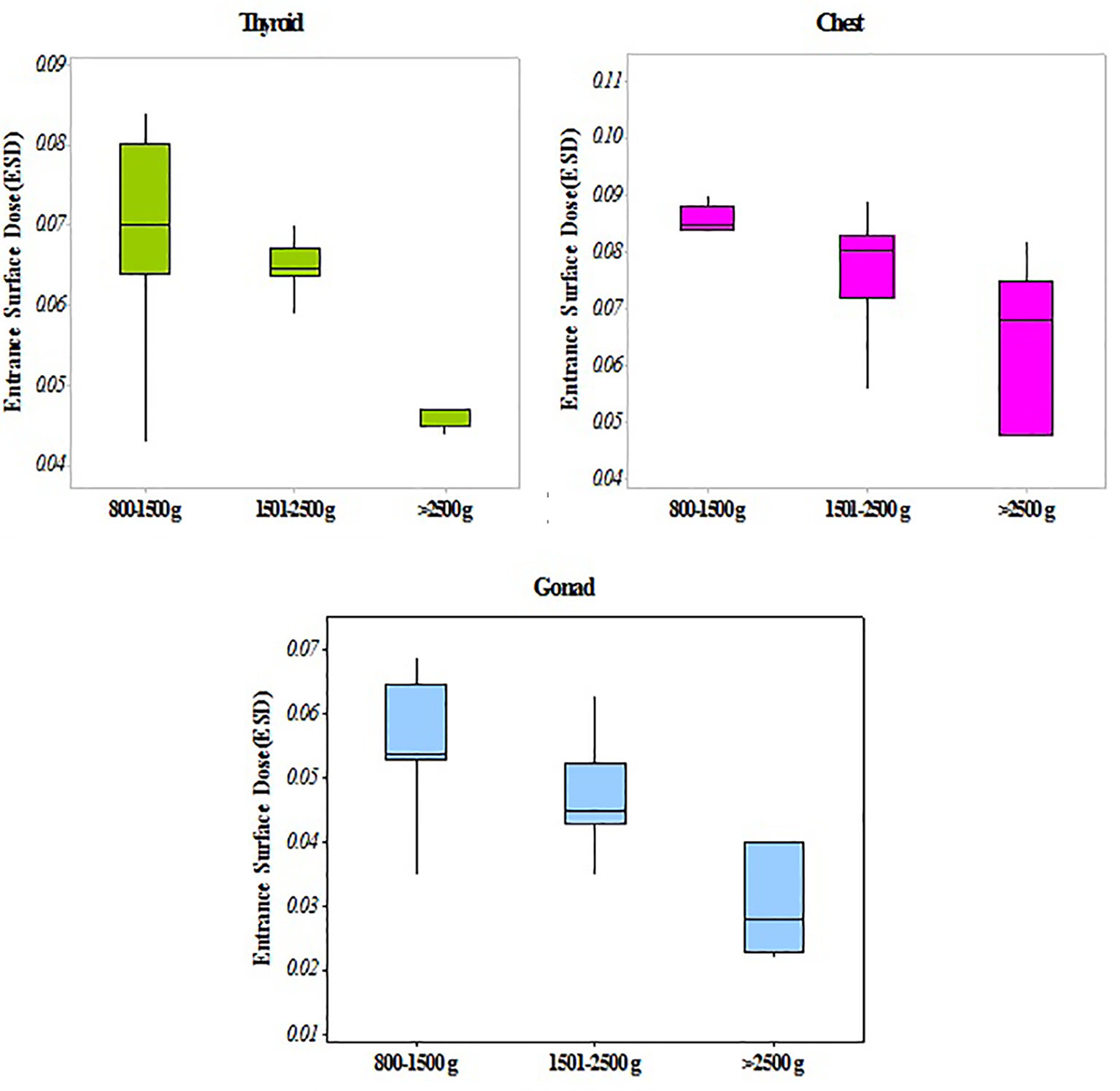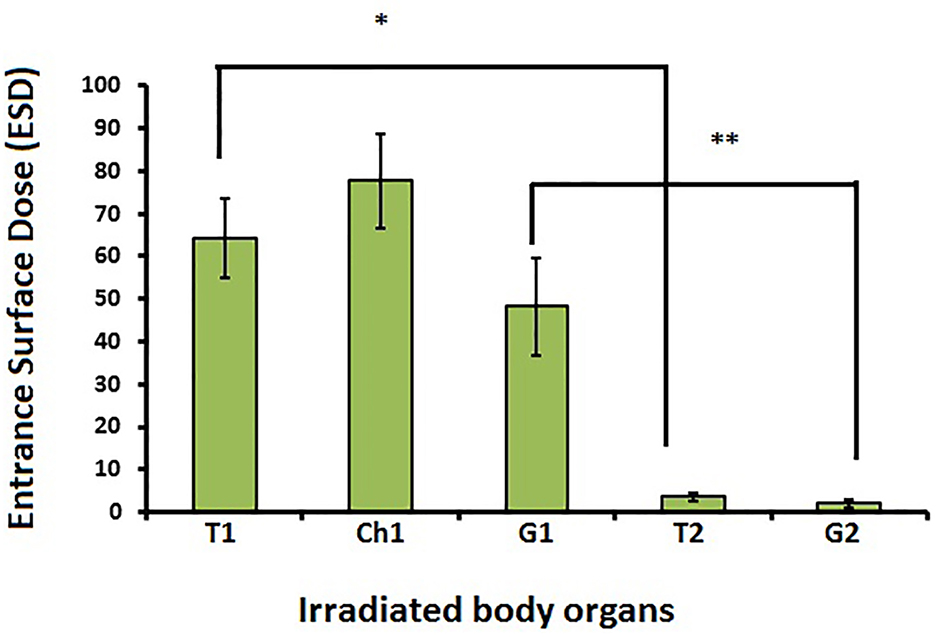
Figure 1. Comparison between mean ESD (mSv) in different infant’s body organs. T1: thyroid of first newborn; Ch1: chest of first new born; G1: gonad of first newborn; T2: thyroid of second newborn; G2: gonad of second newborn. *Comparison of ESD between T1 and T2 (P < 0.001). **Comparison of ESD between G1 and G2 (P < 0.001).