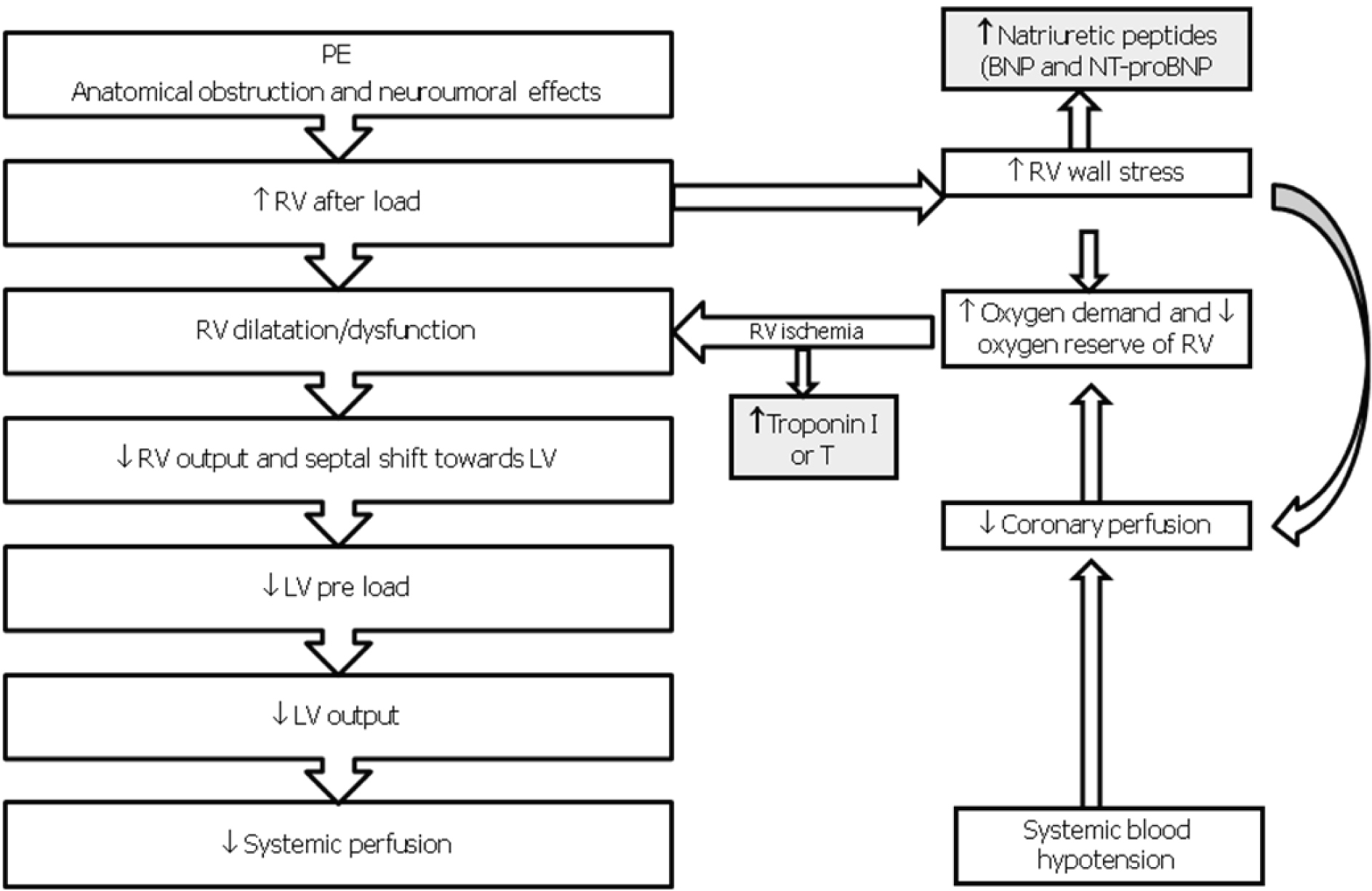
Figure 1. Pathophysiology of hemodynamic instability due to PE. RV, Right Ventricle; LV, Left Ventricle; BNP, Brain Natriuretic Peptide; NT-proBNP, AminoTerminal-proBrain Natriuretic Peptide.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 1, Number 1, April 2009, pages 1-7
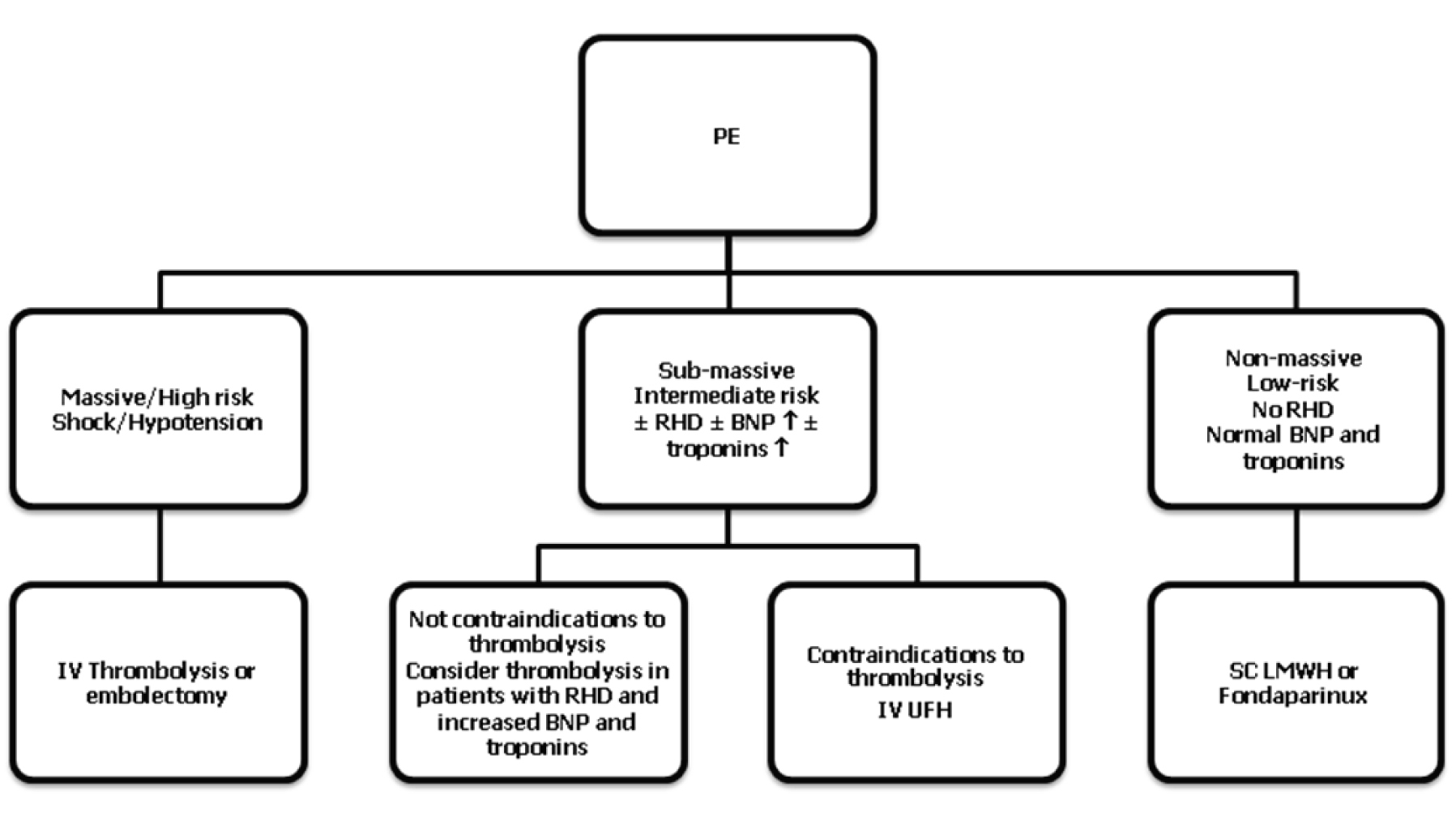
The Risk-based Treatment of Acute Pulmonary Embolism
Figures

Tables
| ATS, American Thoracic Society; ESC, European Society of Cardiology; BTS, British Thoracic Society; ACEP; American College of Emergency Physicians; ACCP; American College of Chest Physicians; RHD; right heart dysfunction. |
ATS 1999, ESC 2000, BTS 2003, ACEP 2003, ACCP 2004, ACCP 2008
|
ESC 2008
|
| Risk (mortality in acute phase %) | Shock/hypotension | Echocardiographic and biomarkers findings of RHD (↑BNP or NTpro-BNP) | Findings of myocardial injury: ↑ troponin I or T |
|---|---|---|---|
| *generally present but not necessary to define high risk | |||
| High (15%) | Present | Present* | Present* |
| Intermediate (3 - 15%) | Absent Absent Absent | Present Absent Present | present Present Absent |
| Low (< 3%) | Absent | Absent | Absent |
Absolute
|
Relative
|