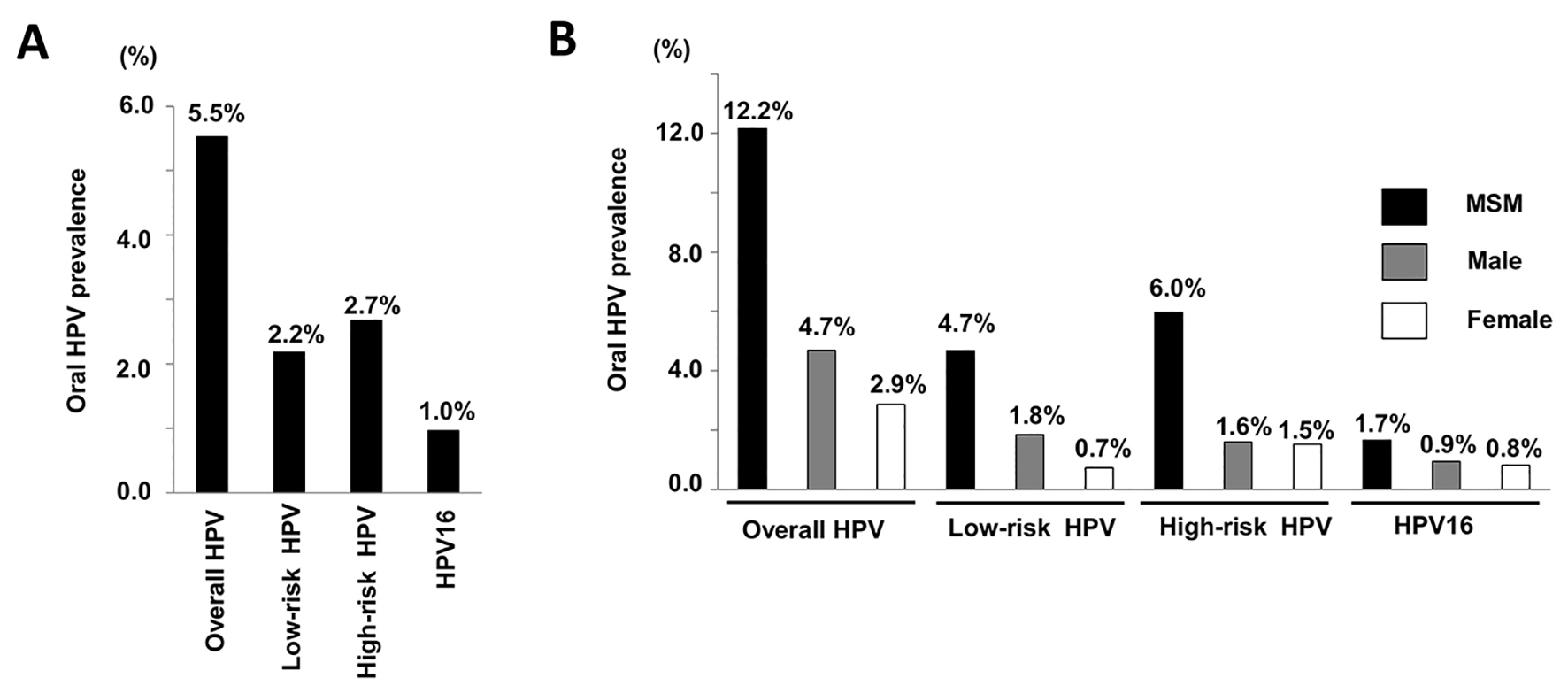
Figure 1. HPV prevalence of MSM, male and female. (A) Mean prevalence of overall HPV, low-risk type HPV, high-risk type HPV and HPV16. The prevalence rates for overall HPV, low- and high-risk type HPV, and HPV16 were 5.5%, 2.2%, 2.7%, and 1.0%, respectively. (B) Mean prevalence of selected oral HPV groups and HPV16 among MSM, male and female. The prevalence of all HPV types was considerably higher in the MSM group as compared to males and females.
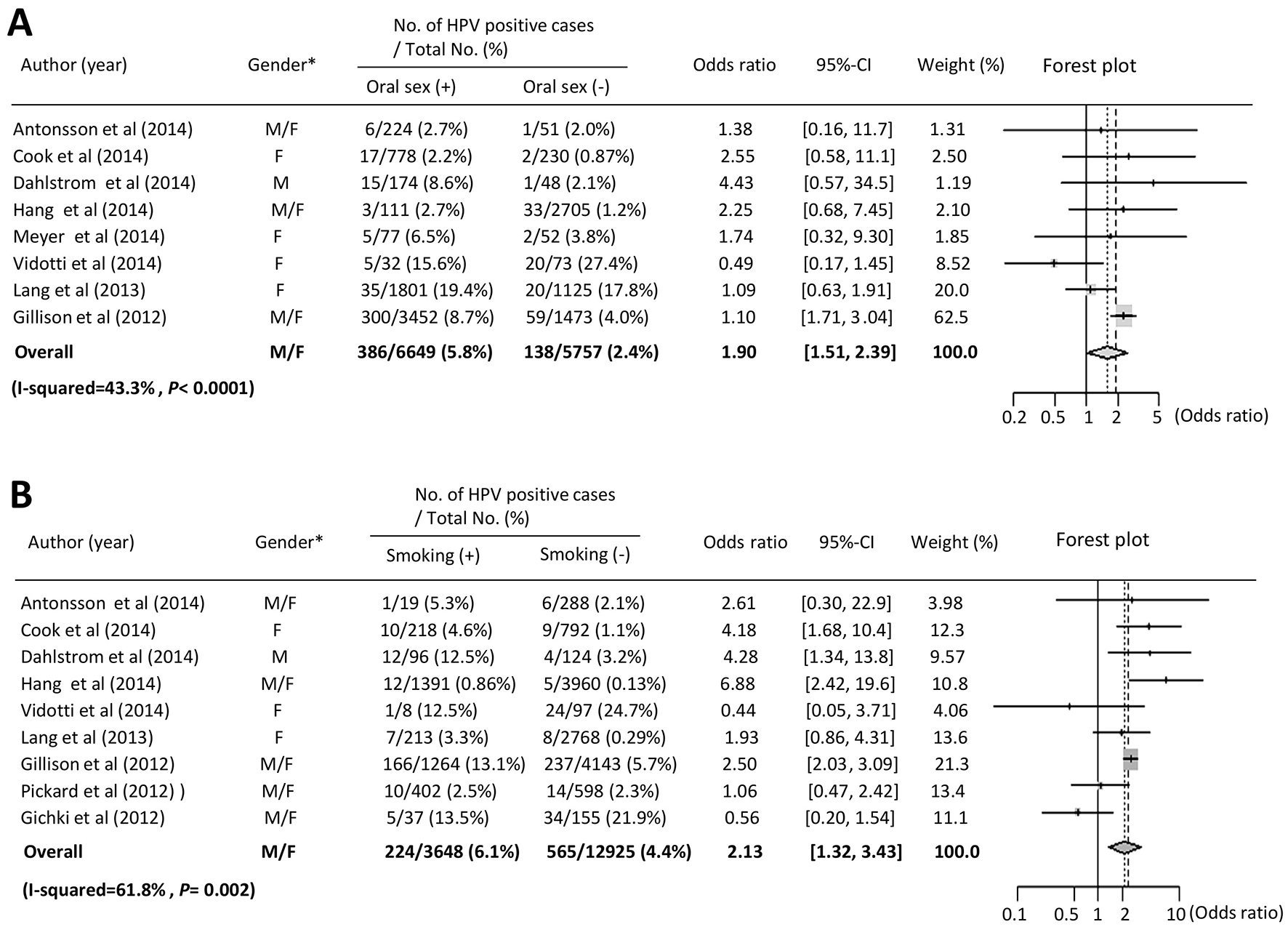
Figure 2. Meta-analysis of the association between oral HPV infection and sexual behavior, smoking and drinking. (A) Forest plot of overall oral HPV infection and oral sex. Meta-analysis using a fixed effects model demonstrated that oral sex was significantly correlated with oral HPV infection (P < 0.0001). *Gender: M: male; F: female. (B) Forest plot of overall HPV infection and smoking. Meta-analysis using a random effects model demonstrated that smoking status was significantly correlated with oral HPV infection (P = 0.002). *Gender: M: male; F: female.

