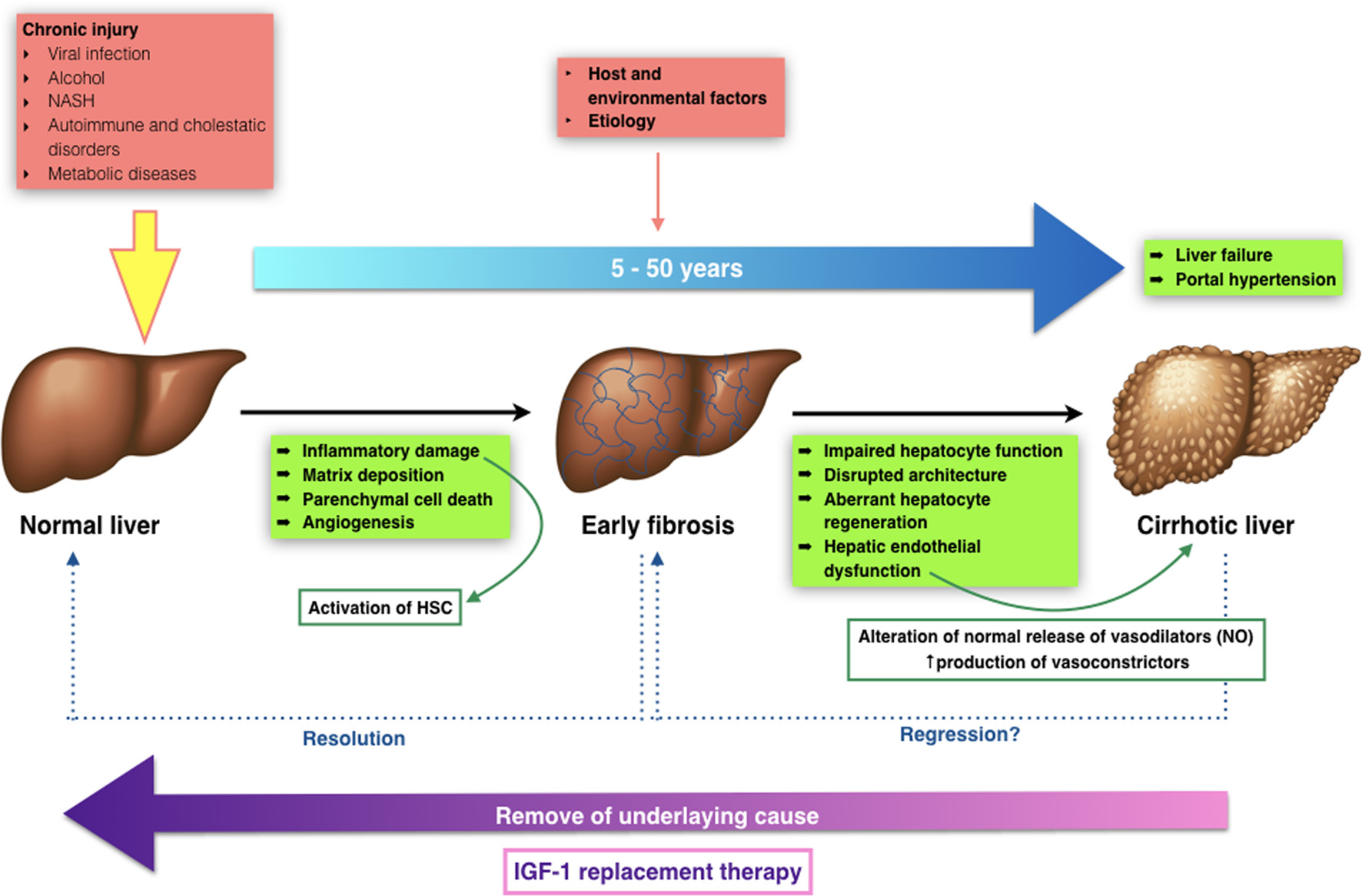
Figure 1. Transition from normal to liver cirrhosis.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 9, Number 4, April 2017, pages 233-247
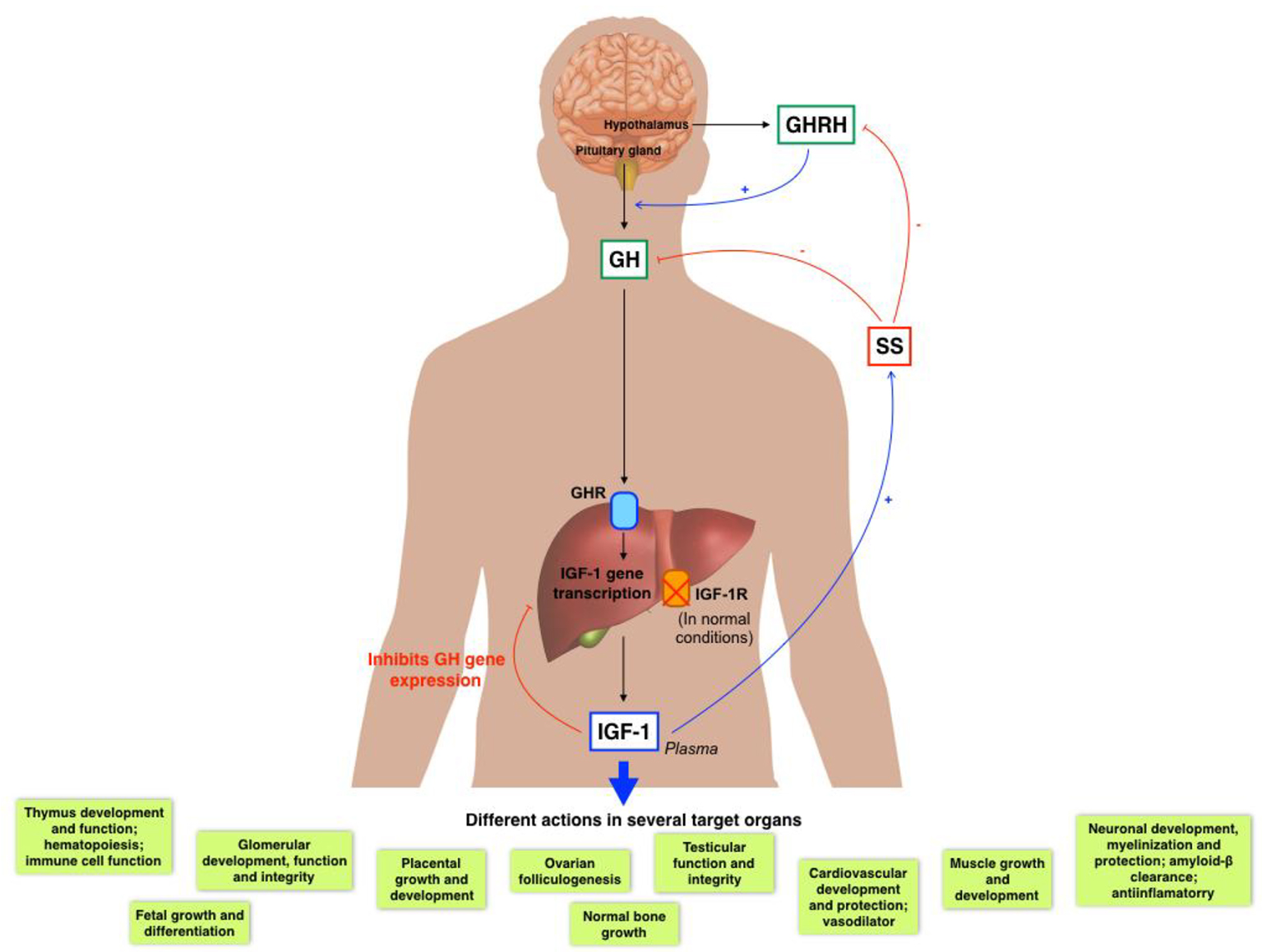
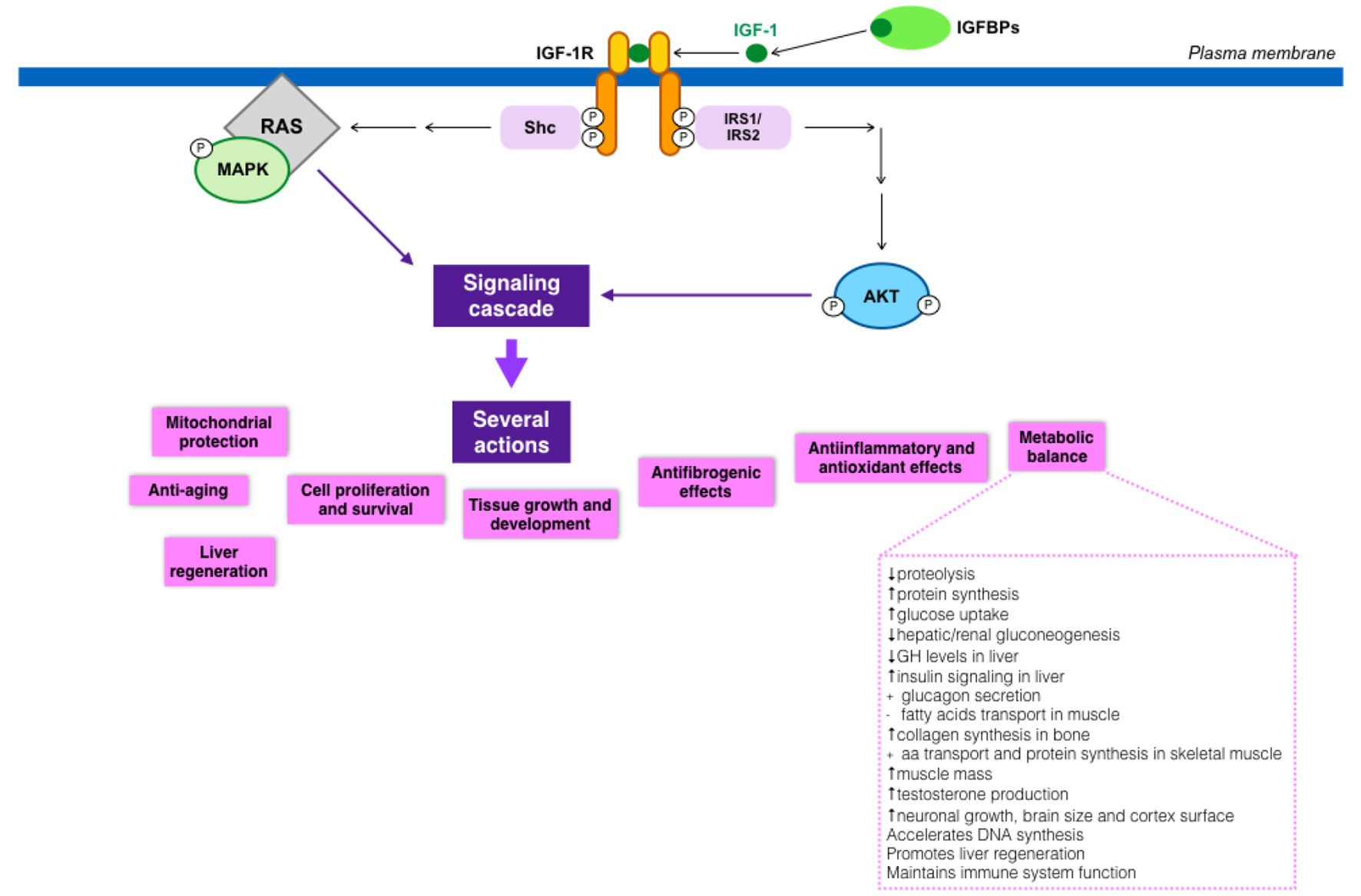
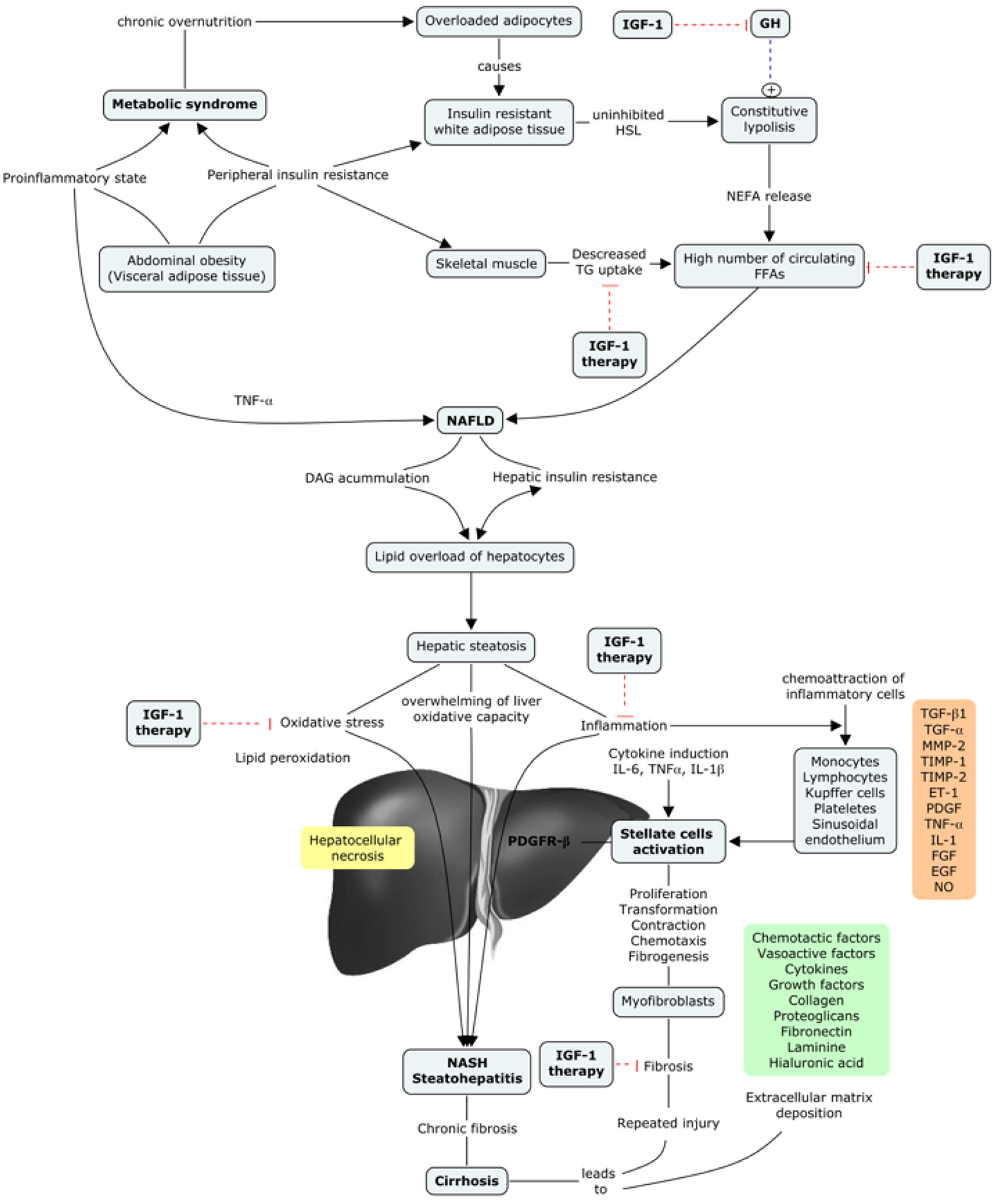
Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Deficiency and Cirrhosis Establishment
Figures

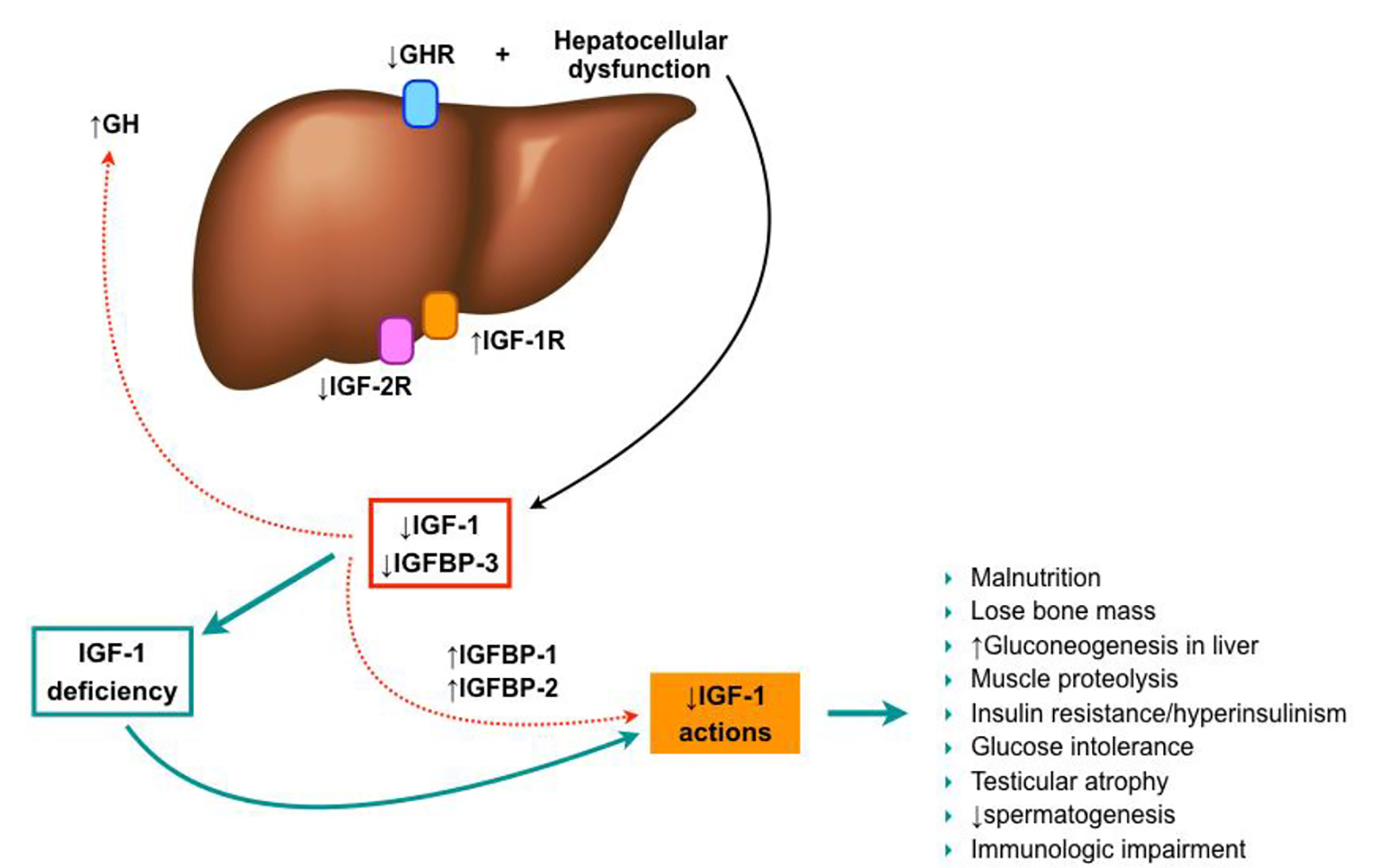
Tables
| Region name | Alcohol | Hepatitis B | Hepatitis C | Other* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Not attributable to chronic alcohol intake, and tested negative to anti-VHC antibodies and HbsAg. Adapted from Mokdad et al, BMC Medicine 2014;12:145. | ||||
| Asia Pacific, high income | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.20 |
| Asia, Central | 0.16 | 0.36 | 0.18 | 0.29 |
| Asia, East | 0.18 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.26 |
| Asia, South and Southeast | 0.40 | 0.58 | 0.44 | 0.59 |
| Australia | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.18 | 0.21 |
| Caribbean | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.36 |
| Europe, Central | 0.27 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.36 |
| Europe, Eastern | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.34 |
| Europe, Western | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.30 | 0.27 |
| Latin America, Andean | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.36 |
| Latin America, Central | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.26 | 0.37 |
| Latin America, Southern | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.28 | 0.29 |
| Latin America, Tropical | 0.31 | 0.06 | 0.27 | 0.37 |
| North America, high income | 0.33 | 0.06 | 0.29 | 0.32 |
| North Africa, Middle East | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.36 |
| Sub-Saharan Africa, Central | 0.15 | 0.37 | 0.20 | 0.27 |
| Sub-Saharan Africa, East | 0.16 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.30 |
| Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern | 0.19 | 0.37 | 0.18 | 0.27 |
| Sub-Saharan Africa, West | 0.15 | 0.38 | 0.18 | 0.28 |
| Oceania | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.17 | 0.26 |
| Tipo | Mediator | Target cells and mechanisms of action | Liver disease/model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adapted from Seki et al, Hepatology, 2015. | |||
| Inflammatory cytokines | IL-1 | Up-regulates TIMP-1 and down-regulates BAMBI in HSCs. Promotes HSC survival. Promotes lipid accumulation and cell death in hepatocytes during NASH and ALD. | Experimental fibrosis induced by BDL or TAA; experimental NASH by CDAA diet; experimental ALD model induced by Lieber-DeCarli and ethanol binge injection. |
| IL-33 | Secreted from damaged hepatocytes, stimulating ILC2 to produce IL-13 that in turn activates HSC. | Human liver cirrhosis; experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4, TAA or Schistosoma mansonii infection. | |
| TNF-α | Induces apoptosis of the hepatocytes. Up-regulates TIMP-1 and down-regulates BAMBI in HSCs. Promotes HSC survival and proliferation. Activates liver macrophages. | Experimental fibrosis induced by BDL; experimental NASH model induced by MCD diet. | |
| IL-17 | Stimulates KCs and HSC to produce IL-6, TNF-α, and TGF-β. Activates NF-kB and STAT3 in KCs and HSCs. HSCs activation through STAT3. | Hepatitis B, experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4 or BDL. | |
| IL-20 | Promotes activation, proliferation, and migration of HSCs. Prevents hepatocyte injury. | HBV- and HCV-induced liver cirrhosis; experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4. | |
| IL-22 | Induces HSC senescence through STAT3-p53. HSC senescence inhibits liver fibrosis. | HBV-, HCV- and alcohol-induced liver cirrhosis; experimental fibrosis induced by CCL4. | |
| IFN-γ | Suppresses HSC proliferation and activation. Activates NK cells to promote HSC killing. | Experimental fibrosis induced CCl4. | |
| Chemokines | CCl2 (MCP-1) | Macrophage and HSC recruitment; HSC activation. | Experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4 or BDL; experimental NASH model induced by MCD or CDAA diet. |
| CCL5 | Macrophage and HSC recruitment; HSC activation. | Experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4. | |
| CXCL9 | Suppresses HSC activation. Inhibits angiogenesis that inhibits liver fibrosis. | Experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4. | |
| CXCL10 | Promotes hepatocyte death and HSC activation. Inhibits NK cell-mediated HSC inactivation. | Experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4. | |
| CX3CL1 | Prolongs KC survival. Promotes anti-inflammatory property in KCs. | Experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4 or BDL. | |
| Gut microbiota axis/TLR pathway | TLR4 | Directly stimulates HSC to down-regulate BAMBI and produce chemokines in BDL and CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. Stimulates KCs to produce proinflammatory and fibrogenic cytokines that activate HSCs in ALD and NASH. Stimulates LSECs to induce angiogenesis that promotes HSC activation and fibrosis. | Experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4 or BDL; experimental NASH model induced by MCD or CDAA diet; experimental ALD model induced by Lieber-DeCarli or Tsukamoto-French model. |
| TLR2 | Stimulates KCs to produce cytokines that activate HSCs in NASH. Stimulates macrophages in intestine, which promote bacterial translocation. | Experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4 or BDL; experimental NASH model induced by CDAA diet. | |
| TLR9 | Stimulates KCs to produce cytokines that activate HSCs in NASH. Stimulates HSCs by host DNA released from apoptotic Hepatocytes. | Experimental NASH model induced by CDAA diet; experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4 or BDL. | |
| TLR3 | Stimulates NK cells to produce IFN-c that induces antifibrotic effect by killing HSCs. | Experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4 or Lieber-DeCarli plus CCl4. | |
| TLR7 | Stimulates DCs to produce type I IFN that inhibits liver fibrosis. | Experimental fibrosis induced by CCl4 or BDL. | |
| Up-regulated hepatoprotective factors | Down-regulated profibrogenic factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Same factors could be involved in the positive clinical outcome seen when supplementing with rhIGF-1. | |||
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor | Activated HSC | Activated hepatic stellate cells |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteases | αSMA | α-smooth muscle actin |
| HNF4α | Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α | TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-β |
| STAT3a | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3a | STAT3b | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3a |
| Egfr | Epidermal growth factor receptor | TIM1 and TIM2 | Tissue inhibitors of MMPs |
| Hnf6 | Hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 | PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| Prlr | Prolactin receptor | CTGF | Connective tissue growth factor |
| Lifr | Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor | WT-1 | Wilm’s tumor 1 |