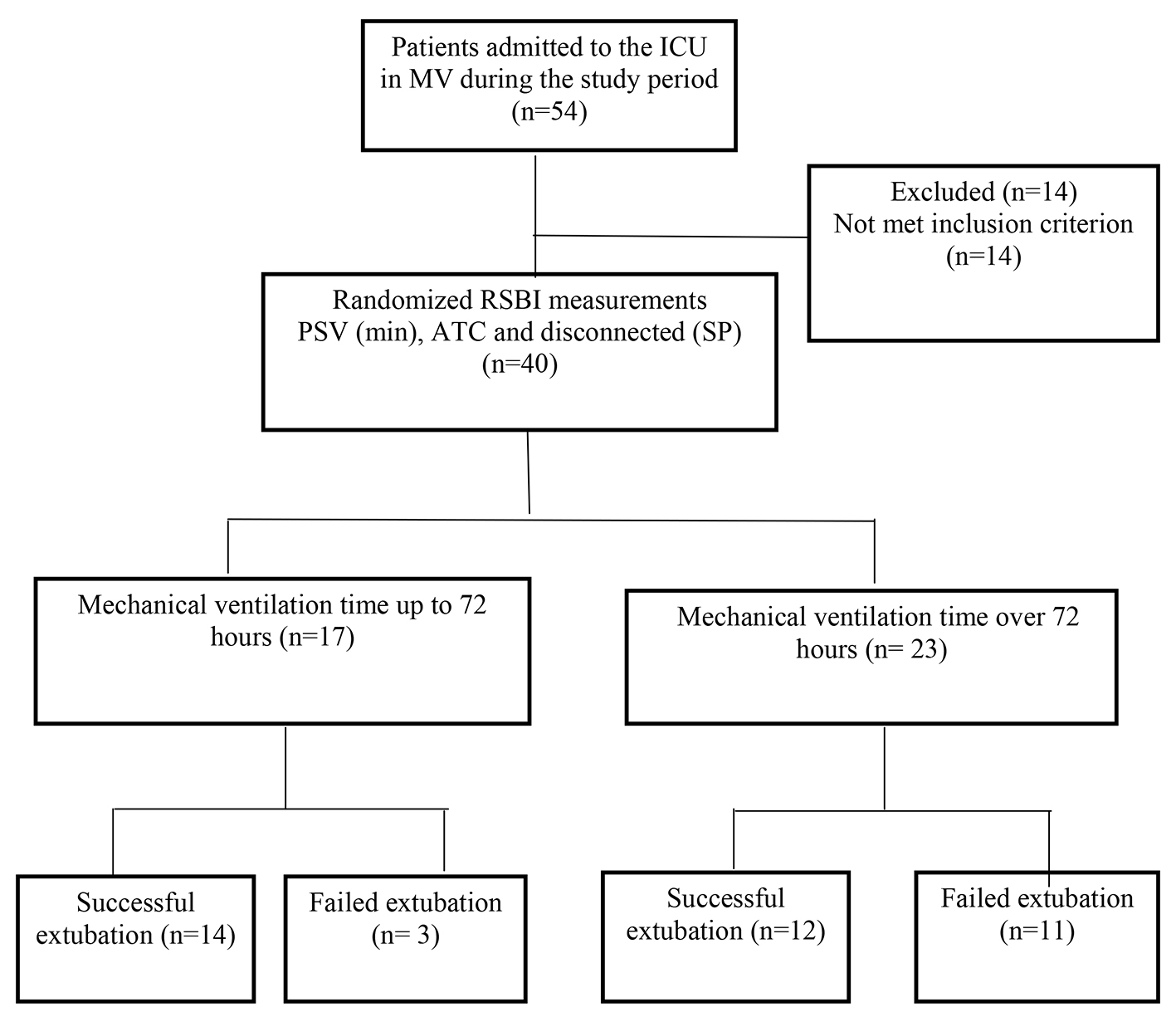
Figure 1. Flowchart of the study design.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 9, Number 4, April 2017, pages 289-296
How Mechanical Ventilation Measurement, Cutoff and Duration Affect Rapid Shallow Breathing Index Accuracy: A Randomized Trial
Figure

Tables
| Characteristics | General (n = 40) | Group submitted to MV < 72 h (n = 17) | Group submitted to MV > 72 h (n = 23) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MV: mechanical ventilation; APACHE II: Acute physiology age chronic health evaluation; NS: without statistical significance. Values expressed as the mean and standard deviation. | ||||
| Age (years) | 58 ± 15 | 52 ± 14 | 58 ± 15 | NS |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 24 (60%) | 10 | 14 | |
| Female | 16 (40%) | 7 | 9 | |
| APACHE II score | 24 ± 7 | 24 ± 9 | 23 ± 6 | NS |
| Period of intubation (days) | 6 ± 4 | 2 ± 1 | 8 ± 3 | < 0.003 |
| Causes of respiratory insufficiency | ||||
| Cardiovascular | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| Hematological | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| Renal metabolism | 6 | 2 | 4 | |
| Neurological | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| Respiratory | 8 | 3 | 5 | |
| Trauma/surgical | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
| Oncological | 3 | 0 | 3 | |
| Vascular | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Others | 7 | 3 | 4 | |
| Up to 72 h of MV (n = 18) | Over 72 h of MV (n = 23) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSBI_MIN | RSBI_ATC | RSBI_SP | RSBI_MIN | RSBI_ATC | RSBI_SP |
| RSBI: rapid shallow breathing index; MIN: obtained with pressure support of 5 cm H2O and PEEP of 5 cm H2O; ATC: obtained in the automatic tube compensation mode and PEEP of 5 cm H2O); SP: obtained with the patient disconnected from mechanical ventilation; NS: without statistical significance. *Intragroup comparison ( RSBI_SP). #Intergroup comparison ( RSBI_SP over 72 h). | |||||
| 38 ± 18# | 46 ± 24# | 55 ± 22# | 39 ± 14* | 51 ± 19* | 78 ± 29 |
| CI: -59.69 to -20.06 #P = 0.000 | CI: 12.41 - 52.05 #P = 0.000 | CI: -43.22 to -3.58 #P = 0.039 | CI : -57.62 to -21.07 *P = 0.000 | CI: 8.46 - 45.01 *P = 0.000 | |
| Group | Up to 72 h of MV | Over 72 h of MV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSBI_MIN | RSBI_ATC | RSBI_SP | RSBI_MIN | RSBI_ATC | RSBI_SP | |
| RSBI: rapid shallow breathing index; MIN: obtained with pressure support of 5 cm H2O and PEEP of 5 cm H2O; ATC: obtained in the automatic tube compensation mode and PEEP of 5 cm H2O; SP: obtained with the patient disconnected from mechanical ventilation; NS: without statistical significance. *Intragroup comparison ( RSBI_SP). #Intergroup comparison ( RSBI_SP failed). | ||||||
| Success | 38 ± 20# CI: -89.61 to -6.5 #P = 0.01 | 45 ± 26 | 51 ± 22 | 37 ± 16*# CI: -54.77 to -1.22 *P = 0.03 CI: -85.25 to -30.49 #P = 0.00 | 45 ± 19# CI: 21.99 - 76.75 #P = 0.000 | 58 ± 18# #P = 0.02 CI: -29.87 to -57.25 |
| Failed | 39 ± 7 | 52 ± 5 | 73 ± 9 | 41 ± 10 *CI: -81.33 to -25.39 *P = 0.000 | 58 ± 18 *CI: 8.30 - 64.24 *P = 0.001 | 93 (28) |
| Cutoff | Method | Sensitivity | Specificity | Positive predictive value | Negative predictive value | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSBI: rapid shallow breathing index; MIN: obtained with pressure support of 5 cm H2O and PEEP of 5 cm H2O; ATC: obtained in the automatic tube compensation mode and PEEP of 5 cm H2O; SP: obtained with the patient disconnected from mechanical ventilation. | ||||||
| 50 | RSBI_MIN | 0.92 | 0.27 | 0.58 | 0.75 | 0.61 |
| RSBI_ATC | 0.75 | 0.55 | 0.64 | 0.67 | 0.65 | |
| RSBI_SP | 0.33 | 0.91 | 0.80 | 0.56 | 0.61 | |
| 78 | RSBI_MIN | 0.92 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 0.48 |
| RSBI_ATC | 0.92 | 0.27 | 0.58 | 0.75 | 0.61 | |
| RSBI_SP | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.74 | |
| 105 | RSBI_MIN | 1.0 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.50 |
| RSBI_ATC | 1.0 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 1.00 | 0.52 | |
| RSBI_SP | 0.92 | 0.27 | 0.58 | 0.75 | 0.61 | |