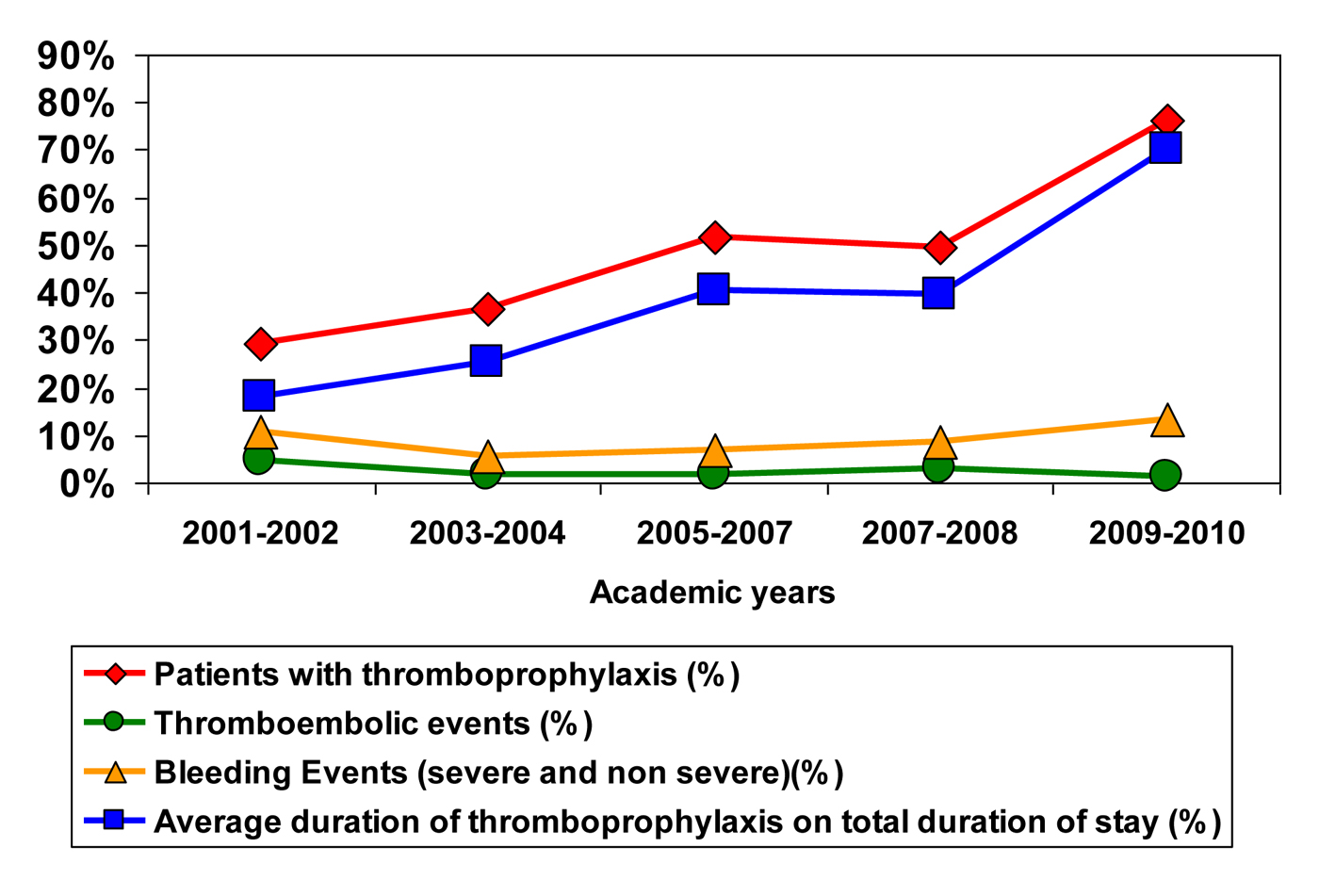
Figure 1. Proportion of patients and duration of thromboprophylaxis with incidence of thromboembolic and bleeding events.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 6, Number 2, April 2014, pages 91-97
Lack of Clinical Benefit of Thromboprophylaxis in Patients Hospitalized in a Medical Unit Over a 10-year Span
Figure

Tables
| Total population (%) | High risk patients (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| DVT: deep vein thrombosis; MSK: musculosquelettal; PE: Pulmonary embolism; psy: psychiatric; VTE: venous thromboembolic event. | ||
| Number of patients | 2369 | 1302 |
| Male gender | 967 (40.8) | 567 (43.5) |
| Female gender | 1402 (59.2) | 735 (56.5) |
| Average length of stay (days) | 15 | 18 |
| Age on admission (year) | 68 | 70 |
| Diagnosis on admission | ||
| Non-specified generalized weakness | 218 (9.2) | 113 (8.7) |
| Neurologic disease | 233 (9.8) | 153 (11.8) |
| Pulmonary disease | 65 (2.7) | 45 (3.5) |
| Cardiovascular disease | 186 (7.9) | 97 (7.5) |
| Gastrointestinal disease | 173 (7.3) | 65 (5.0) |
| Nephro - endo - metab | 167 (7.1) | 72 (5.5) |
| Hematologic disease (no cancer) | 129 (5.4) | 44 (3.4) |
| Neoplasia | 321 (13.6) | 286 (21.9) |
| Rhumatologic and inflammatory | 133 (5.6) | 40 (3.1) |
| Infectious disease | 363 (15.3) | 278 (21.3) |
| Substance withdrawal or intox | 59 (2.5) | 33 (2.5) |
| Dermato - psy - MSK - allergy | 184 (7.8) | 76 (5.9) |
| Thromboembolic disease | 138 (5.8) | 0 |
| Palliative care | 222 (9) | 196 (15) |
| Risk factors for VTE | ||
| Average number of risk factors | 1.11 | 1.56 |
| Congestive heart failure | 406 (17.1) | 305 (23.5) |
| Severe respiratory condition | 570 (24.1) | 465 (35.7) |
| Active cancer or on treatment | 435 (18.4) | 387 (29.8) |
| Previous DVT or PE | 159 (6.7) | 84 (6.5) |
| Systemic infection or sepsis | 479 (20.2) | 413 (31.7) |
| Acute neurologic disease | 315 (13.3) | 283 (21.8) |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 32 (1.4) | 28 (2.2) |
| Post-op or trauma < 3 months | 79 (3.3) | 66 (5.1) |
| 2001-2002 | 2003-2004 | 2005-2006 | 2007-2008 | 2009-2010 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage in parentheses. DVT: deep vein thrombosis; MSK: musculosquelettal; PE: pulmonary embolism; psy: psychiatric; VTE: venous thromboembolic event. | |||||
| Number of patients | 254 | 326 | 272 | 237 | 214 |
| Male gender | 107 (41.9) | 141 (43.3) | 111 (40.8) | 114 (48.1) | 95 (44.3) |
| Female gender | 147 (58.1) | 185 (56.8) | 161 (59.2) | 123 (51.9) | 118 (55.7) |
| Average length of stay (days) | 19.9 | 18.8 | 17.0 | 16.5 | 18.2 |
| Age on admission (year) | 66.8 | 69.9 | 71.7 | 70.8 | 71.6 |
| Diagnosis on admission | |||||
| Non-specified generalized weakness | 25 (9.5) | 21 (6.4) | 28 (10.3) | 20 (8.4) | 21 (9.4) |
| Neurologic disease | 28 (11.1) | 53 (16.3) | 25 (9.2) | 25 (10.6) | 22 (10.4) |
| Pulmonary disease | 7 (2.8) | 5 (1.5) | 5 (1.8) | 19 (8.0) | 9 (4.2) |
| Cardiovascular disease | 21 (8.3) | 19 (5.8) | 24 (8.8) | 17 (7.2) | 16 (7.6) |
| Gastrointestinal disease | 7 (2.8) | 15 (4.6) | 20 (7.4) | 13 (5.5) | 10 (4.7) |
| Nephro - endo - metab | 14 (5.5) | 15 (4.6) | 25 (9.2) | 12 (5.1) | 6 (2.8) |
| Hematologic disease (no cancer) | 11 (4.4) | 11 (3.4) | 9 (3.3) | 7 (2.9) | 6 (2.8) |
| Neoplasia | 72 (28.5) | 77 (23.6) | 37 (13.6) | 44 (18.6) | 35 (16.5) |
| Rhumatologic and inflammatory | 2 (0.8) | 14 (4.3) | 8 (2.9) | 9 (3.8) | 7 (3.3) |
| Infectious disease | 53 (20.9) | 66 (20.2) | 46 (16.9) | 48 (20.3) | 64 (30.2) |
| Substance withdrawal or intox | 7 (2.8) | 6 (1.8) | 6 (2.2) | 6 (2.5) | 8 (3.8) |
| Dermato - psy - MSK - allergy | 7 (2.77) | 24 (7.36) | 19 (6.98) | 17 (7.17) | 9 (4.24) |
| Thromboembolic disease | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Palliative care | 52 (20.6) | 34 (10.4) | 52 (19.1) | 25 (10.6) | 32 (15.1) |
| Risk factors for VTE | |||||
| Congestive heart failure | 55 (21.8) | 60 (18.4) | 99 (36.4) | 45 (19.0) | 46 (21.7) |
| Severe respiratory condition | 89 (35.2) | 102 (31.3) | 106 (39.0) | 91 (38.4) | 76 (35.9) |
| Active cancer or on treatment | 84 (32.8) | 108 (33.1) | 77 (28.3) | 66 (27.9) | 53 (25.0) |
| Previous DVT or PE | 18 (7.1) | 21 (6.4) | 19 (7.0) | 13 (5.5) | 14 (6.1) |
| Systemic infection or sepsis | 81 (32.0) | 104 (31.9) | 64 (23.5) | 67 (28.3) | 96 (45.3) |
| Acute neurologic disease | 44 (17.4) | 90 (27.6) | 51 (18.8) | 48 (20.3) | 50 (23.6) |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 3 (1.2) | 5 (1.5) | 3 (1.1) | 11 (4.6) | 6 (2.8) |
| Post-op or trauma < 3 months | 11 (4.4) | 24 (7.4) | 10 (3.7) | 9 (3.8) | 8 (3.8) |
| Patients with thromboprophylaxis | Patients without thromboprophylaxis | |
|---|---|---|
| Percentage in parentheses. DVT: deep vein thrombosis; HIT: heparin-induced thrombocytopenia; PE: pulmonary embolism; VTE: venous thromboembolic event. | ||
| Number of patients | 615 | 687 |
| Palliative care | 94 (15.3) | 101 (14.7) |
| Risk factors for VTE | ||
| Congestive heart failure | 162 (26.4) | 143 (20.9) |
| Severe respiratory condition | 225 (36.6) | 239 (34.8) |
| Active cancer or on treatment | 171 (27.8) | 216 (31.5) |
| Previous DVT or PE | 42 (8.8) | 42 (6.1) |
| Systemic infection or sepsis | 214 (34.9) | 198 (28.9) |
| Acute neurologic disease | 150 (24.4) | 133 (19.4) |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 13 (2.1) | 15 (2.2) |
| Post-op or trauma < 3 months | 54 (8.8) | 12 (1.8) |
| Thromboembolic events | ||
| Total thromboembolic disease | 21 (3.4) | 11 (1.6) |
| Proximal DVT | 5 (0.8) | 4 (0.6) |
| Distal DVT | 7 (1.1) | 6 (0.9) |
| Pulmonary embolism | 10 (1.6) | 2 (0.3) |
| Fatal pulmonary embolism | 3 (0.5) | 1 (0.1) |
| Complications | ||
| Total bleeding events | 50 (8.1) | 61 (8.9) |
| Non-severe bleeding | 21 (3.4) | 35 (5.1) |
| Severe bleeding | 29 (4.7) | 26 (3.8) |
| HIT | 1 (0.2) | 0 |