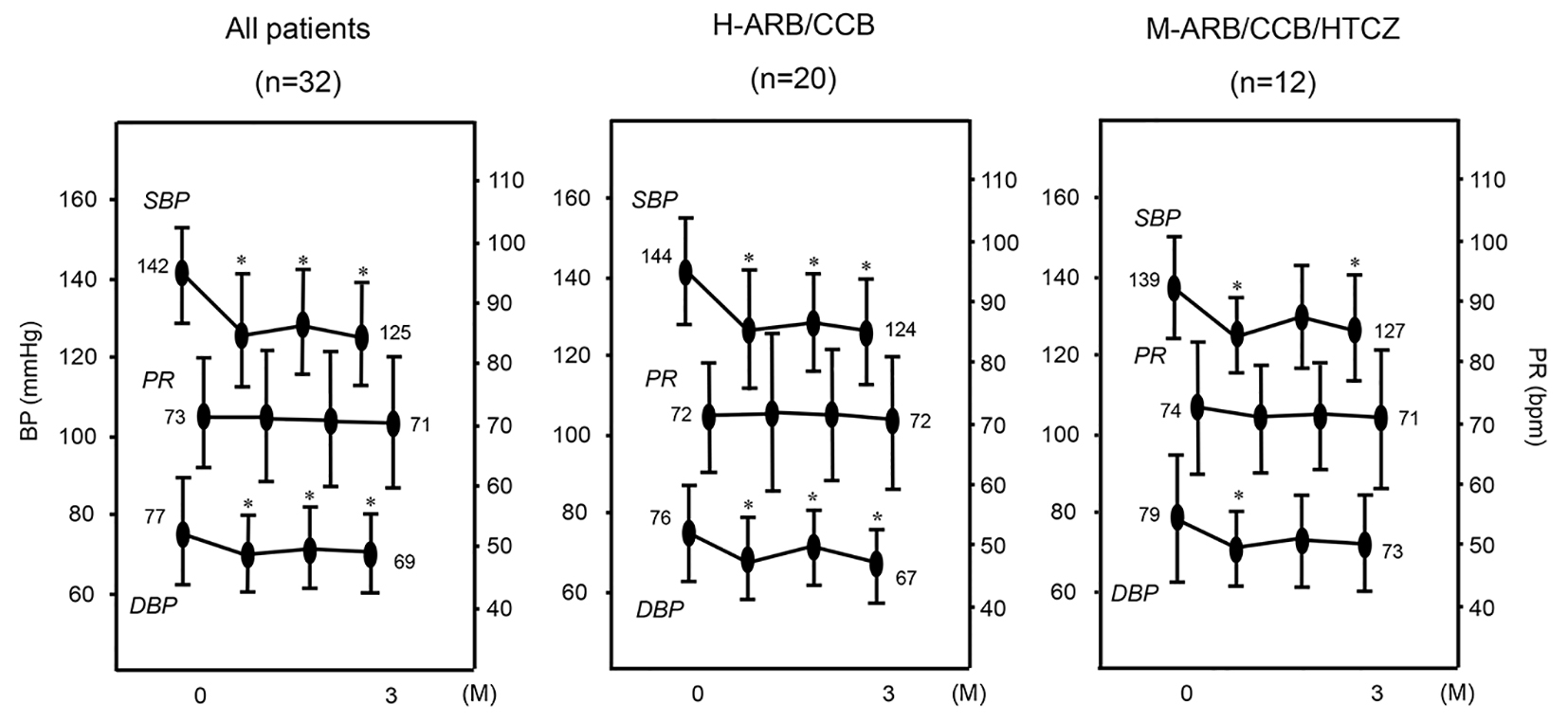
Figure 1. Changes in SBP, DBP and PR in all patients (n = 32) and in the H-ARB/CCB (n = 20) and M-ARB/CCB/HCTZ (n = 12) groups. *P < 0.05 vs. 0 months (M).
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 9, Number 2, February 2017, pages 98-103
Efficacy and Safety of Combination Therapy Consisting of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blocker, Calcium Channel Blocker and Hydrochlorothiazide in Patients With Hypertension
Figures

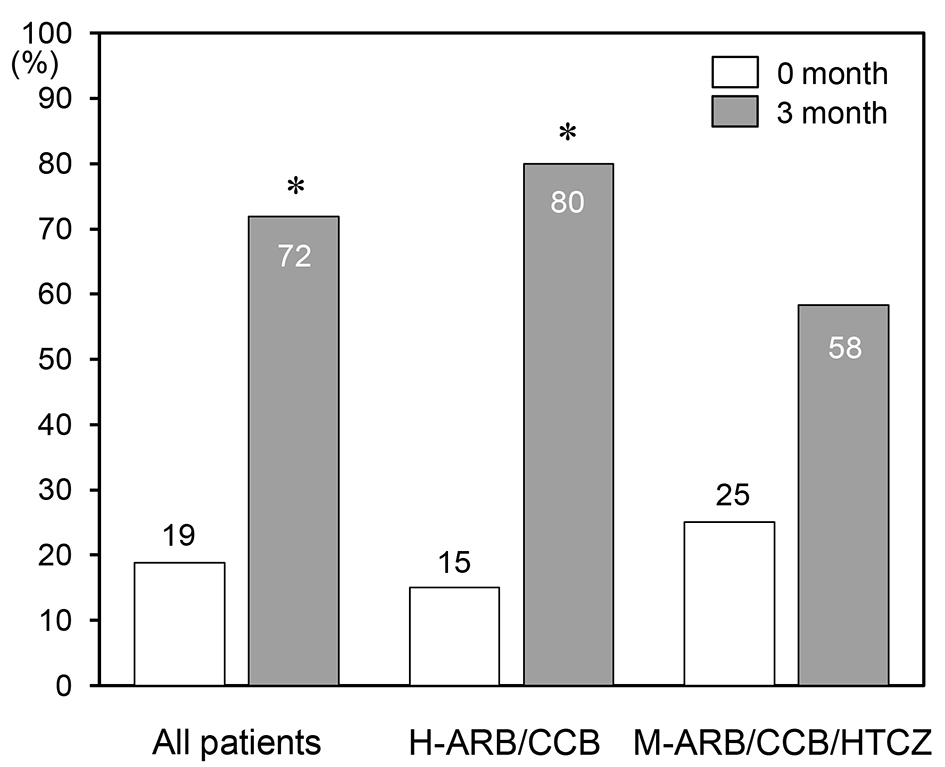
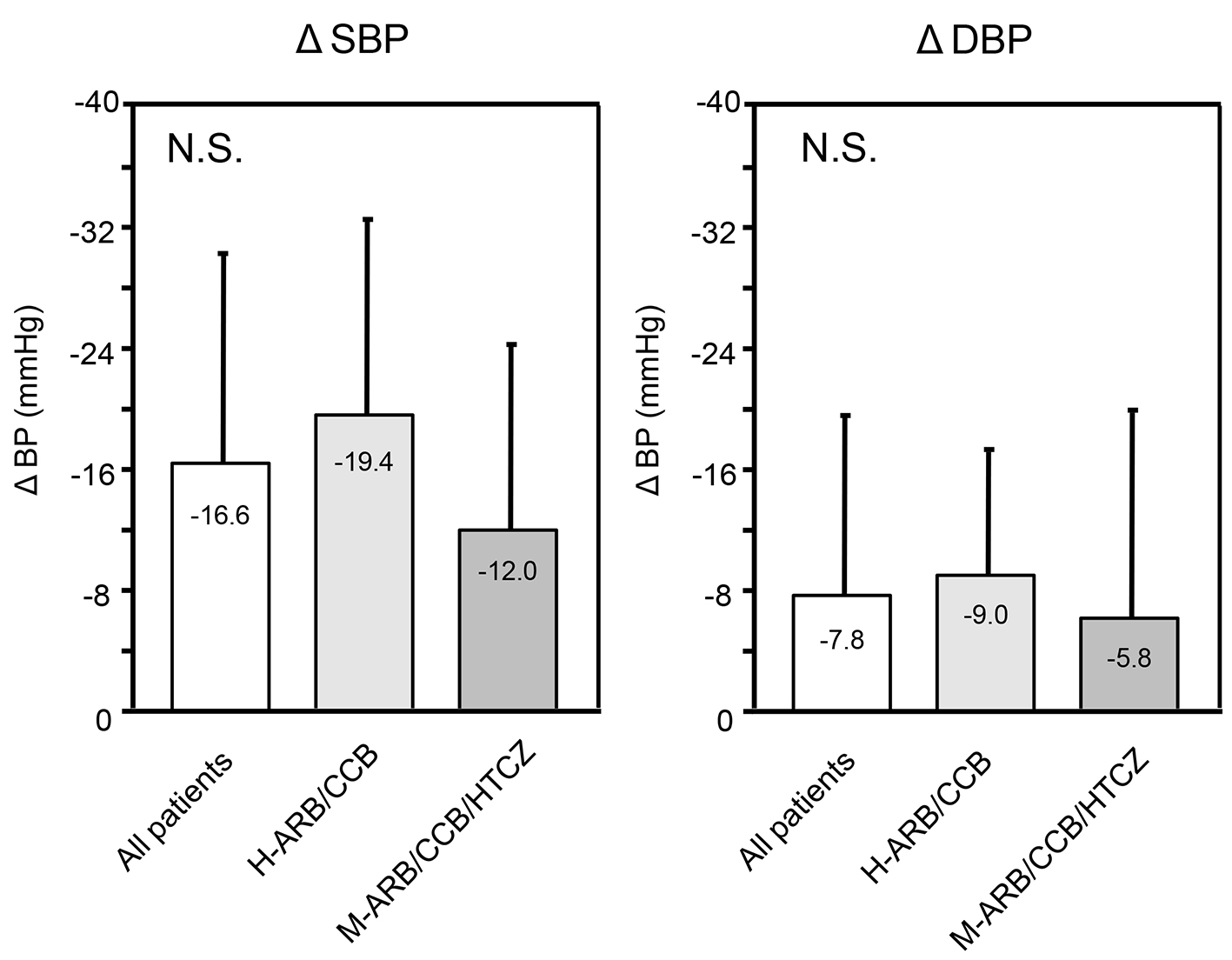
Tables
| All patients (n = 32) | H-ARB/CCB (n = 20) | M-ARB/CCB/HTCZ (n =12) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± SD. BMI: body mass index; WC: waist circumference; DL: dyslipidemia; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG: triglyceride; DM: diabetes mellitus; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; HU: hyperuricemia; UA: uric acid; CAD: coronary artery disease. | |||
| Age, years | 69 ± 15 | 69 ± 16 | 68 ± 13 |
| Gender (male), n (%) | 16 (50) | 11 (55) | 5 (42) |
| Smoking, n (%) | 11 (34) | 8 (40) | 3 (25) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.9 ± 4.3 | 23.8 ± 4.6 | 24.0 ± 3.9 |
| WC, cm | 85.7 ± 10.2 | 86.1 ± 11.1 | 87.0 ± 8.9 |
| DL, n (%) | 18 (56) | 10 (50) | 8 (67) |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 104 ± 32 | 106 ± 35 | 100 ± 27 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 52 ± 12 | 51 ± 13 | 52 ± 10 |
| TG, mg/dL | 145 ± 92 | 138 ± 92 | 155 ± 95 |
| DM, n (%) | 5 (16) | 3 (15) | 2 (17) |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 102 ± 29 | 102 ± 35 | 103 ± 16 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.3 ± 0.9 | 5.4 ± 1.0 | 5.2 ± 0.5 |
| HU, n (%) | 6 (19) | 4 (20) | 2 (12) |
| UA, mg/dL | 5.4 ± 1.3 | 5.3 ± 1.2 | 5.7 ± 1.4 |
| CAD, n (%) | 4 (13) | 4 (20) | 0 (0) |
| All patients (n = 32) | H-ARB/CCB (n = 20) | M-ARB/CCB/HTCZ (n = 12) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCBs: calcium channel blockers; ARBs: angiotensin II receptor blockers; HCTZ: hydrochlorothiazide. | |||
| Medication use | |||
| CCBs | |||
| Nifedipine 40 mg, n (%) | 25 (78) | 14 (70) | 11 (92) |
| Amlodipine 5 mg, n (%) | 7 (22) | 6 (30) | 1 (8) |
| β-blocker, n (%) | 1 (3) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) |
| α-blocker, n (%) | 1 (3) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) |
| Medication use before changeover | |||
| ARBs, n (%) | 20 (63) | 20 (100) | 0 (0) |
| Telmisartan 80 mg, n (%) | 12 (38) | 12 (60) | 0 (0) |
| Olmesartan 40 mg, n (%) | 6 (19) | 6 (30) | 0 (0) |
| Valsartan 160 mg, n (%) | 2 (6) | 2 (10) | 0 (0) |
| Losartan 50 mg + HCTZ 12.5 mg, n (%) | 12 (38) | 0 (0) | 12 (100) |
| All patients (n = 32) | H-ARB/CCB (n = 20) | M-ARB/CCB/HTCZ (n = 12) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 months | 3 months | 0 months | 3 months | 0 months | 3 months | |
| BUN: blood urea nitrogen; Cr: creatinine; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; UA: uric acid; Na: sodium; K: potassium; TG: triglyceride; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; FPG: fast plasma glucose; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide. *P < 0.05 vs. 0 months. | ||||||
| BUN, mg/dL | 18 ± 11 | 20 ± 12 | 17 ± 12 | 21 ± 15 | 20 ± 7 | 19 ± 6 |
| Cr, mg/dL | 0.9 ± 0.4 | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 0.9 ± 0.5 | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 0.9 ± 0.4 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 63 ± 21 | 61 ± 23 | 67 ± 22 | 63 ± 25 | 56 ± 18 | 60 ± 20 |
| UA, mg/dL | 5.4 ± 1.3 | 6.0 ± 1.3* | 5.3 ± 1.2 | 6.0 ± 1.3* | 5.7 ± 1.4 | 6.2 ± 1.3 |
| Na, mEq/L | 141 ± 2 | 140 ± 3 | 141 ± 2 | 140 ± 3 | 140 ± 2 | 140 ± 3 |
| K, mEq/L | 4.0 ± 0.5 | 4.1 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ± 0.6 | 4.2 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ± 0.4 | 4.1 ± 0.6 |
| TG, mg/dL | 145 ± 92 | 135 ± 72 | 138 ± 92 | 120 ± 61 | 155 ± 95 | 159 ± 84 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 104 ± 32 | 102 ± 30 | 106 ± 35 | 104 ± 34 | 127 ± 46 | 129 ± 31 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 52 ± 12 | 56 ± 16 | 51 ± 13 | 58 ± 18 | 52 ± 10 | 52 ± 10 |
| FPG, mg/dL | 102 ± 229 | 116 ± 81 | 102 ± 35 | 122 ± 10 | 103 ± 16 | 106 ± 24 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.3 ± 0.9 | 5.5 ± 0.8* | 5.4 ± 1.0 | 5.5 ± 1.0 | 5.2 ± 0.5 | 5.4 ± 0.5 |
| BNP, pg/mL | 67 ± 92 | 55 ± 72 | 66 ± 70 | 66 ± 87 | 70 ± 124 | 36 ± 28 |