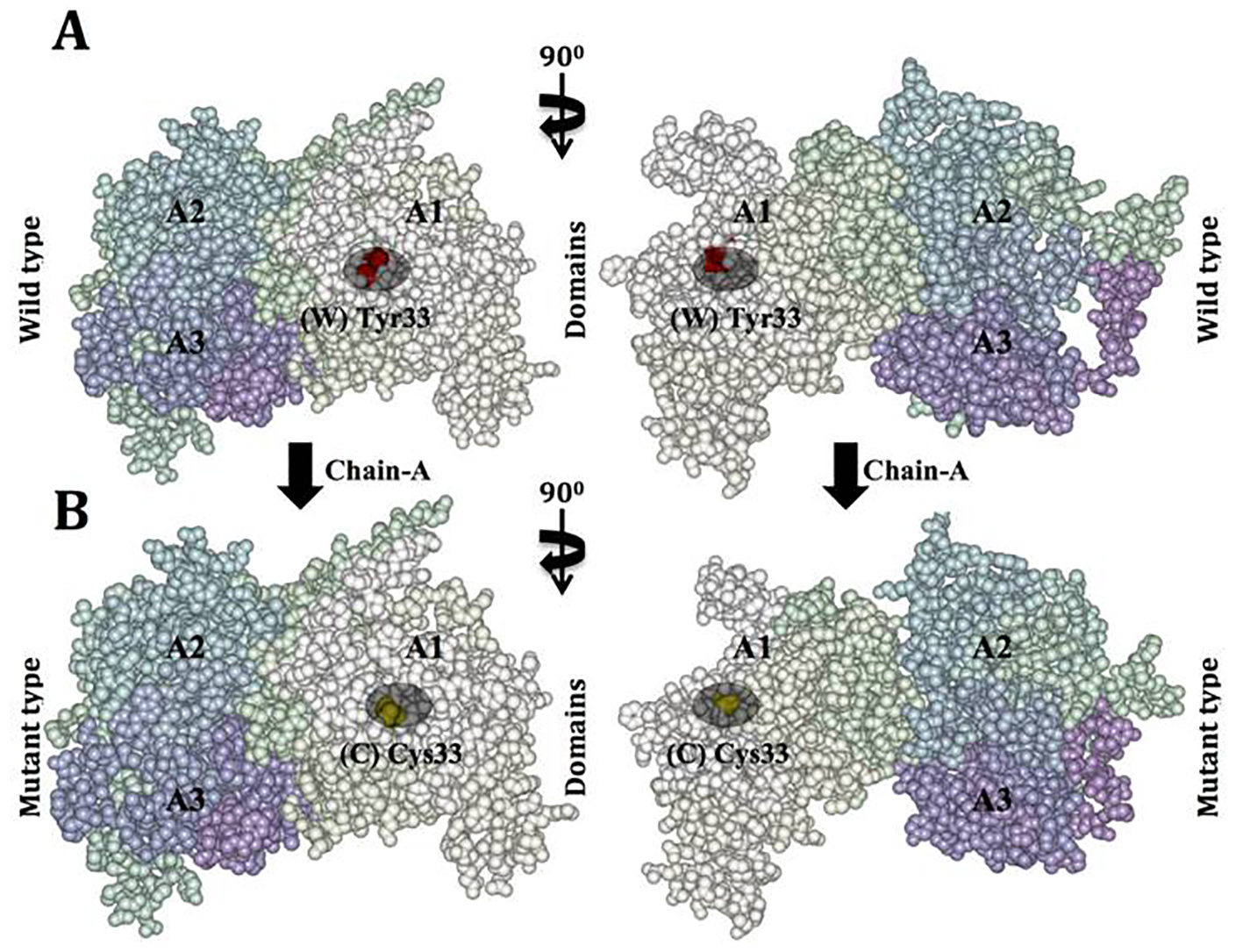
Figure 7. Van der Waals surface spacefill model of factor VIII protein A1, A2, and A3 domains showing solvent-exposed mutation on the surface. In this surface representation of quaternary structure of human factor VIII domains (A1, A2 and A3), the region of hemophilic mutation site is depicted as a cluster. (A) Chain A contains domain A1-A2-A3 labeled, in domain A1 the native residue W 33 is represented as (W) in red cluster. (B) Chain B surface model contains domain A1-A2-A3 labeled. Domain A1 has a mutated residue C 33 is represented in yellow color cluster (C).
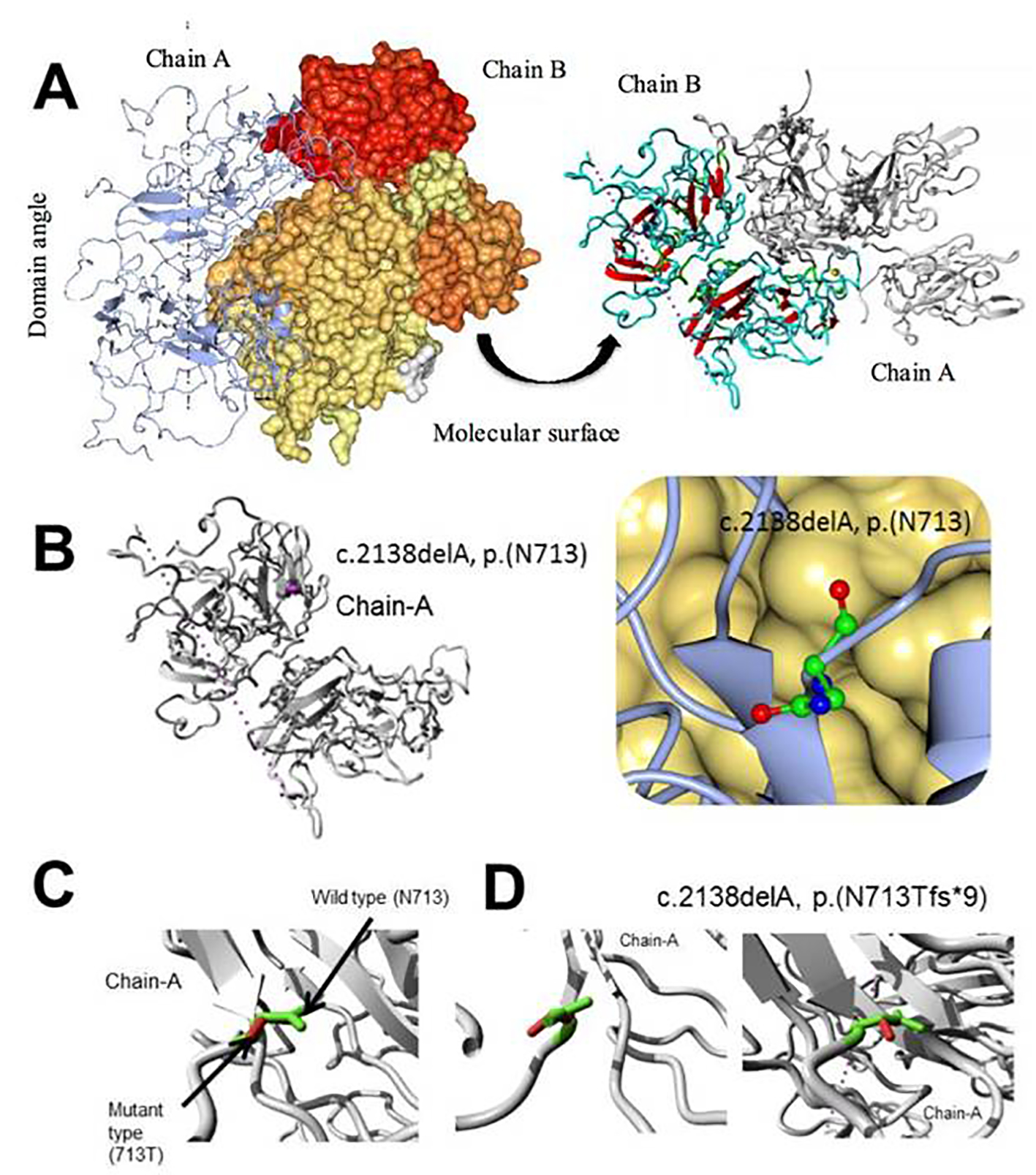
Figure 8. Molecular dynamics simulation of factor VIII, c.2138delA, p. (N713Tfs*9) novel frame shift mutation. (A) Overview of the protein in ribbon-presentation. The protein is colored by element α-helix (blue), β-strand (red), turn (green), 3/10 helix (yellow) and random coil (cyan). (Other molecules in the complex are colored gray). (B) Overview of the protein in ribbon-presentation. The protein is colored gray; the side chain of the mutated residue is colored magenta and shown as small balls. (C) Close-up of the mutation. The protein is colored gray; the side chains of both the wild type and the mutant residue are shown and colored green and red, respectively. (D) Close-up of the mutation (seen from a slightly different angle). The protein is colored gray; the side chains of both the wild type and the mutant residue are shown and colored green and red, respectively.
Tables
Table 1. Representative Hemophilia Patient’s Clinical Characteristics
| Patient code | Gender | Age (months) | Deficiency | Type of care | Treatment products | Joint disability | PTT |
|---|
| PDCFC: plasma-derived clotting factor concentrates; PTT: prothrombin time testing. |
| UQU-HA33 | Male | 2.00 | Severe | Prophylaxis | More than one | Right knee | 99.5 |
| UQU-HA34 | Male | 1.00 | Severe | Episodic | More than one | Left elbow | 94 |
| UQU-HA35 | Male | 2.00 | Severe | Episodic | PDCFC | Both knees | 118.8 |
| UQU-HA36 | Male | 6.00 | Severe | Episodic | PDCFC | Right knee, Left elbow and ankle | 125.4 |
| UQU-HA37 | Male | 1.00 | Moderate | Episodic | PDCFC | Left knee | 49.6 |
| UQU-HA38 | Male | 1.00 | Mild | Episodic | PDCFC | No | NA |
| UQU-HA39 | Male | 1.00 | Moderate | Episodic | PDCFC | No | NA |
| UQU-HB1 | Male | 2.00 | Severe | Episodic | PDCFC | No | 74.5 |
| UQU-HB2 | Male | 1.00 | Severe | Prophylaxis | More than one | Right ankle | 64 |
| UQU-HB3 | Male | 1.00 | Severe | Episodic | More than one | Left ankle | 50.9 |
| UQU-HB4 | Male | 6.00 | Severe | Episodic | More than one | No | 60.1 |
| UQU-HB5 | Male | 12.00 | Mild | Episodic | Fresh frozen plasma | No | 47.3 |
| UQU-HB6 | Male | 11.00 | Severe | Episodic | Fresh frozen plasma | Right knee | 52.2 |
| UQU-HB7 | Male | 16.00 | Severe | Episodic | Fresh frozen plasma | Right knee and both ankles | 53.2 |
| UQU-HB8 | Male | 1.00 | Severe | Episodic | Factor IX concentrates | Both knees | 105.1 |
| UQU-HB9 | Male | 1.00 | Moderate | Episodic | PDCFC | Unable to flex knees fully | 51.4 |
| UQU-HB10 | Male | 1.00 | Mild | Episodic | Factor IX concentrates | Unable to flex knees fully | 45.8 |
| UQU-HB11 | Male | 1.00 | Severe | Episodic | Factor IX concentrates | Unable to flex elbow, knee | 148.3 |
| UQU-HB12 | Male | 12.00 | Mild | Episodic | PDCFC | Unable to flex knees fully | 73.1 |
Table 2. Summary of Mutations Detected in Saudi Arabian Hemophilia Patients
| Patient code | Gene | Mutation type/effect | SIFT/PolyPhen | Exon | Novel/reported | Mutation found |
|---|
| UQU-HA33 | Factor VIII | Point | Missense | Deleterious | 6 | Reported | c.760A>G, p. N254D |
| UQU-HA34 | Factor VIII | Point | Missense | Deleterious | 12 | Reported | c.1835G>C, p. R612P |
| UQU-HA35 | Factor VIII | Point | Missense | Deleterious | 12 | Reported | c.1835G>C, p. R612P |
| UQU-HA36 | Factor VIII | Point | Missense | Deleterious | 4 | Reported | c.409A>C, p. T137P |
| UQU-HA37 | Factor VIII | Point | Splicing site | Tolerated | 23 | Novel | c.6430 - 1G>A, splicing acceptor site |
| UQU-HA38 | Factor VIII | Point | Missense | Deleterious | 1 | Novel | c.99G>T, p. W33C |
| UQU-HA39 | Factor VIII | Deletion | Frameshift | Deleterious | 14 | Novel | c.2138DelA, p. N713Tfs*9 |
| UQU-HB1 | Factor IX | Point | Missense | Deleterious | 8 | Reported | c.1136G>A, p. R379Q |
| UQU-HB2 | Factor IX | Polymorphism | Missense | Tolerated | 6 | Reported | c.580G>A, p. A194T |
| UQU-HB3 | Factor IX | Polymorphism | Missense | Tolerated | 6 | Reported | c.580G>A, p. A194T |
| UQU-HB4 | Factor IX | Point | Missense | Deleterious | 8 | Reported | c.1025C>T, p. T342M |
| UQU-HB5 | Factor IX | Point | Missense | Deleterious | 4 | Reported | c.316G>A, p. G106S |
| UQU-HB6 | Factor IX | Point | Non-sense | Deleterious | 8 | Reported | c.880C>T, p. R294* |
| UQU-HB7 | Factor IX | Point | Non-sense | Deleterious | 8 | Reported | c.880C>T, p. R294* |
| UQU-HB8 | Factor IX | Polymorphism | Missense | Tolerated | 6 | Reported | c.580G>A, p. A194T |
| UQU-HB9 | Factor IX | Polymorphism | Missense | Tolerated | 6 | Reported | c.580G>A, p. A194T |
| UQU-HB10 | Factor IX | Polymorphism | Missense | Tolerated | 6 | Reported | c.580G>A, p. A194T |
| UQU-HB11 | Factor IX | Point | Missense | Deleterious | 8 | Novel | c.855G>C, p. E285D |
| UQU-HB12 | Factor IX | Polymorphism | Missense | Tolerated | 6 | Reported | c.580G>A, p. A194T |







