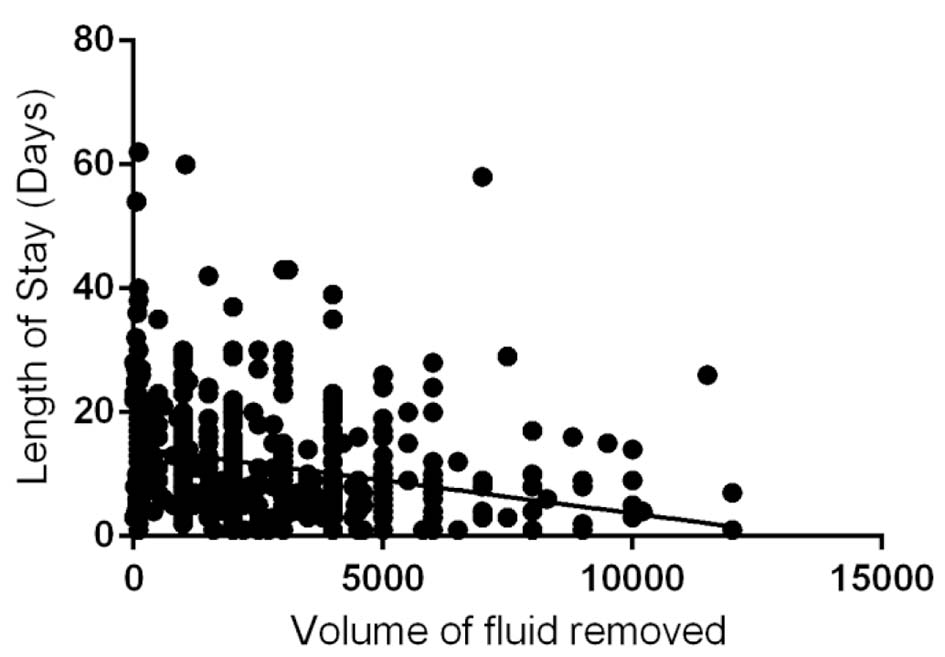
Figure 1. Correlation between volume of ascetic fluid (mL) and hospital length of stay (P < 0.0001; 95% CI of slope -0.001398 to -0.0007311; R2 = 0.07076).
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 9, Number 2, February 2017, pages 92-97
Computerized Tomography-Guided Paracentesis: An Effective Alternative to Bedside Paracentesis?
Figure

Tables
| Characteristic | Bedside paracentesis | CT-guided paracentesis | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| †MELD scoring is a system for assessing the severity of chronic liver disease and is calculated by the formula: MELD = 3.78(Ln serum bilirubin (mg/dL)) + 11.2(Ln INR) + 9.57(Ln serum creatinine (mg/dL)) + 6.43. ¶NSBB: non-selective beta blockers. ‡P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. | |||
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 57.45 ± 10.11 | 58 ± 11 | 0.55 |
| Race | |||
| African American | 126 (46.3) | 112 (45.3) | 0.86 |
| Hispanics | 144 (52.9) | 134 (54.2) | 0.79 |
| Others | 2 (0.73) | 1 (0.4) | 1 |
| Male sex, no. (%) | 195 (71.7) | 137 (55.3) | 0.0002‡ |
| MELD† score, mean ± SD | 18.79 ± 7.55 | 20.99 ± 7.25 | 0.0006‡ |
| Medications, no. (%) | |||
| Lactulose | 196 (72) | 188 (76) | 0.31 |
| NSBB¶ | 146 (53.7) | 136 (57.02) | 0.79 |
| Aspirin | 82 (30.1) | 69 (27.9) | 0.62 |
| Plavix | 9 (0.03) | 4 (0.016) | 0.26 |
| Variable | Bedside paracentesis | CT-guided paracentesis | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| †Therapeutic paracenteses only. Diagnostic paracenteses were excluded. †P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. ΩDefined as drop in hemoglobin by 1 g/dL or local complications like hematoma formation. €Defined as positive ascitic fluid (removed with either of the therapeutic procedures) bacterial cultures after an initial negative culture result during same admission (thus ruling out SBP). ¥Defined as absolute increase of ≥ 0.3 mg/dL in serum creatinine concentration or a ≥ 50% increase in the serum creatinine concentration within 48 h of procedure. | |||
| Volume of fluid removed (L), mean ± SD | 2.15 ± 2.06 | 3.54 ± 2.61 | 0.0001‡ |
| Patients requiring repeat Paracentesis† within 1 year, no. (%) | 144 (52.9) | 130 (52.6) | 0.86 |
| Interval between successive paracenteses† in days (no. of patients), mean ± SD | 38.69 ± 33.72 (144) | 53.88 ± 50.03 (130) | 0.0032‡ |
| Length of hospital stay, mean ± SD | 12.24 ± 8.54 | 10.49 ± 9.97 | 0.0318‡ |
| Complications, no. (%) | |||
| BleedingΩ | 4 (1.4) | 0 (0) | 0.12 |
| Infections€ | 1 (0.36) | 4 (1.6) | 0.19 |
| Bowel perforation | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.00 |
| ARF¥ | 2 (0.008) | 3 (0.01) | 1.00 |
| Deaths due to the procedure | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.00 |
| Deaths in index admission, no. (%) | 20 (8.26) | 12 (4.85) | 0.28 |
| Discharge diuretic dose, mg | |||
| Spironolactone (no. of patients), mean ± SD | 83.5 ± 53.4 (250) | 64.80 ± 60.13 (234) | 0.0003‡ |
| Furosemide (no. of patients), mean ± SD | 48 ± 26.05 (124) | 44.55 ± 38.14 (101) | 0.42 |